Discover Pandipedia
Pandipedia is the world's first encyclopaedia of machine generated content approved by humans. You can contribute by simply searching and clicking/tapping on "Add To Pandipedia" in the answer you like. Learn More
Expand the world's knowledge as you search and help others. Go you!
The study by Wessel et al. (2020) contributes to the understanding of digital transformation by distinguishing it from IT-enabled organizational transformation. They integrate literature from organization science and information systems with longitudinal case studies to develop a conceptualization that highlights two key differences: first, digital transformation activities leverage digital technology to (re)define an organization’s value proposition, while IT-enabled transformation supports the existing value proposition.
Second, digital transformation leads to the emergence of a new organizational identity, whereas IT-enabled transformation enhances an existing identity. The authors synthesize these differences into a process model, providing a framework for understanding various types of transformations and suggesting avenues for future research[1].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.

Engaging in sports offers a multitude of psychological benefits that extend far beyond physical fitness. Research highlights the significant impact of sports participation on mental health, including improvements in mood, self-esteem, and social skills. Here is a comprehensive overview of the psychological advantages associated with participating in sports.
Enhanced Mental Health

Participation in sports is strongly associated with better mental health outcomes. Regular engagement in physical activity can lead to improvements in psychological well-being, including higher self-esteem, better mood, and reduced feelings of anxiety and depression. Studies indicate that individuals who exercise regularly tend to experience fewer symptoms of mental distress compared to those who do not engage in physical activity[1][2]. Exercise influences the body’s hormonal balance, enhancing the production of endorphins, which are known to contribute to feelings of happiness and pleasure, ultimately facilitating better emotional regulation[2].
One systematic review indicated that participation in community and elite-level sports is related to improved psychological well-being, including lower levels of depression, anxiety, and stress[1]. Specifically, team sports are linked to a greater sense of belonging and connectivity, contributing positively to mental health[1][3]. For example, children who participate in team sports have exhibited lower rates of anxiety and depression compared to their peers who engage in individual sports like wrestling or gymnastics[5].
Social Skills Development

In addition to individual mental health improvements, participation in sports fosters essential social skills. Engaging in team sports helps individuals learn how to interact with peers, manage emotions, and resolve conflicts, which translates to better social functioning in everyday life[3][6]. The structured and cooperative environment of team sports encourages children to develop problem-solving abilities and learn teamwork[3].
Moreover, individuals involved in organized sports tend to have lower feelings of social isolation and greater psychological resilience, making them better equipped to handle adverse situations in life[1][6]. The relationships formed within sports teams provide a support system, which is crucial, especially for those experiencing familial adversities[3]. This communal aspect of sports can bolster emotional health and create a sense of stability and support.
Long-Term Psychological Resilience
Participating in sports not only impacts immediate mental health but also contributes to long-term psychological resilience. Research shows that adolescents involved in team sports are less likely to experience significant mental health challenges later in life, such as depression and anxiety[3]. This protective effect is thought to stem from the social bonds formed during team interactions and the development of coping strategies learned through sports participation.
Furthermore, the commitment required in sports cultivates discipline and resilience, qualities that are invaluable in adult life[1][3]. Children learn to manage time effectively, set goals, and cope with pressure in sports, preparing them for future challenges.
Stress Relief and Mood Improvement
Engagement in sports serves as an effective stress reliever. Physical activity is known to decrease levels of the body’s stress hormones, such as cortisol, while simultaneously increasing the production of endorphins, inducing a natural mood boost[2][6]. This biological reaction underscores the connection between physical activity and improved mental health, reinforcing the idea that exercise serves as a vital tool for managing stress and enhancing overall well-being.
Research supports that any level of physical activity can yield positive psychological benefits, making it an accessible means for promoting mental health[2][6]. Activities like yoga, in addition to traditional sports, are recognized for their calming effects and ability to reduce anxiety[2].
Importance of Structured Participation
It’s also crucial to consider the role of adults and coaches in facilitating a positive sports environment. Proper guidance can help mitigate the pressures associated with competition. Studies suggest that nurturing coaching and positive peer relationships in sports can maximize the psychological benefits while minimizing stress and anxiety from competition[5]. Engaging children in sports should ideally be about fun, skill development, and personal growth rather than solely focusing on winning[3].
Conclusion
The psychological benefits of participating in sports are extensive, influencing various aspects of mental health and social interactions. From improved well-being and reduced symptoms of anxiety and depression to the development of crucial social skills, sports participation offers comprehensive advantages that can enhance overall life satisfaction. Encouraging active participation in sports can provide individuals with lifelong tools for managing stress, fostering emotional resilience, and building meaningful social connections. These benefits underscore the importance of organized sports as a positive influence on mental health, especially in children and adolescents[1][3][6].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

