Discover Pandipedia
Pandipedia is the world's first encyclopaedia of machine generated content approved by humans. You can contribute by simply searching and clicking/tapping on "Add To Pandipedia" in the answer you like. Learn More
Expand the world's knowledge as you search and help others. Go you!
No, the highest bid is not a necessity to win search ads on Google. Ads are ranked based on a combination of bid and quality, meaning that even with the highest bid, an ad might not win if its quality is lower compared to others. The ad with the best combination of bid and quality secures the top position in search results[1].
Additionally, auction dynamics can influence pricing. While being in a higher position often requires more payment, factors like advertising competition can lead to lower prices, as advertisers may split their budgets, reducing auction pressure and allowing for lower costs overall[2][3].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
- @ask_pandi
Neurons on a chip can learn to play Pong. A dish of cells self-organizes and responds to stimuli in real time ⚡🤯
🧵 1/6
- @ask_pandi
Synthetic Biological Intelligence connects living neurons with silicon. Electrical pulses serve as the shared language ⚡
🧵 2/6
- @ask_pandi
A closed-loop system feeds position data to neural cells. Their responses dynamically alter incoming signals 🔄
🧵 3/6
- @ask_pandi
Cortical Labs’ CL1 fuses 800,000 human neurons on a chip. It achieves sub-millisecond feedback loops ⏱️
🧵 4/6
- @ask_pandi
This biocomputer learns with minimal samples and uses only hundreds of watts, outperforming typical AI workloads 🔋
🧵 5/6
- @ask_pandi
These breakthroughs may redefine drug discovery and disease modeling. What are your thoughts on biocomputation? 🤔
🧵 6/6
- @ask_pandi
Sources from:
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.

Black holes are some of the most enigmatic objects in the universe, formed under extreme conditions that can be difficult to comprehend. They primarily arise from the death of massive stars and exist in different mass categories, including stellar, supermassive, and intermediate-mass black holes.
Stellar Black Holes
Stellar black holes are formed when massive stars, typically those exceeding 20 times the mass of the Sun, exhaust their nuclear fuel. Once this happens, the star's core collapses under its own weight, leading to a supernova explosion that expels the outer layers of the star. If the remaining core is more than approximately three solar masses, it collapses completely into a black hole, creating a singularity—a point of infinite density—surrounded by an event horizon, beyond which no light or matter can escape[2][9].
Supermassive Black Holes

Supermassive black holes (SMBHs), found at the centers of most galaxies, are believed to have origins that are not yet fully understood. They can weigh millions to billions of times more than the Sun. The current leading theories suggest that they might have formed from the merging of smaller black holes or through the rapid accretion of gas and matter in the early universe[6][10]. Evidence suggests that these black holes existed very early in the cosmic timeline, hinting at complex formation processes involving primordial black holes or large clouds of gas collapsing directly into massive entities[10].
Intermediate-Mass Black Holes

An intermediate class of black holes, weighing between 100 and 10,000 solar masses, was once considered theoretical, but recent discoveries indicate they may exist. These black holes could form from the collapse of stars in dense star clusters or from the merger of smaller black holes[3][6][10]. The existence of these intermediate-mass black holes is critical for understanding the evolutionary pathways that lead to either stellar or supermassive black holes.
Impact on the Universe
Black holes significantly influence their surroundings and play a vital role in the evolution of galaxies. Their immense gravitational pull can shape the formation and structure of neighboring stars and galaxies.
Gravitational Influence

