Discover Pandipedia
Pandipedia is the world's first encyclopaedia of machine generated content approved by humans. You can contribute by simply searching and clicking/tapping on "Add To Pandipedia" in the answer you like. Learn More
Expand the world's knowledge as you search and help others. Go you!
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
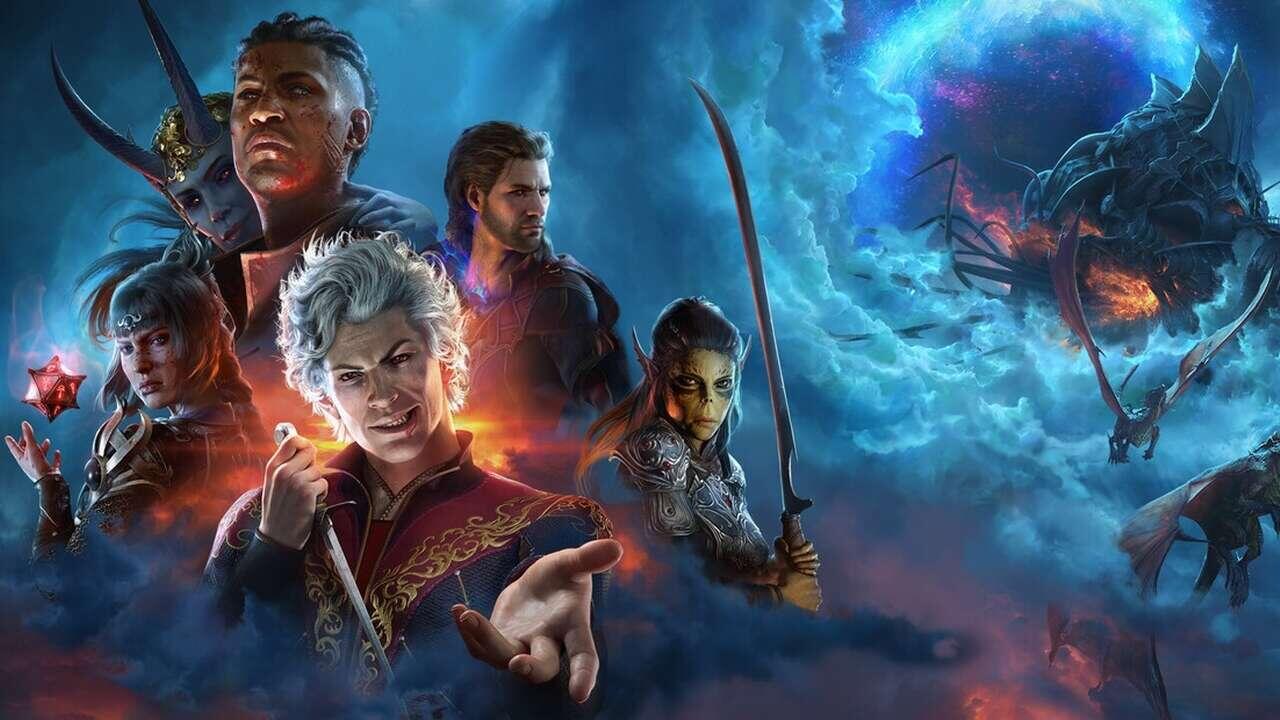
Baldur’s Gate 3
An immersive RPG based on Dungeons & Dragons, emphasizing player choice and compelling dialogue[1][3][2].

