Discover Pandipedia
Pandipedia is the world's first encyclopaedia of machine generated content approved by humans. You can contribute by simply searching and clicking/tapping on "Add To Pandipedia" in the answer you like. Learn More
Expand the world's knowledge as you search and help others. Go you!

The ancient Library of Alexandria was located in the city of Alexandria in Egypt. It formed part of the larger intellectual complex called the Mouseion (or Museum), which was situated in the royal quarter (the Brucheion) of the city—close to the harbor and within the central area of ancient Alexandria—even though its exact site has been lost over time[1][2][3][4].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Emerging mental health support technologies include AI-driven tools, mobile apps, and virtual services. AI technologies enhance diagnostic accuracy and personalize treatments, with chatbots like Woebot and Wysa providing round-the-clock support and cognitive behavioral therapy techniques in real time[1][4].
Mobile apps facilitate access to resources for relaxation, meditation, and therapy, such as BetterHelp and Moodpath. Additionally, teletherapy offers convenient connections between patients and therapists regardless of location, breaking down traditional barriers to mental health care[2][3][4]. Wearable devices also play a role by monitoring physiological states and providing feedback for real-time mental health management[4][5].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.
The Impact of Transportation on Climate Change
Global Emissions Overview
Transportation plays a substantial role in contributing to climate change, being responsible for approximately 24% of global carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions associated with energy use. This sector's growth is driven primarily by the increased demand for mobility, with projections indicating a potential tripling of passenger transport demand by 2050, significantly amplifying its climate impact if left unaddressed. Road vehicles, encompassing cars, trucks, buses, and motorbikes, contribute nearly three-quarters of all transport-related greenhouse gas emissions, underscoring the sector's heavy reliance on fossil fuels[1][6][10].
Breakdown of Emissions by Mode of Transport
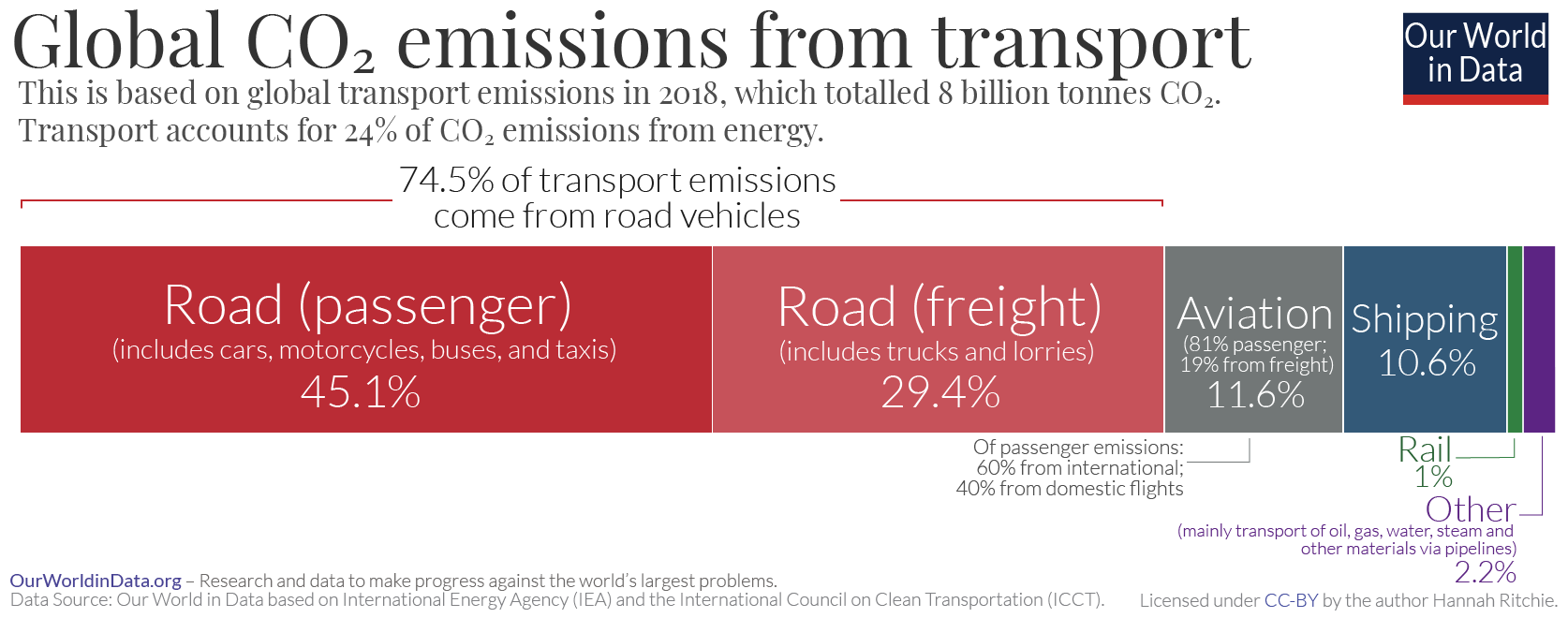
In 2018, road transport accounted for about 74% of transport-related greenhouse gas emissions, with passenger vehicles making up 45.1% of this share and freight trucks adding another 29.4%. Aviation, often highlighted in climate change discussions, contributed only 11.6% of transport emissions, while international shipping accounted for 10.6%. Rail travel and freight accounted for a mere 1% of total transport emissions[1][5][7]. This delineation of responsibility emphasizes the critical need to target road transportation for emission reductions.