In recent years, the movement toward sustainable gardening has gained significant momentum as more individuals seek to create eco-friendly environments while cultivating their gardens. Whether working with limited urban spaces or vast backyards, gardeners are increasingly adopting practices that not only nurture their plants but also reduce their ecological footprint. This report outlines the top eco-friendly gardening practices based on comprehensive sources.
Embracing Native Plants

One foundational practice for sustainable gardening is the incorporation of native plants. These plants are naturally adapted to local climates and ecosystems, requiring less water and maintenance compared to non-native varieties. By choosing native species, gardeners can support local wildlife, including pollinators such as bees and butterflies. This enhances biodiversity and fosters a healthier ecosystem within the garden itself[3][6][11].
Benefits of Biodiversity
Biodiverse gardens that feature a variety of plant species can better support local wildlife, creating a balanced ecosystem. This includes the strategic planting of flowers that attract beneficial insects, which in turn assist in pollination and pest control[10]. By making eco-friendly choices about plants, gardeners effectively reduce their reliance on chemical pesticides, promoting a healthier environment[8].
Water Conservation Techniques
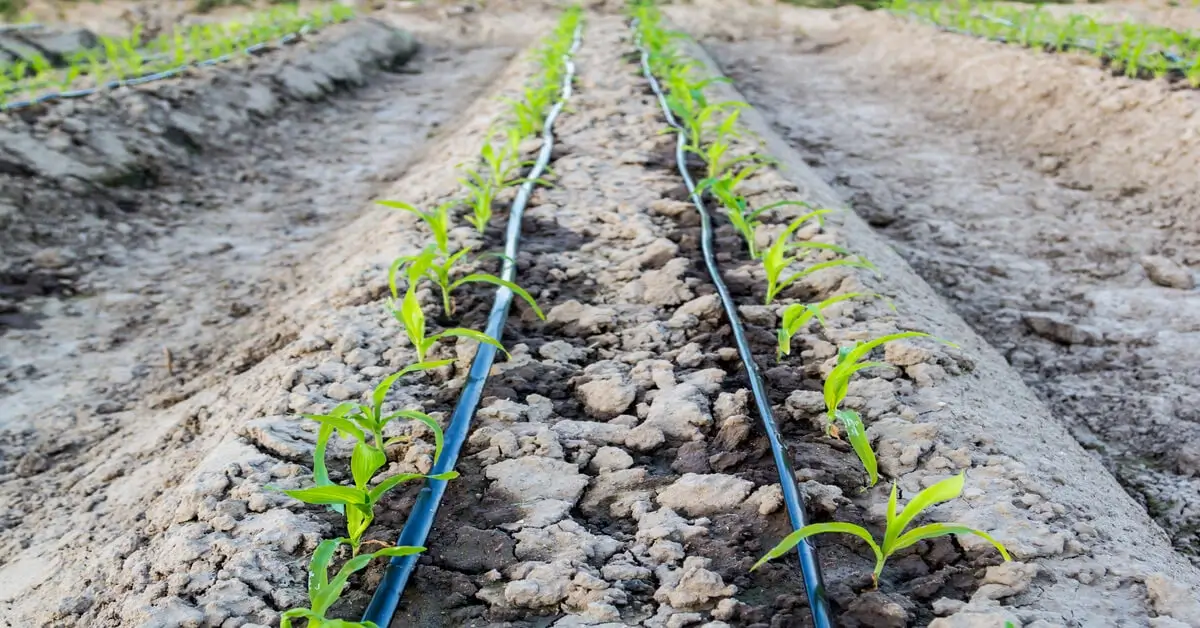