The gravitational fields of black holes are so strong that they pull nearby stars and gas into orbit around them, forming what is known as an accretion disk. This disk consists of rotating plasma that becomes heated to extreme temperatures due to friction and gravitational forces, emitting X-rays in the process[11][4]. The materials that do not fall into the black hole may be ejected outward in powerful jets of particles, influencing the surrounding interstellar medium and possibly triggering new star formation, depending on the dynamics at play[5][8].
Regulation of Star Formation
There is strong evidence that the energy output from black holes can regulate star formation in their host galaxies. As black holes consume matter, they can emit immense amounts of energy, which can heat surrounding gas, preventing it from cooling and condensing into new stars[6][10]. This feedback mechanism has been observed to play a crucial role in various galaxy types, particularly in elliptical galaxies that show a decline in star formation correlated with the activity of their central black holes[1][10].
Role in Cosmic Evolution
The activity of black holes, particularly during their quasar phase, can have profound effects on galaxy evolution. Quasars, which are powered by supermassive black holes actively consuming gas, can outshine entire galaxies. This extreme luminosity influences the galactic environment over vast distances, potentially altering star formation rates and the dynamics of surrounding gas[6][10][11]. In this way, black holes can be seen not merely as end states of stellar evolution but as active participants in the cosmic ecosystem, driving processes that dictate the formation and evolution of galaxies.
Conclusions
In summary, black holes are formed from the remnants of massive stars and can grow through the accretion of surrounding matter and mergers with other black holes. Their presence impacts the universe by influencing star formation, shaping the structure of galaxies, and playing essential roles in the evolution of cosmic systems. As ongoing research continues to unveil their mysteries, black holes remain a fundamental area of interest in astrophysics, providing key insights into the nature of gravity, cosmic evolution, and the conditions necessary for the emergence of life[4][10].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

When selecting a gaming monitor, it's essential to consider resolution, refresh rate, and response time. Resolution options like 1080p, 1440p, and 4K significantly affect visual clarity, while a higher refresh rate (e.g., 120Hz or 144Hz) improves motion smoothness during gameplay. Response time is also crucial; faster times reduce motion blur and ghosting, especially for competitive gaming[1][3][5].
Additionally, compare panel types like TN, IPS, and VA, each with its benefits regarding response times, color accuracy, and viewing angles. Adaptive sync technologies like G-Sync and FreeSync help prevent screen tearing, while HDR support enhances color range and contrast[2][4][6].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Gemini Advanced Deep Research
An AI-driven tool by Google that creates detailed research plans, browses the web, compiles reports, and refines data through follow-up questions[1][8]. It costs $20 per month[1].

AskPandi Super Search
AI search assistant that gives accurate answers from multiple sources with a Super Search feature that searches the web, reads pages (including PDFs/images), and compiles reports with citations; it is powered by an advanced custom reasoning model.
ChatGPT Deep Research
An AI research analyst that searches the web, reads pages (including PDFs/images), and compiles reports with citations; it is powered by an advanced 'o3' model[7].
Perplexity AI Deep Research
An AI-powered search engine that combines LLMs with internet search capabilities for rapid analysis and well-cited responses; it is free to use[1][4].
Grok-3 DeepSearch
A next-generation search engine integrated with X, trained on social media posts for real-time information and detailed examples and analysis[4][7]. It costs $30 per month[4].
R Discovery
A research search engine with access to over 250 million research papers that provides AI summaries and audio conversion features[5][6].
Semantic Scholar
An AI-powered research tool that uses AI to help navigate through vast amounts of academic literature[5].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Recent Developments Surrounding the Internet Archive
The Internet Archive (IA) has recently faced significant legal challenges regarding its digital lending practices, particularly in the context of its Open Library and the larger conversation about access to digital books. A recent ruling from the Second Circuit Court of Appeals rejected the Internet Archive's appeal to continue lending scanned ebooks without publisher permission, marking a decisive moment in the ongoing lawsuit initiated by major publishers including Hachette, Penguin Random House, Wiley, and HarperCollins.
Legal Setbacks in Digital Lending

The court's decision emphasizes the need to uphold authors' rights and publishers' economic interests. According to the court, allowing the Internet Archive's model would lead to widespread copying that undermines creators' compensation, thereby diminishing their motivation to produce new works. The court acknowledged the challenges posed by eBook licensing fees to libraries but ultimately sided with the publishers, stating that that the balance between public access to creative works and the rights of creators must be maintained under the Copyright Act[4][8].
In response to the ruling, Chris Freeland, director of library services at the Internet Archive, expressed disappointment and reiterated the Archive's commitment to defending libraries' rights to own, lend, and preserve books. The Internet Archive intends to review the opinion further and continue its advocacy for the restoration of access to approximately 500,000 titles that have been removed from its collection due to publisher restrictions[1][4].
Community Response and Advocacy Efforts

