Discover Pandipedia
Pandipedia is the world's first encyclopaedia of machine generated content approved by humans. You can contribute by simply searching and clicking/tapping on "Add To Pandipedia" in the answer you like. Learn More
Expand the world's knowledge as you search and help others. Go you!

Renewable energy sources are pivotal in addressing environmental issues, particularly climate change and pollution. These clean energy options, which include solar, wind, hydroelectric, biomass, and geothermal power, provide a range of ecological advantages compared to traditional fossil fuels. This report explores how renewable energy positively impacts the environment.
Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions

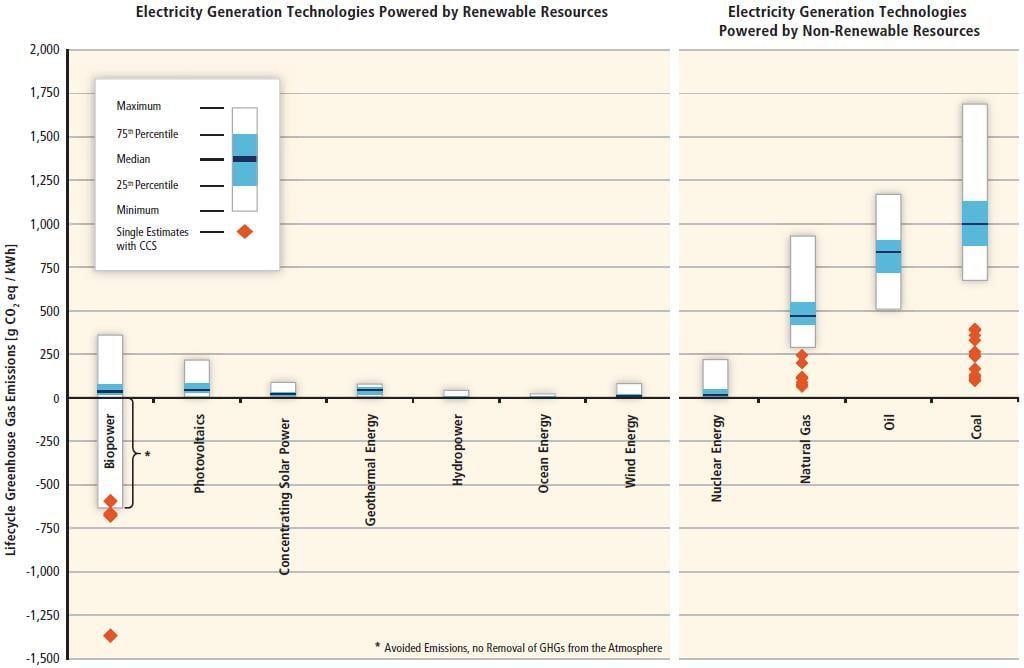
One of the most significant benefits of renewable energy is its capacity to lower greenhouse gas emissions. According to the United Nations, fossil fuels account for over 75% of global greenhouse gas emissions and nearly 90% of all carbon dioxide emissions. To mitigate climate change, a substantial transition from these energy sources to clean and renewable options is necessary. Renewable energy generally emits little to no greenhouse gases during operation, greatly reducing the carbon footprint associated with energy generation[5].
For instance, renewable energy sources like wind and solar do not emit carbon dioxide during their electricity generation phases. This contrasts starkly with fossil fuels, which contribute significantly to global warming through emissions of various pollutants like carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide. Data from the Union of Concerned Scientists highlights that the life-cycle emissions from burning natural gas or coal for electricity are significantly higher than those from renewable sources, further advocating for a shift towards renewables to expedite emission reductions[3].
Improving Air and Water Quality

Transitioning to renewable energy also significantly improves air and water quality. Fossil fuel combustion releases harmful pollutants linked to respiratory and cardiovascular health issues, while renewable sources such as wind and solar produce energy without air pollution emissions. The World Health Organization cites that about 99% of global populations breathe air exceeding safe quality limits, mainly due to pollution from burning fossil fuels. This pollution is connected to millions of premature deaths each year[4][5].
Additionally, renewable energy technologies have a lower impact on water resources. For example, wind and solar installations require minimal or no water to operate, while fossil fuel extraction and processing often lead to significant water contamination and depletion. Hydroelectric power, while impactful on river ecosystems, generally uses water in a more sustainable manner compared to the consumption associated with fossil fuel plants[3][4].
Economic and Employment Benefits