Water conservation is another critical aspect of eco-friendly gardening. Traditional gardening methods often lead to substantial water waste, but sustainable practices can significantly mitigate this issue. Techniques such as installing rain barrels for water collection, using drip irrigation systems, and selecting drought-tolerant plants are effective strategies to conserve water[2][5][11].
Using a watering can instead of a hose for irrigation allows for more targeted and economical use of water, helping to prevent over-watering and ensuring that plants receive adequate moisture[7]. Additionally, mulching can help retain soil moisture, which is vital during dry spells.
Organic Gardening Methods
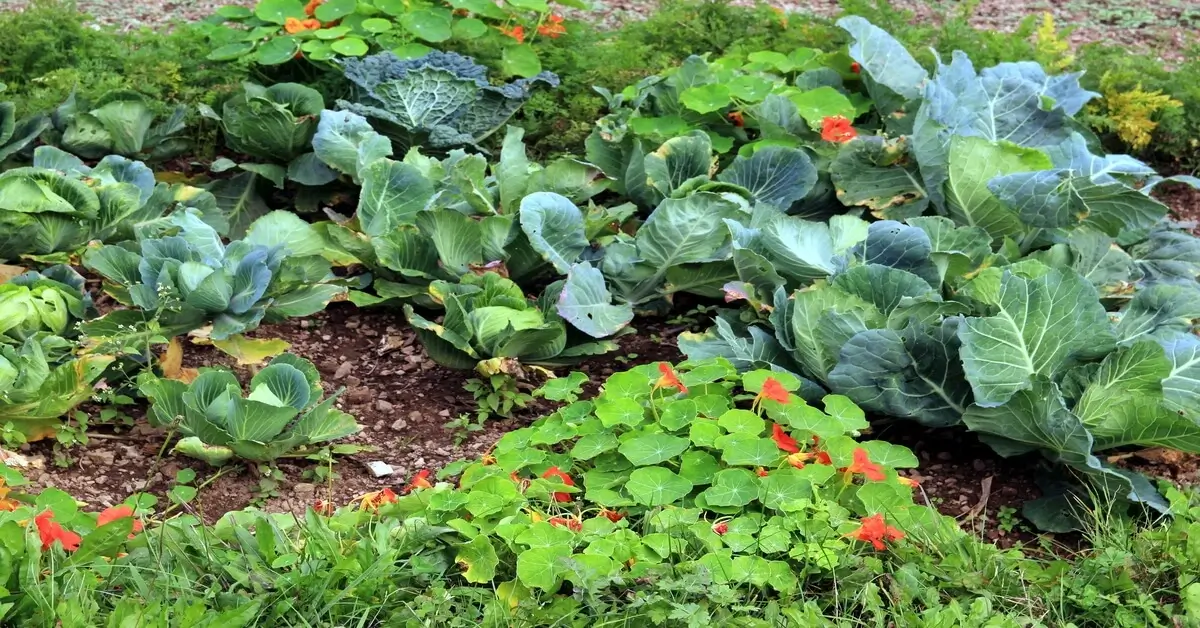

Shifting away from synthetic fertilizers and pesticides towards organic alternatives is another essential practice. Organic gardening not only enhances soil health but also reduces the negative environmental impacts associated with the production and use of chemical fertilizers[2][4][10]. Composting kitchen scraps, garden waste, and other organic materials is a sustainable way to create nutrient-rich soil while minimizing waste sent to landfills[4][10].
Natural Pest Management

Integrated pest management (IPM) techniques allow gardeners to control pests naturally. Companion planting, where compatible plants are grown together to enhance growth and repel pests, is a recommended strategy. For instance, planting marigolds near vegetables can deter harmful insects while attracting beneficial ones[4][10]. Additionally, natural remedies such as soapy water or garlic spray can effectively manage pests without harming the ecosystem[6][9].
Reducing Waste and Reusing Materials