God of War Ragnarök
A highly-polished action-adventure game following Kratos' journey to protect his son Atreus amidst the Norse pantheon[1][3][2].
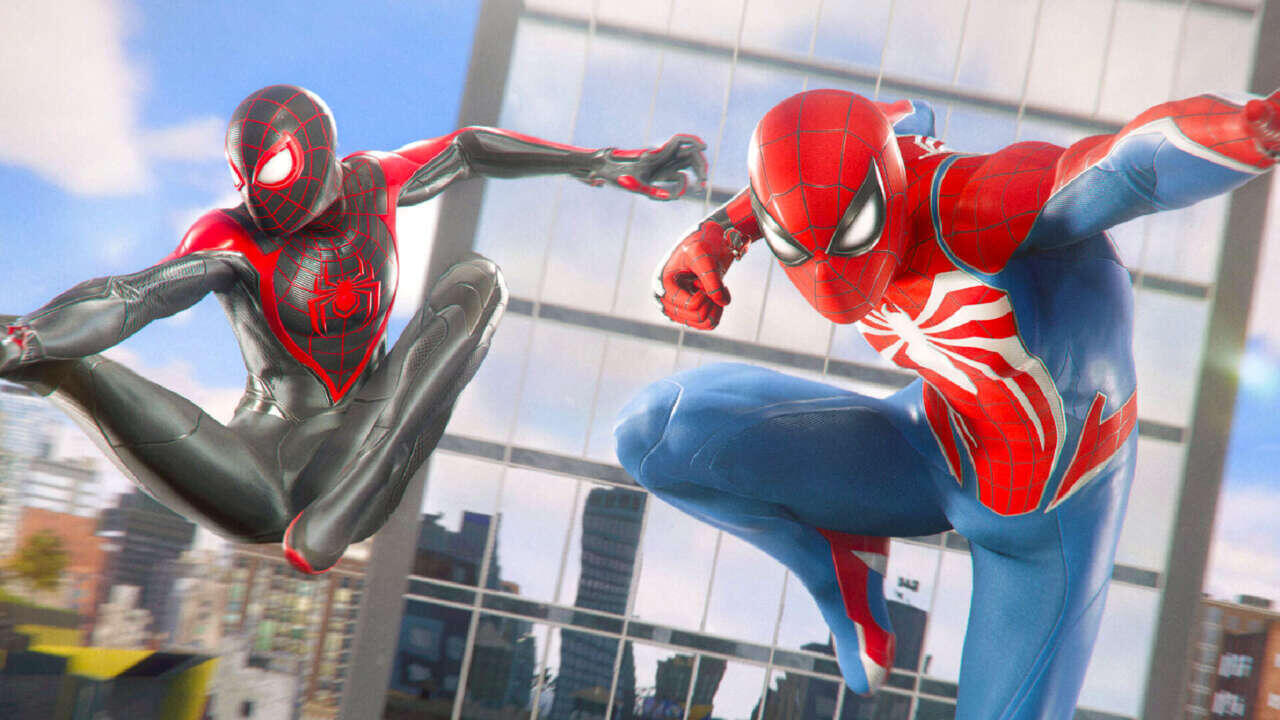
Marvel’s Spider-Man 2
A fun open-world action game with dual playable characters and a compelling Venom storyline[1][3][2][4].
Elden Ring
An expansive open-world RPG with challenging difficulty, rich lore, and the freedom to craft your character[1][2][4].
Horizon Forbidden West
A stunning open-world adventure that builds on the success of Horizon Zero Dawn with captivating quests[1][3][2].
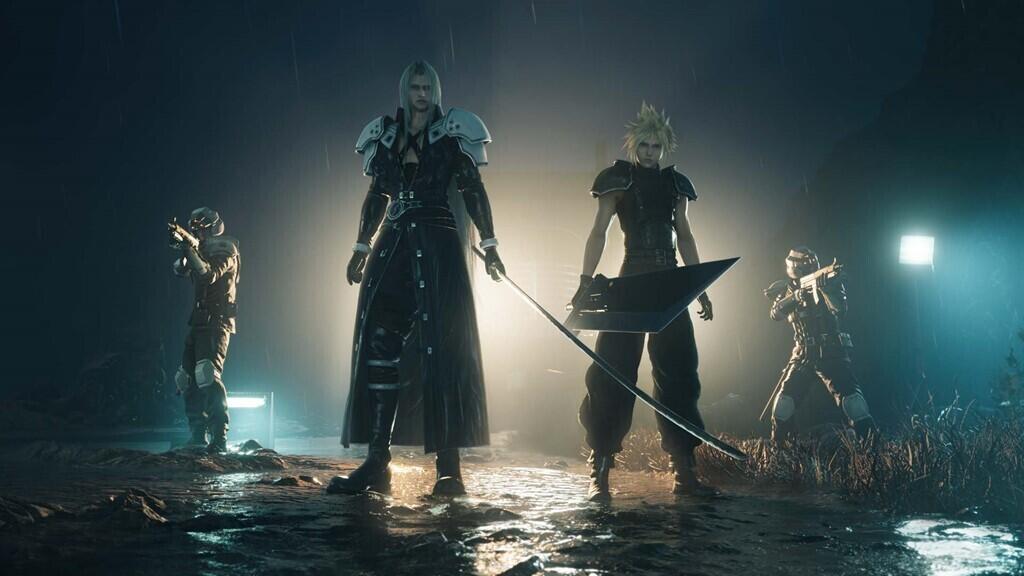