The transportation sector is not static; rather, it faces an urgent need for technological innovation and policy reform as traditional fuels are increasingly outpaced by demands for lower-carbon solutions. The International Energy Agency (IEA) anticipates that without major interventions, transport emissions could double by 2050 due to rising global demand combined with increasing fuel consumption[1][10].
Challenges and Opportunities for Decarbonization
Efforts to decarbonize transportation are hampered by several factors, including the entrenched prevalence of private vehicle use and the slow turnover of existing vehicle and infrastructure stock. Studies show that while electrification and other technologies promise significant gains, achieving widespread adoption and impact requires an integrated approach involving substantial policy changes, infrastructure investments, and shifts in consumer behavior[2][6][9].
The IEA has outlined that achieving net-zero emissions in transportation by 2070 would necessitate a significant transformation across various transport modes. This includes phasing out emissions from motorcycles by 2040, rail by 2050, and small trucks by 2060. The journey toward decarbonization emphasizes that while some sub-sectors have clear paths, others, such as long-distance trucking, aviation, and shipping, present formidable challenges due to their operational complexities and existing infrastructure[1][4].
The Role of Public Transit in Emission Reduction

Public transportation systems, including buses and trains, present one of the best solutions for reducing the carbon footprint of urban travel. Buses can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to two-thirds per passenger per kilometer compared to private vehicles. The World Resources Institute (WRI) notes that increasing reliance on public transit is essential for curbing climate change while simultaneously enhancing societal benefits such as safer streets and improved access to essential services[2][7][10].
Nevertheless, the recovery of public transport ridership post-COVID-19 has varied widely. In many low- and middle-income countries, ridership has rebounded or even surpassed pre-pandemic levels, while high-income regions have seen slower recovery. This highlights the need for robust public transit planning that includes investing in infrastructure and implementing policies that encourage public transport use over private vehicle ownership[2][5][8].
Urban Planning and Behavioral Change
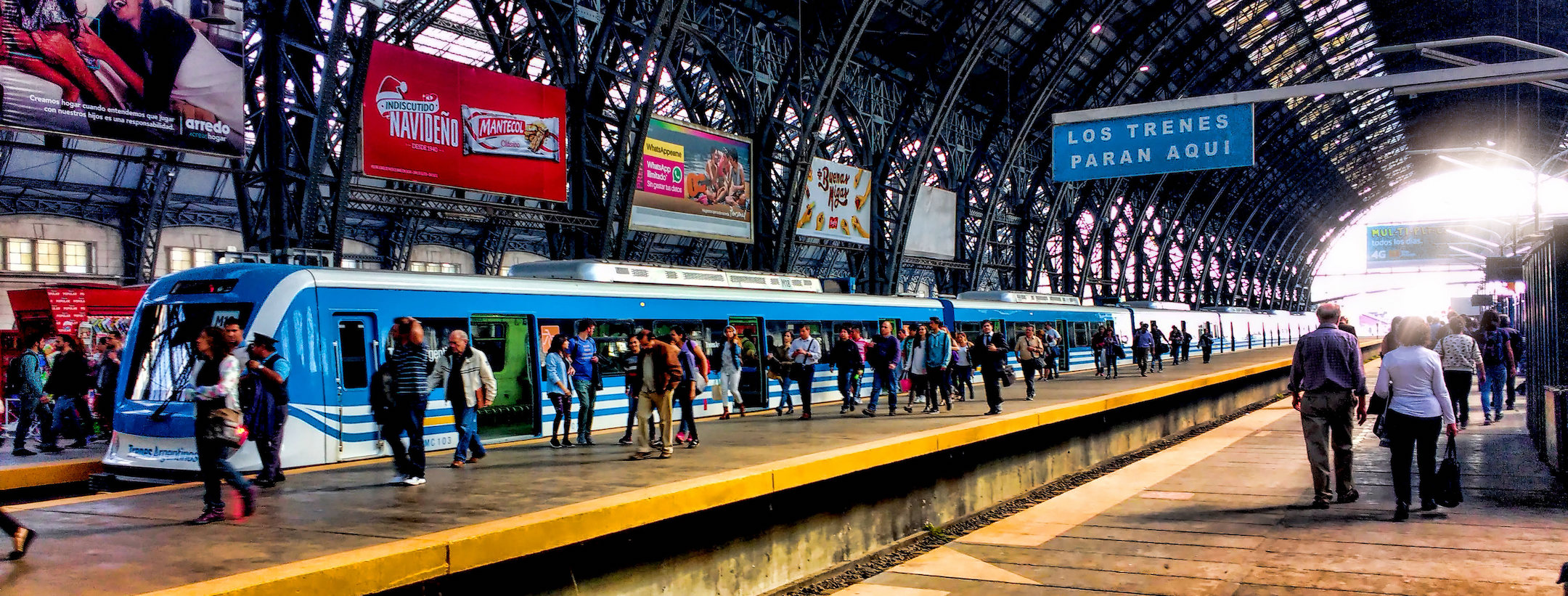

Efforts to mitigate transportation's climate impact must also include changes in urban development and planning. Well-planned cities that encourage walking, cycling, and public transit can significantly reduce the need for private vehicles. Successful examples from countries like the Netherlands demonstrate that connected transit systems, combined with pedestrian-friendly infrastructure and cycling lanes, not only lower emissions but also enhance quality of life for residents[3][10][9].