Eco-friendly gardening practices also involve minimizing waste and utilizing materials creatively. Gardeners are encouraged to collect fallen leaves for compost, repurpose old containers for planting, and avoid single-use plastics[7][11]. By reusing and recycling materials, gardeners can reduce their environmental impact while also infusing unique touches into their spaces.
Sustainable Gardening Technologies
Technological advancements have made it easier than ever to maintain sustainable gardens. Smart tools such as automated watering systems that adjust based on weather data can optimize water usage and ensure healthy plant growth[11]. Integrating technology not only simplifies gardening tasks but also aids in monitoring soil health and moisture levels, allowing for informed decision-making[6].
Community Engagement and Support
Encouraging community engagement through initiatives like community gardens can enhance food security and fellowship among neighbors. These communal spaces allow individuals to grow food together, share resources, and promote sustainability on a larger scale. Engaging with local gardening groups or participating in seed exchange programs can also foster a sense of community and encourage the sharing of knowledge related to sustainable gardening practices[3][5].
Conclusion: A Collective Effort Towards Sustainability
Adopting these eco-friendly practices is not merely a personal endeavor; it represents a collective effort to protect our environment. By prioritizing native plants, conserving water, utilizing organic methods, reducing waste, and embracing technological innovations, gardeners can significantly contribute to ecological health and well-being. As more people adopt sustainable gardening techniques, the cumulative impact will pave the way for a greener future.
With the right practices and community support, every gardener can create a flourishing outdoor space that aligns with environmental goals while reaping the benefits of a vibrant and productive garden.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Addressing Social Justice and Inequality
Contemporary art serves as a powerful vehicle for spotlighting issues of social justice and inequality. Artists such as Ai Weiwei and Kara Walker use their works to critique and highlight human rights abuses and systemic racism. Ai Weiwei's installations frequently critique the Chinese government's human rights policies, while Kara Walker’s silhouettes and sculptures examine the enduring impacts of slavery and racial discrimination in America[1].
Furthermore, art plays a crucial role in social activism by leveraging its visual, emotional, and narrative capacities to provoke critical thought and inspire change. Socially engaged art involves direct collaboration with communities and often addresses significant social issues, fostering a sense of unity and collective purpose[4]. This form of art can stimulate dialogue and promote healing, effectively making art a catalyst for societal transformation[8].
Exploring Identity and Gender

The exploration of identity—encompassing race, gender, and sexuality—is a pivotal aspect of contemporary art. Artists like Cindy Sherman and Shirin Neshat use their photography and film work to critique and redefine gender roles and societal norms. Sherman’s series of self-portraits challenge stereotypical portrayals of women, while Neshat’s works delve into the complexities of gender in Islamic cultures[1].
The art world's increasing focus on intersectionality reflects broader societal debates around identity, aiming to foster inclusivity and promote diverse perspectives[4]. Gender parity and the recognition of female artists have also gained momentum, contributing to a more equitable art scene where creativity transcends gender boundaries[3].
Environmental Concerns and Ecological Art

Environmental sustainability is a prominent theme in contemporary art, reflecting global concerns about climate change and ecological degradation. Artists like Olafur Eliasson and Agnes Denes use their works to raise awareness about environmental issues. Eliasson incorporates natural elements such as ice and water in his installations to confront viewers with the realities of global warming, while Denes juxtaposes natural and urban settings to comment on societal priorities[1].
In 2024, many contemporary artists are introspectively re-evaluating the cultural and environmental impacts of their practices, placing future generations at the core of their considerations. There is an increasing emphasis on sustainable practices, with artists using recycled materials and addressing ecological themes through their works[3][6].
Intersection of Art and Technology

Advancements in technology are reshaping the contemporary art landscape. Digital art and the rise of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) have revolutionized the art market, providing new mediums for artists and redefining how art is created, sold, and experienced. Artists are utilizing immersive experiences, augmented reality, and virtual installations to push creative boundaries[3][4].
The integration of technology not only enhances viewer engagement but also raises important questions about artistic creation and valuation. Blockchain technology and AI are influencing how artworks are authenticated and valued, often prioritizing social factors such as the artist's reputation over the visual qualities of the artwork itself[9].
Migration, Displacement, and Social Struggles
Contemporary art frequently engages with themes of migration and displacement, underscoring the global refugee crisis and national identity issues. Ai Weiwei's 'Good Fences Make Good Neighbors' installation in New York, for instance, used fences and cages to comment on the plight of refugees and sparked public discourse about borders and freedom[1].
This thematic emphasis is part of a broader recognition of art’s role in expressing and addressing the complex experiences of displacement, conflict, and hardship. Artists from various backgrounds utilize their works to highlight the resilience and struggles of displaced communities, fostering empathy and deeper understanding[8].
Conceptual and Minimalist Trends

Conceptual art, focusing on ideas over traditional aesthetics, and minimalist art are experiencing a resurgence in 2024. These movements encourage viewers to engage with the underlying ideas behind the art rather than the visual aspects alone. This approach reflects a growing preference for simplicity and subtlety in conveying complex messages[4].
Influence on Cultural and Global Awareness
Art education plays a significant role in promoting cultural and global awareness, exposing learners to diverse artistic traditions and prompting them to reflect on societal issues. By analyzing works that address inequality, discrimination, and environmental crises, students develop critical thinking skills and empathy, enhancing their understanding of different cultural contexts[2].
Artists, as cultural architects, continue to challenge established norms and foster inclusive narratives that reflect the diversity of human experience. This drive towards inclusivity enhances the richness of artistic expression and strengthens community engagement[7].
Economic and Community Impact