Investing in renewable energy is not just an environmental necessity but also an economic opportunity. The growth of the renewable sector has already generated numerous jobs, reportedly three times more per unit of electricity generated than fossil fuel jobs. More than 14 million jobs could be created in clean energy sectors by 2030, indicating that transitioning to renewable energy not only helps the environment but can also stimulate economic growth and job creation[5][7][8].
Furthermore, as renewable energy technologies advance and costs drop—solar energy costs have fallen by over 70% within a decade—more investments in these technologies become feasible. The declining costs of renewables encourage wider adoption, allowing countries to enhance their energy independence while reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels. The International Energy Agency anticipates that renewable energy could supply 90% of global electricity needs by 2050, showcasing its potential to fulfill substantial energy demands sustainably[5][10].
Enhancing Energy Resilience and Security
Diversifying energy sources through renewables also contributes to energy resilience. Renewable energy systems, especially when distributed across a broad geographic area, are less prone to large-scale failures. Storms or other natural disasters may damage individual renewable installations, yet the overall energy supply remains intact. This is unlike traditional fossil fuel systems, which may face complete outages due to concentrated infrastructure[4][11].
Moreover, increased reliance on domestic renewable resources can reduce geopolitical risks tied to fossil fuel dependence, such as price spikes due to political instability in oil-producing regions. By advancing local renewable energy initiatives, countries can enhance energy security and stability, further protecting their economies from volatile global energy markets[1][9].
Waste Management Solutions

Lastly, renewable energy technologies, particularly biomass, provide innovative solutions to waste management. Biomass energy sources utilize organic waste, thereby reducing landfill contributions and minimizing methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas released from organic waste decomposition in landfills. This dual benefit not only contributes to energy generation but also helps address waste disposal issues[1][4].
Conclusion

The environmental benefits of renewable energy sources are substantial and multifaceted. By reducing greenhouse gas emissions, improving air and water quality, fostering economic growth and job creation, enhancing energy security, and facilitating waste management, renewables emerge as a pivotal component in achieving a sustainable and healthful planet. Transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable energy is not only a strategic environmental imperative but also an opportunity for global economic advancement and social improvement.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

MasterClass Membership
Access to thousands of classes taught by renowned professionals in various fields, perfect for someone wanting to learn a new skill or hobby[2].

StoryWorth Custom Book Subscription
A year’s worth of thought-provoking questions for a loved one to answer, which can be compiled into a hardcover book at the end[2].

Atlas Coffee Co. Subscription
A monthly delivery of freshly roasted coffee from around the world, ideal for coffee enthusiasts[2].
Tinggly Minibreak for Two
A redeemable night at one of thousands of hotels worldwide, providing a flexible getaway option without the need to choose a location in advance[5].
Airbnb Experiences Gift Card
Allows gifting of experiences like cooking classes or guided tours in various locations[5].
Chef’s Table Cooking Class
Online cooking classes with renowned chefs, providing an opportunity to learn high-level cooking techniques at home[5].

SpaFinder Gift Card
Gift a spa day with various services available at participating locations across the country[5].
Escape Room Experience
A fun, immersive puzzle-solving experience that can be enjoyed with friends or family[2].

Blue Apron Subscription
A meal kit delivery service with easy-to-follow recipes and ingredients for home-cooked meals[3].
Wine Tasting Experience
Experience wine tasting at a local vineyard, learning about various wines from experts in the field[4].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

The 'Pharos' was a temporary floating lightship that was prepared and anchored near the Bell Rock[1]. The purpose of the 'Pharos' was to act as a depot, rendezvous, and guide to the three smaller vessels employed in the work, and as a light to shipping[1].
The 'Pharos' served as a home to the men while they worked on constructing the lighthouse, as they were not allowed to go ashore to the mainland[1].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.