Behavioral change is crucial. Campaigns to encourage walking and cycling for short trips, as well as initiatives like carpooling, can represent low-hanging fruit in emission reduction strategies[3][8]. There is evidence suggesting that adjusted driving habits and an increased focus on sustainable travel can reduce personal carbon footprints meaningfully.
Policy Measures and Investments for a Sustainable Future
To effectively tackle transportation emissions, comprehensive policy frameworks are essential. Governments can implement a range of measures such as congestion pricing, improved vehicle standards, and incentives for public transit usage. Structural reforms and investments in renewable energy infrastructure will also play a vital role in transitioning the sector to low-carbon alternatives[6][9][10].
The transport sector's financing remains a significant hurdle. Many investments in sustainable transport systems are perceived as risky, requiring innovative funding mechanisms to encourage private sector participation[6][10]. Sustainable urban planning, combined with investment in renewable energy sources for public transport, can create the groundwork for resilient and low-carbon transportation systems, ultimately leading to lower emissions and improved urban experiences.
Conclusion
Transportation significantly impacts climate change, with emissions largely driven by road travel and private vehicle reliance. Decarbonization requires a multi-faceted approach involving technology, policy reform, enhanced public transit systems, and urban planning that encourages sustainable mobility options. Collaborative efforts from governments, private sectors, and communities will be essential to achieve lasting change and mitigations against climate change effects in the transportation sector.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Yes, there are several AI tools specifically designed to assist digital nomads in enhancing their productivity and managing various tasks. For instance, tools like Trello and Asana utilize AI to automate task prioritization and provide smart reminders to help stay on top of deadlines, while Notion and ClickUp offer features that streamline project management and organizational efforts across time zones[1][3].
Additionally, writing assistants like Grammarly and Jasper AI improve the quality of communication, and translation tools like DeepL facilitate seamless interaction in different languages. AI-powered travel tools, such as Hopper, can predict the best time to book flights, enhancing overall travel planning for remote workers[2][4].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Starting the Day with a Consistent Morning Routine
Digital nomads begin their day by establishing a routine that sets the tone for both professional productivity and personal well‐being. Many wake early—sometimes around 5:30–6:00 AM—to engage in physical activity such as a morning run and to enjoy a quiet moment with a cup of local coffee. One digital nomad detailed waking, hydrating, and then hitting the pavement before heading to check emails and prepare for team calls later in the morning[10]. This structured start helps in transitioning from the leisure of sleep into the focus required for a productive coworking day.