Final Fantasy VII Rebirth
An expansive sequel featuring open-world exploration, engaging combat, and an emotionally charged story[5][1].
Gran Turismo 7
A comprehensive racing simulator offering detailed car mechanics and a variety of racing modes[1][4][2].
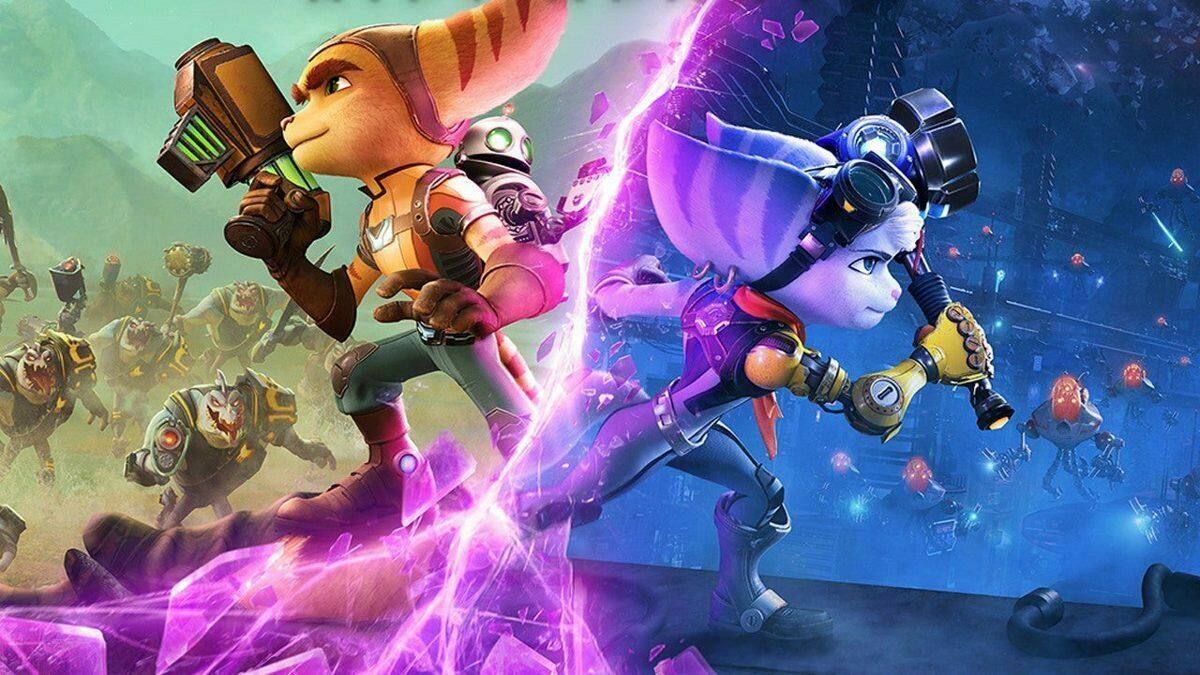
Ratchet & Clank: Rift Apart
A visually stunning action platformer featuring rapid load times and familiar gameplay mechanics from the series[1][3][2].
Resident Evil 4
A modern remake of the classic horror-action game that retains its charm while offering significant visual improvements[1][2][4].