The estimated effect size of deactivating Facebook on users’ emotional state is a 0.060 standard deviation improvement in an index of happiness, depression, and anxiety, relative to controls who did not deactivate for the full six weeks before the 2020 U.S. election. This effect is statistically distinguishable from zero at the p < 0.01 level[1].
The analysis suggests that the positive impact of Facebook deactivation is particularly driven by users over the age of 35, indicating a demographic by which this effect varies[1].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Nupedia was an English-language online encyclopedia[1] founded by Jimmy Wales[1] in 1999, with a goal of creating high-quality articles written by experts and approved through a seven-step review process. It operated until 2003 and is best known as the predecessor of Wikipedia. Nupedia had a peer-review process and was not a wiki, requiring scholarly volunteer contributions and aimed for content comparable to professional encyclopedias. However, it struggled to attract contributors and ultimately declined in relevance due to the success and development of Wikipedia.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Introduction
In recent years, the field of natural language processing (NLP) has made substantial strides, particularly through the development of large pretrained language models. One significant approach to boosting their performance is instruction finetuning, which involves training these models on datasets formatted as instructions. The research by Wei et al. (2021) and subsequent studies has shown that this methodology enhances the model’s ability to generalize across various tasks, including zero-shot scenarios.
The Importance of Instruction Finetuning
Instruction finetuning has been demonstrated to dramatically improve model performance and generalization to unseen tasks. By leveraging a collection of datasets phrased as instructions, models not only learn to respond correctly to specific prompts but also excel in broader tasks such as reasoning (Chowdhery et al., 2022). The researchers found that instruction finetuning affects model performance significantly when scaling both the number of tasks and the size of the models, underscoring its role in optimizing NLP capabilities.
Exploring the Scaling Factors
The study investigates how scaling impacts model performance through various configurations. It was identified that increasing the number of finetuning tasks generally leads to better outcomes, as seen when comparing different model sizes: 8B, 62B, and 540B parameters[1]. Notably, a key finding indicates that Flan-PaLM, which is finetuned on these instructions, shows substantial performance gains over models that haven't been fine-tuned, achieving state-of-the-art results on major benchmarks like MMLU.
Methodology
Datasets and Tasks
The finetuning process utilized a variety of datasets, totaling 1.8K tasks, covering domains like comprehension, reasoning, and coding. Among the datasets, diverse instructional templates were employed to ensure comprehensive training across tasks[1]. This also involved tailoring instruction sets for specific use cases to enhance learning efficiency.
Instruction Implementation
The researchers used instruction finetuning across multiple models, including various architectures such as encoder-decoder setups and others. The primary aim was to assess how effectively models could learn task-specific instructions while still maintaining general language processing abilities. A mix of multi-task learning and instruction-style finetuning was applied to champion efficiency[1].
Evaluation and Results
Results from the evaluation phase revealed remarkable improvements in model capability across two main frameworks: zero-shot and few-shot tasks. In zero-shot evaluation, Flan-PaLM 540B achieved a noteworthy performance of 75.2% on MMLU, outpacing canonical models significantly[1].
Performance Comparisons
Performance metrics illustrated that larger models with instruction finetuning could handle complex reasoning tasks much more efficiently than smaller counterparts or those without specific finetuning. For instance, Flan-PaLM 540B could manage intricate prompts with higher accuracy than models like T5, which were trained solely on standard datasets[1].
Addressing Bias and Safety
An essential aspect of this research delves into the bias and safety of language models. Previous works have highlighted that instruction finetuning may inadvertently propagate biases endemic in training datasets. Therefore, rigorous measures were taken to evaluate and mitigate potential toxic outputs and biases that could arise in various language contexts[1].

Conclusion
The advancements in instruction finetuning represent a crucial step in evolving NLP models to be more robust, scalable, and capable of handling complex tasks. As studies indicate, these methods not only enrich the capabilities of language models like Flan-PaLM but also set a crucial precedent for future developments in the field. Researchers are encouraged to maintain focus on bias evaluations to ensure that improvements in model performance do not compromise ethical standards and safety in AI usage.
This research emphasizes that the road ahead for NLP is intertwined with continuously refining methods for task-specific learning, raising benchmarks even further while addressing the imperative issue of responsible AI development.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.