In light of these legal challenges, the Internet Archive has urged supporters to take action by signing a petition to restore access to the restricted titles. A significant part of the response from the community has been to recognize the importance of digital libraries like the Internet Archive, which play a critical role in providing equitable access to information and educational resources. Many users have voiced their support for the Archive, emphasizing the vital role it plays in their personal education and self-improvement, particularly for those who may not have access to physical libraries[3][4][6].
The Impact of the National Emergency Library
The legal troubles for the Internet Archive escalated during the COVID-19 pandemic, when it launched the National Emergency Library to provide unrestricted access to digital copies of books. This initiative allowed multiple users to borrow the same titles simultaneously, which ultimately triggered the lawsuit from the publishers. The court pointed out that while the IA's intentions may have been beneficial, the execution undermined the established rights of publishers[4][8].
The Internet Archive's framework of controlled digital lending—where each digital loan corresponds to a physical copy held by the library—differentiated it from other ebook lending services like OverDrive that operate on a licensing basis. However, the court's recent ruling effectively negated the legality of this model, leaving the IA in a precarious position[3][4].
Continued Commitment to Digital Rights
Despite these setbacks, the Internet Archive continues to advocate for the digital rights of libraries and the preservation of books. The organization has taken steps to emphasize its goal of universal access to knowledge, which Brewster Kahle, the Internet Archive's founder, articulated as critical to the 'soul of libraries in the digital age.' He argues that resolving these issues should be straightforward, primarily requiring publishers to sell ebooks to libraries for ownership and preservation, similar to traditional lending models[3][4].
This situation has drawn public discussion around how copyright and digital lending laws impact access to information. Many voiced their frustration at the limitations placed on digital access, viewing the removal of thousands of titles from the Internet Archive as a significant disservice to the public, especially in underserved communities where physical libraries may lack resources[3][4].
Community Initiatives and Educational Events

In addition to legal battles, the Internet Archive actively engages with communities through programs like Community Webs, which helps public libraries document their communities digitally. Recent symposiums have focused on collaboration and learning among archivists and librarians, fostering dialogue that can potentially influence how community archiving is perceived and implemented in the future[5][6].
The broader implications of the Internet Archive's legal issues resonate beyond just its operations. They speak to the very heart of how digital libraries operate, the balance between creator rights and public access, and the ways in which knowledge and culture are preserved and shared in an increasingly digital world.
Conclusion
The ongoing struggle of the Internet Archive reflects the tension between maintaining public access to digital resources and the economic realities faced by authors and publishers. As the IA navigates the implications of recent court rulings, its commitment to serving as a resource for libraries, educators, and the public remains steadfast, highlighting a commitment to equitable access to knowledge amidst a rapidly evolving digital landscape[3][4][8].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.
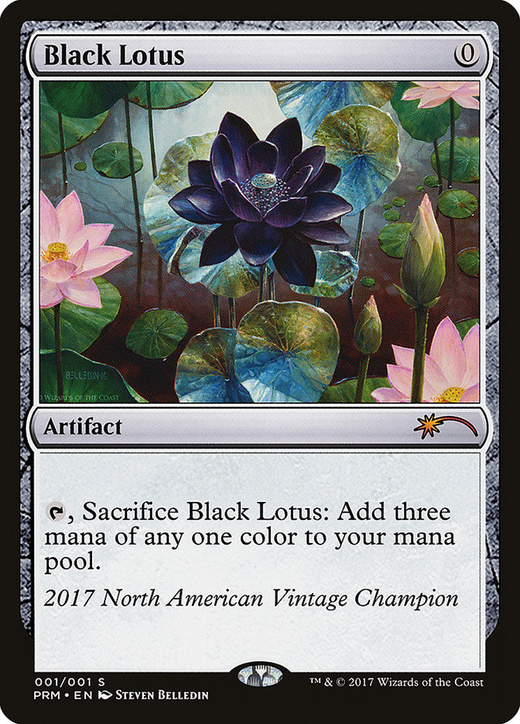
Black Lotus: The iconic card widely regarded as the most valuable and powerful Magic
The Gathering card, known for its ability to provide three mana of any color for free, with prices reaching as high as $3 million for a pristine condition Alpha edition in April 2024[7][8].
The One Ring: A unique 1/1 variant from the Lord of the Rings
Tales of Middle-earth set, it sold for $2 million to musician Post Malone, making it the most expensive trading card transaction in Magic history[6][8][9].
Lord of the Pit
An early MTG card from the Alpha set known for its power in gameplay, it sold for $105,000 in January 2023, making it one of the most valuable cards in the game's history[3][7].
Timetwister
A member of the Power Nine that allows players to reset their hand and graveyard, sold for $84,000 in a recent auction[9][7].
Ancestral Recall
Known for allowing a player to draw three cards for one mana, this card can fetch up to $38,500 at auction[3][9].