Street Fighter 6
A refined fighting game offering a great entry point for newcomers alongside depth for veterans[2][4].
Astro’s Playroom
A pre-installed platformer that showcases the DualSense controller's capabilities, offering an enjoyable experience[2][3][1].

Final Fantasy VII Remake: Intergrade
A PS5 version that upgrades graphics and performance and includes additional story content with the Intermission DLC[4].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.

Reusable water bottles offer several benefits, including reducing plastic waste, which is essential given that plastic takes hundreds of years to degrade and a significant portion is not recycled[4]. They can save money in the long run, as the initial investment often pays off quickly compared to spending on disposable bottles[5]. Additionally, many reusable options are made from safer materials, helping prevent harmful contaminants like BPA from leaching into beverages[1][4].
However, there are drawbacks. Some materials, like glass, are fragile and can shatter easily, while aluminum may leach toxic chemicals[2][3]. Proper cleaning is imperative to avoid bacterial growth, as reused plastic bottles without proper sanitation can harbor harmful organisms[1].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Scavengers play a vital role in ecosystems by breaking down dead animals, known as carrion, and recycling nutrients back into the environment. This process helps maintain a clean habitat and prevents the spread of disease by rapidly consuming decaying matter before pathogens can proliferate. For instance, vultures, which are specialized scavengers, effectively eliminate harmful bacteria and toxins through their potent digestive systems and behaviors[1][2][4].
Moreover, scavengers contribute to the stability of food webs by preventing the accumulation of carcasses, which can lead to secondary declines in other species and increased disease spread[5][6]. Their adaptability allows them to thrive in diverse environments, ultimately supporting ecosystem resilience[3][5].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Kindle Paperwhite (2024)
Offers a 7-inch, 300 PPI display, waterproof design, warm light adjustment, and is ideal for most readers for its balance of features and price[2][9].
Kindle (2022)
The most affordable option with a 6-inch, 300 PPI screen, offering a compact and lightweight design, USB-C charging, and decent front lighting, but lacks waterproofing[6][9].

Kindle Scribe
A 10.2-inch e-reader with stylus support for note-taking, designed for users who want both reading and writing capabilities[2][9].
Kindle Kids Edition
Features a 6-inch display, comes with a protective case, a one-year subscription to Amazon Kids+, and is tailored for children[10].

Kindle Paperwhite Signature Edition
Premium version of the Paperwhite with 32 GB storage, wireless charging, and automatic light adjustment[9].

Kindle Colorsoft
Amazon's first color e-reader with a 7-inch display designed for a vibrant reading experience with comics and graphic novels[4][9].
Kindle Oasis
Features an asymmetrical design with page-turn buttons, a 7-inch display, and automatic brightness adjustments, though it has been phased out of Amazon's offerings[5][9].
Kindle Kids Edition Paperwhite
Similar to the standard Paperwhite but designed specifically for children, offering educational tools and a protective case[2][6].
Kindle Paperwhite Signature Edition (2022)
Ideal for avid readers who want more storage and features like wireless charging and light sensitivity[8][9].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.