Art significantly contributes to both cultural enrichment and economic development. Through exhibitions, performances, and the creation of intellectual properties, artists drive economic growth and foster vibrant, innovative communities[2][7].
Strengthening community engagement through art education and public art initiatives also promotes social cohesion and cultural understanding, encouraging active participation and civic responsibility[2].
Conclusion
Contemporary art today serves as a mirror to society, reflecting and addressing pressing social, political, and environmental issues. It is a dynamic field that not only critiques and challenges societal norms but also fosters inclusivity, promotes dialogue, and inspires change. From addressing social justice and identity to engaging with environmental concerns and integrating technological advancements, contemporary art continues to shape and be shaped by the evolving cultural landscape.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.
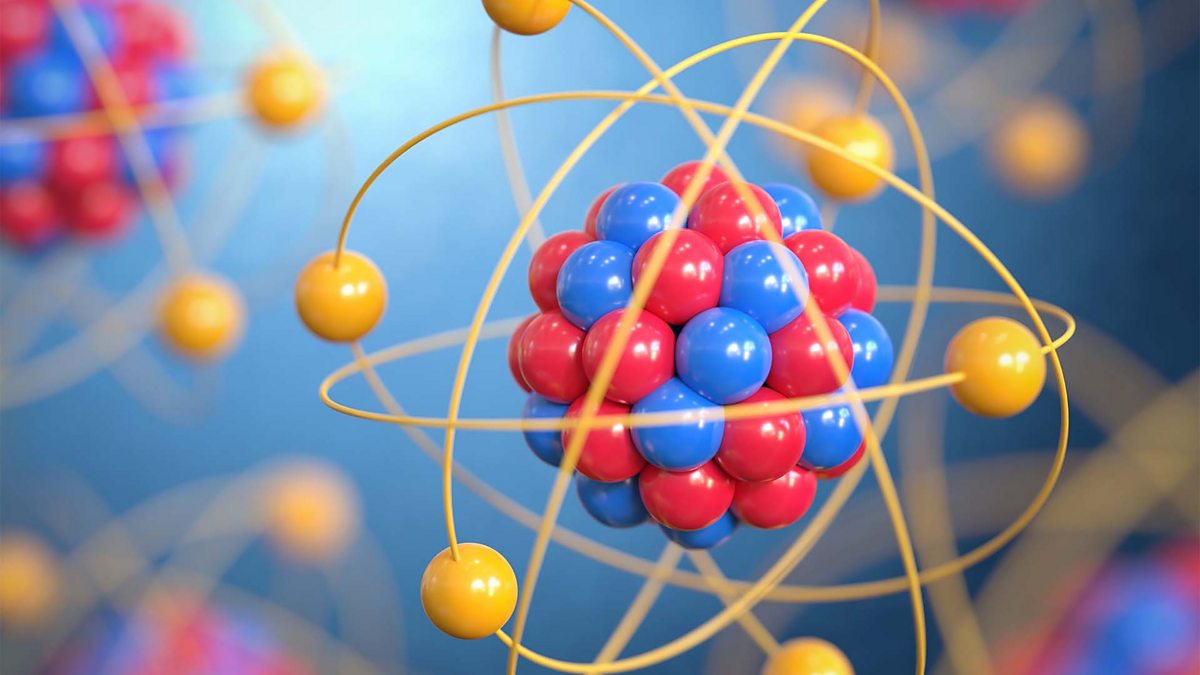
An atom is the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of a chemical element. It consists of a central nucleus made up of protons, which carry a positive charge, and neutrons, which are neutral. Electrons, which have a negative charge, orbit the nucleus in designated energy levels called electron shells. Most of the mass of the atom is concentrated in the nucleus, while the electrons orbit far away, making the atom predominantly empty space[1][4][5].
The atomic number, which is the number of protons in the nucleus, determines the element's identity. In a stable, neutral atom, the number of protons equals the number of electrons, resulting in no net charge[2][6].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Section 174[1] refers to a provision in the tax code that allows businesses to deduct or amortize certain[1] research and development (R&D) costs. It applies to all taxpaying entities, including corporations, small businesses, startups, and sole proprietorships. Qualifying expenses include salaries, supplies, patent costs, overhead expenses, and contract research expenses. However, not all R&D expenses are deductible under Section 174[1], and it's important to determine conformity to this provision at the state level.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Globalization is a multifaceted phenomenon that shapes the cultural landscape of nations around the world. As societies become increasingly interconnected through trade, communication, and technology, the implications for cultural preservation are profound and twofold, encompassing both opportunities and challenges.
Positive Aspects of Globalization