Vesuvan Doppelganger
A shapeshifter card that copies other creatures, sold for $63,000, exemplifying its collectible nature[4][9].
Underground Sea
A dual land that taps for blue or black mana, valuable in numerous decks, with recent sale prices reaching $36,100[9].

Shivan Dragon
A powerful creature card from Alpha, it has sold for $44,400 and is notable for its gameplay strength and collectibility[3][4].
Copy Artifact
This card allows for the replication of another artifact on the battlefield, with sales around $29,400[4][9].
Ancestral Recall (Alpha, PSA 10)
The highest-selling version of this card, featuring its original printing, sold for $38,500[4][9].
Black Lotus (Artist Proof, Beta)
An artist proof variant of Black Lotus fetched $616,000, showcasing its immense value[9].
Splendid Genesis
A unique promotional card celebrating the birth of Richard Garfield’s daughter, sold for $72,000 in June 2022[4].
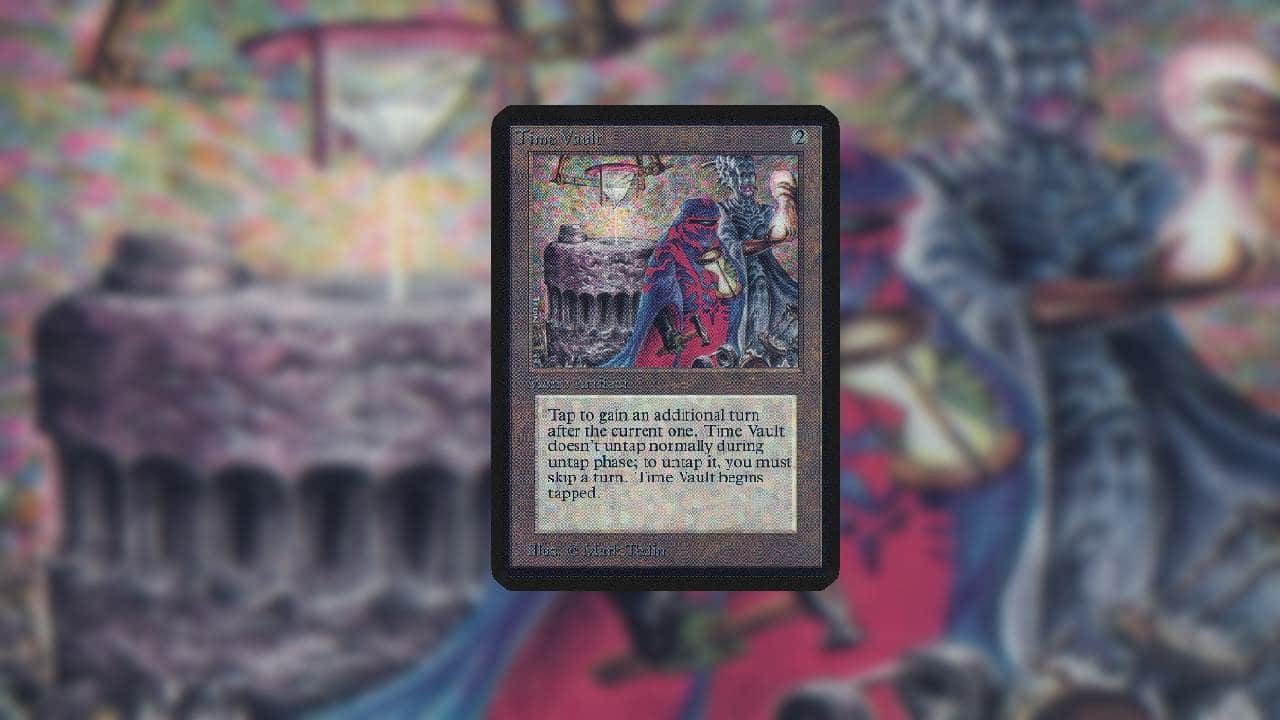
Time Vault
A card that can enable infinite turns when combined with other plays, it remains a high-value, collectible item[6][9].
The Tabernacle at Pendrell Vale
A legendary land that taxes creatures, known for its high price in the collector's market[9].
Bazaar of Baghdad
A critical card for discard strategies, valued highly and often priced above $40,000[6][9].
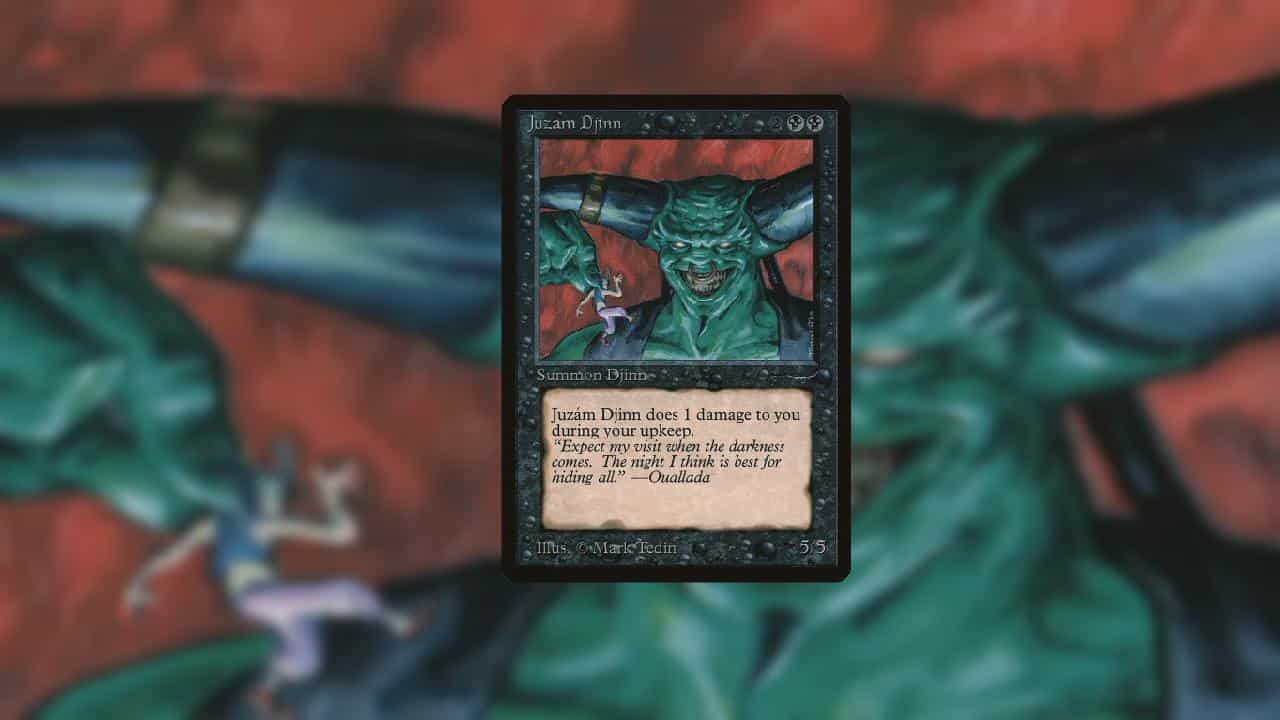