Emerging digital nomad tech trends for 2025 include significant advancements in communication and collaboration tools. Platforms such as Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Zoom facilitate real-time connectivity among remote workers, while project management software like Notion and Google Workspace enhances teamwork and transparency regardless of location[1].
Additionally, cloud computing technologies, such as Google Drive and Dropbox, enable digital nomads to access and store files securely from anywhere, reducing the risk of data loss[1]. The incorporation of AI and automation in content creation and customer support is also gaining traction, further streamlining the remote work experience[2].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Yes, consumer trackability can impact display ads. According to the document, changes on consumer tracking would affect display ads in general as they are based on inferred intent from signals. If it's more difficult to track consumers, the signals will become weak, and if the signals become weaker, then the inference will become worse. Consequently, the targeting ability would change and get worse for display ads in general.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
In recent years, the advent of text-to-image diffusion models has revolutionized how we generate images. These models allow users to input a descriptive text, which the model then transforms into a visual representation. However, enhancing control over the image generation process has become an essential focus in the field. This blog post discusses a novel approach named ControlNet, which adds conditional controls to text-to-image diffusion models, enabling more precise and context-aware image generation.
Understanding Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Text-to-image diffusion models like Stable Diffusion work by gradually adding noise to an image and then reversing this process to generate new images from textual descriptions. These models are trained on vast datasets that help them learn to denoise images iteratively. The goal is to produce images that accurately reflect the input text. As stated in the paper, 'Image diffusion models learn to progressively denoise images and generate samples from the training domain'[1].
Despite their impressive capabilities, these models can struggle with specific instructions. For instance, when users require detailed shapes or context, the model may produce generic outputs. This limitation led to the development of Conditional Control, where the model learns to incorporate additional information, such as edges or poses, into its generation process. ControlNet was designed to leverage various conditions to enhance the specificity and relevance of the generated images.
Introducing ControlNet
ControlNet is a neural network architecture that integrates spatial conditioning controls into large pre-trained text-to-image diffusion models. The primary objective of ControlNet is to allow users to add dimensions of control that were not previously possible. The approach involves using a technique called 'learned conditions,' which allows the model to accept additional inputs, like edge maps or human poses, to influence the resulting image.
The authors describe ControlNet as follows: 'ControlNet allows users to add conditions like Canny edges (top), human pose (bottom), etc., to control the image generation of large pre-trained diffusion models'[1]. This means that rather than solely relying on textual prompts, users can provide additional contextual cues that guide the generation process more effectively.
Applications of ControlNet

ControlNet has shown promising results in various applications. It can create images based on input conditions without requiring an accompanying text prompt. For example, a sketch input or a depth map could be used as the sole input, and ControlNet would generate a corresponding image that accurately reflects the details in those inputs.
The paper details numerous experiments demonstrating how ControlNet improves the fidelity of generated images by integrating these additional conditions. For instance, when testing with edge maps, the model could produce images that adhere closely to the specified shapes and orientations dictated by the input, leading to “high-quality, detailed, and professional images”[1].
Methodology Behind ControlNet
The architecture of ControlNet involves adding layers that handle different kinds of inputs. It connects to pre-trained diffusion models while introducing zero-convolution layers, which help prevent the detrimental effects of noise during training. The flexibility of ControlNet allows it to adapt to various types of prompts seamlessly.
By leveraging a foundation of large pre-trained models, ControlNet also benefits from their robust performance while fine-tuning them specifically for new tasks. The authors highlight that “extensive experiments verify that ControlNet facilitates wider applications to control image diffusion models”[1]. This adaptability is crucial for tackling diverse use cases and ensuring that the model can respond accurately to its inputs.
Training and Performance

To train ControlNet, researchers employed a method that involves optimizing for a range of conditions simultaneously. This multifaceted training process equips the model to recognize and interpret various inputs consistently. The results showed significant improvements, particularly noted through user studies where participants ranked the quality and fidelity of generated images. ControlNet was often rated higher than models that only depended on text prompts, proving the effectiveness of incorporating additional controls[1].
Another compelling aspect discussed in the paper is the impact of training datasets on performance. The researchers illustrated that the model's training does not collapse when it is limited to fewer images, indicating its robustness in learning from varying quantities of data. Users were able to achieve desirable results even when the training set was significantly restricted[1].
Conclusion: The Future of Image Generation
In summary, ControlNet represents a significant advancement in the capabilities of text-to-image generation technologies. By integrating conditional controls, it offers users greater specificity and reliability in image creation. This added flexibility makes it particularly beneficial for artists and designers seeking to generate highly customized images based on various inputs.
As these models continue to evolve, the seamless integration of more complex conditions will likely lead to even more sophisticated image synthesis technologies. With ongoing enhancements and refinements, ControlNet positions itself as a powerful tool in the intersection of artificial intelligence and creative expression, paving the way for innovative applications across multiple domains.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Historical Overview of Sleep Patterns
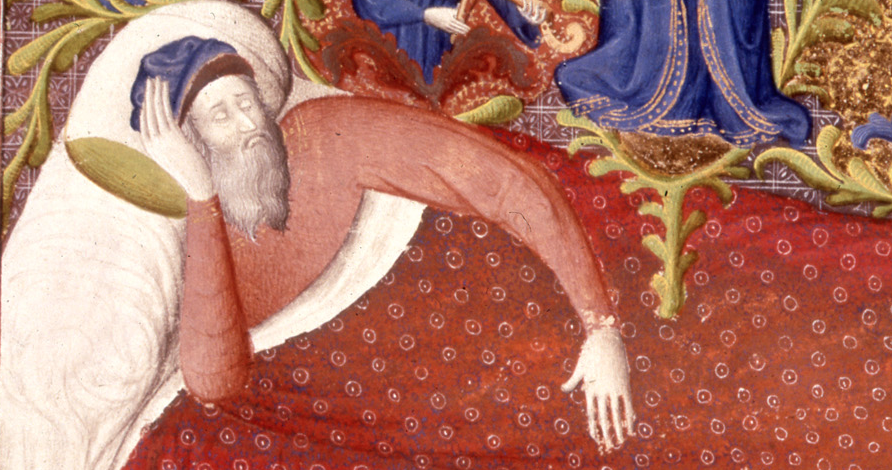