Globalization can stimulate cultural evolution and economic development by facilitating greater cultural exchange and interactions. According to research, globalization fosters the 'speedier cultural evolution' and enhances the ability of societies to adapt to environmental changes[1]. This phenomenon often results in transformative innovations that can lead to economic growth, as societies become more interconnected and incorporate diverse cultural practices into their economies[2]. Additionally, the hyper-connectivity provided by global communication technology allows for the flourishing of cultural diversity as communities become more informed about different ways of life and traditions[1][8]. This interconnectedness can promote cultural enrichment, as individuals share and learn from one another beyond geographical boundaries.
Moreover, globalization helps minority and underrepresented groups leverage global platforms to share their narratives, thereby contributing to cultural preservation. Initiatives that emphasize the involvement of local communities in heritage preservation can lead to more inclusive representational practices. For instance, the World Monuments Fund emphasizes the significance of integrating diverse perspectives in cultural discussions, which can enhance the recognition and safeguarding of lesser-known cultural heritages[2].
Challenges Posed by Globalization
However, globalization simultaneously poses significant challenges to cultural preservation. The influx of global culture, driven by media and commerce, often leads to the homogenization of cultural expressions, threatening the uniqueness of local traditions. Many scholars contend that cultural globalization can result in 'a standardization of cultural expressions around the world,' thus creating concerns about cultural erosion and identity loss[3]. This notion is further evidenced by the experiences of various communities in different regions, as rural areas express apprehensions about the impact of dominant cultural narratives that overshadow local customs[5].
As communities assimilate into the global culture, they may face pressure to abandon their traditional practices and languages in favor of more popularized or commodified forms of expression. The loss of ethnobotanical knowledge and the decline of traditional languages are significant consequences attributed to this cultural shift[1]. Additionally, the commodification of culture can lead to the exploitation of cultural symbols and practices, which often strips them of their authentic significance[5][6]. This commodification can be especially damaging to indigenous communities, where cultural appropriation may dilute their heritage while undermining their authority over their cultural narratives[2][3].
Cultural displacement also manifests as a critical issue stemming from globalization. People migrating from rural to urban areas or relocating internationally may lose touch with their cultural roots, contributing to a lack of cultural continuity. The connection between traditional knowledge and the younger generations gradually diminishes, leading to a further risk of cultural extinction[4]. Additionally, rapid urbanization can displace traditional lifestyles, making it difficult for communities to maintain their unique ways of life in the face of modernization[6].
Strategies for Cultural Preservation
In light of the challenges posed by globalization, various strategies can be employed to safeguard cultural heritage while embracing the benefits of global interconnectedness. Educational initiatives play a significant role, as integrating cultural education within formal curriculums can help nurture a sense of cultural identity among younger generations[6]. Documenting and archiving cultural practices and artifacts is vital for preserving traditions for future generations, as these resources serve as repositories of cultural knowledge that can counteract the effects of cultural erosion[5].
Community involvement is essential in implementing effective cultural preservation strategies. Empowering local populations to take ownership of their cultural heritage leads to more sustainable practices. Governments also play a crucial role in creating supportive policies and legal frameworks to protect cultural sites and traditional knowledge[4][6].
Moreover, leveraging technology can provide new avenues for cultural expression and preservation. Digital platforms can facilitate the sharing of cultural narratives, allowing broader engagement and raising awareness about the importance of cultural heritage[2]. This approach not only protects cultural expressions but also democratizes access to cultural knowledge, fostering a deeper understanding of diverse heritages[7].
Conclusion
In conclusion, globalization exerts a dual influence on cultural preservation, offering both opportunities for exchange and significant challenges that threaten the uniqueness of local traditions. By strategically navigating these complexities, communities and organizations can work towards fostering cultural resilience in our increasingly interconnected world. Establishing proactive measures to safeguard cultural identities will be key in determining the future of cultural diversity in the age of globalization.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.