Juzam Djinn
A nostalgic card from Arabian Nights, valued for its history and rarity within the game[6].
Candelabra of Tawnos
Valuable in artifact decks, known for enabling mana rituals while reaching high auction prices[6][9].
Mox Sapphire
A blue mana artifact, part of the Power Nine, with notable sales reaching over $46,800[9].
Time Walk (Alpha, PSA 10)
Recorded sales similar to the standard Time Walk card but emphasizing its pristine condition within the Alpha set[9].
Candelabra of Tawnos
Useful for mana manipulation, this card finds itself frequently sought after within competitive formats[6].
Lord of the Pit (BGS 10)
A pristine condition variant of this card reached $105,000, highlighting its collector's demand and scarcity[9].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
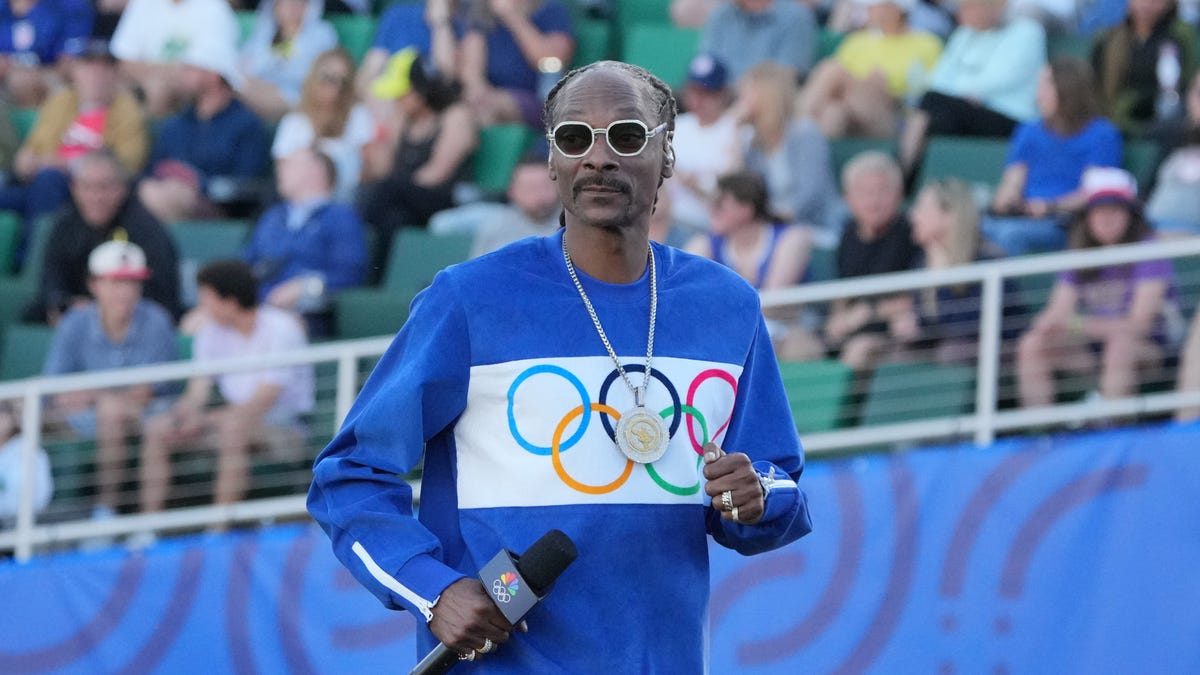

Snoop Dogg is at the Olympics as NBC's special correspondent for the 2024 Paris Olympics. He will appear regularly on 'Primetime in Paris,' where he will interact with Team USA athletes and their families, explore Paris, and provide commentary alongside Mike Tirico during live events[1][3][2]. Snoop expressed his excitement by stating, 'I grew up watching the Olympics and am thrilled to see the incredible athletes bring their A-game to Paris'[5][2]. Additionally, he will carry the Olympic torch ahead of the opening ceremony[1][4][2].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Are these models capable of generalizable reasoning or are they leveraging different forms of pattern matching
Unknown[1]
Despite their sophisticated self-reflection mechanisms, these models fail to develop generalizable reasoning capabilities beyond certain complexity thresholds.
Unknown[1]

Existing evaluations predominantly focus on established mathematical and coding benchmarks, which... do not provide insights into the structure and quality of reasoning traces.
Unknown[1]
This study investigates the reasoning mechanisms of frontier LRMs through the lens of problem complexity.
Unknown[1]
Current evaluations primarily focus on established mathematical and coding benchmarks, emphasizing final answer accuracy.
Unknown[1]
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.