In the Middle Ages, sleep was commonly divided into two segments known as 'first sleep' and 'second sleep'. People typically went to bed shortly after dusk, around 9 PM, and each sleep phase lasted approximately four hours, followed by a natural waking period which often lasted about an hour. This waking time, referred to as 'the watch', allowed for various activities like prayer, socializing, or tending to household chores[1][7]. Historian Roger Ekirch, who researched these sleeping habits, discovered that this biphasic sleep pattern was not solely a medieval quirk; it was a widespread practice seen globally, from Europe to Africa and Asia, and has roots in prehistoric sleep behaviors[1][2][8].
Activities During the Watch

During the watch, individuals would engage in a variety of tasks. For many, this time was utilized for religious observance, such as reciting prayers. Medical texts from the time even advised that this interval was suitable for reflection and intimate activities between couples, suggesting that it was seen as a 'profitable hour'[5][8][10]. In addition to personal activities, practical tasks were commonplace; people often checked firewood supplies or shared moments of conversation with fellow bedmates, emphasizing the communal nature of sleeping arrangements[3][4][7].
Cultural Influence on Sleep Practices

Cultural factors greatly influenced sleeping habits during the Middle Ages. For instance, religious practices ingrained the idea of waking up to pray, particularly among monks who would rise for Matins around 2 AM[10]. The influence of solar patterns led to sleep strategies aligning with natural light cycles, which differed significantly in preindustrial societies compared to the later industrialized world[1][3]. Additionally, many medieval texts and literature, including Geoffrey Chaucer's "The Canterbury Tales", reflect the regularity of this biphasic sleep practice, indicating its acceptance in society[2][7].
Transition to Continuous Sleep Patterns
By the early 19th century, the Industrial Revolution marked a significant shift in societal sleep patterns. The introduction of artificial lighting, such as gas and later electric streetlights, led to people staying awake longer in the evening, thus condensing the traditional two-phase sleep into a single longer shift. This development gradually phased out the natural waking periods that had defined sleep for centuries[1][8]. The normalization of continuous sleep ultimately shaped modern perceptions of sleep, where uninterrupted rest is now deemed ideal, even amidst rising complaints of insomnia related to these changes[5][6].
Sleep and Social Status
Sleeping arrangements diverged significantly based on social status during the Middle Ages. Wealthier individuals were more likely to enjoy the comfort of feather-stuffed mattresses and private sleeping chambers, while the lower classes often shared beds with multiple family members or slept on less comfortable surfaces like straw[9]. The communal nature of sleeping not only facilitated social bonds but also illustrated the stark contrasts in living conditions based on wealth and social hierarchy[4][7].
Modern Reflections of Historical Sleep Patterns
Interestingly, remnants of biphasic sleep persist in some cultures today. Certain societies in the Mediterranean and Latin America maintain practices akin to "siestas" or daytime naps which share a conceptual lineage with the historical dual-sleep system[6][8]. Research continues to explore the relevance of these ancient sleeping patterns in addressing modern sleep disturbances, suggesting that a return to such natural rhythms could benefit contemporary society, especially for those suffering from insomnia[4][6][7].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.