Choosing and Setting Up the Coworking Environment
After the morning routine, nomads typically travel to a coworking space that is specifically designed to foster productivity. These workspaces, as described by several sources, are well equipped with high‐speed internet, ergonomic furniture, and essential office amenities. For instance, one guide emphasizes that a coworking space’s success lies in offering reliable Wi-Fi, quiet zones, adjustable desks, and meeting rooms that can support both deep work and spontaneous meetings[1][6]. Nomads often utilize a portable work setup that includes an external monitor, ergonomic keyboard, and noise‐canceling headphones to create a personal bubble of concentration even in bustling environments[2]. This preparation ensures that upon arrival they can quickly transition into “work mode,” signaling to themselves and to others that it is time to focus.
Deep Work and Structured Work Sessions
Once settled in the coworking space, digital nomads devote the bulk of their working hours to intensive, focused work sessions. They frequently use techniques like time blocking and the Pomodoro Technique to break their day into segments dedicated to deep work, administrative tasks, and remote team meetings. One nomad described setting aside an early block, for example from 8:00 AM to 10:00 AM, for deep work—capitalizing on the quiet hours immediately after arrival at the workspace[9]. During the day, team calls might be scheduled with colleagues in different time zones, ensuring communication remains seamless. Maintaining a structured work schedule, even when the environment is dynamic, helps these professionals meet deadlines while balancing creative and analytical tasks[9][10].
Taking Breaks and Engaging in Networking
To combat potential burnout and maintain a high level of productivity, regular breaks are scheduled throughout the day. Nomads frequently step out for lunch or enjoy an extended coffee break in communal areas, giving them a chance to decompress. In many coworking spaces, these breaks also serve as networking opportunities. Interaction with other professionals in the space not only sparks collaboration but also helps in building a supportive community. One source highlights the value of informal conversations over shared coffee breaks, noting that these interactions can lead to new ideas and sometimes even future business partnerships[6][3]. By alternating between intense work sessions and restorative social or reflective breaks, digital nomads manage to maintain clarity and motivation throughout their day.
Adapting Work Hours and Balancing Time Zones
A key component of a typical digital nomad coworking day is the ability to adapt working hours to suit both local conditions and the demands of remote teams located in different time zones. Many digital nomads adjust their schedules based on factors such as local business hours, weather, and the need to attend virtual meetings with teams overseas. For example, one nomad recounted how, when working in a region with high daytime temperatures, they shifted their deep work to early mornings and resumed work in the evening when conditions cooled[4]. This flexibility, paired with digital calendaring tools that automatically adjust for time zones, ensures that communication with remote clients and colleagues remains efficient while still allowing ample time for local exploration.
Midday Use of Facilities and Continued Productivity
During the midday period, many digital nomads make full use of the coworking facilities. The structured environment often includes access to soundproof phone booths, meeting rooms for private discussions, and communal spaces designed for collaboration. Some even attend scheduled workshops or networking events organized within the coworking space. These offerings not only enhance productivity but also provide additional training and learning opportunities, reinforcing professional skills and building personal networks[5][7]. The synergy between the physical environment and the organizational tools available allows digital nomads to pivot rapidly from individual work to collaborative sessions whenever necessary.
Wrapping Up and Transitioning to Leisure
As the workday draws to a close, digital nomads begin winding down by revisiting the key tasks completed and planning for the following day. This wrap‐up phase may involve finishing up loose ends on ongoing projects and updating shared calendars with upcoming meetings. After leaving the coworking space, many nomads take advantage of their surroundings by engaging in local cultural experiences, such as visiting night markets, exploring cafes, or simply relaxing in a scenic outdoor setting[10]. This transition from work to leisure is essential in helping maintain a balanced lifestyle—a principle that has been repeatedly emphasized across various accounts[8][9].
Flexibility, Consistency, and the Overall Digital Nomad Experience
Throughout the day, a recurring theme is the balance between flexibility and structured consistency. While digital nomads benefit from the freedom to set their own schedules, the reliance on coworking spaces ensures that they maintain a professional environment that mirrors the expectations of traditional office work. This combination of rigid work blocks and flexible break times embodies the evolution of work into a mobile, boundary-defying activity. As several studies note, even though the digital nomadic lifestyle is built on the promise of freedom from the conventional office, many nomads find themselves replicating office-like structures—such as fixed start and end times and dedicated work sessions—to support productivity and professionalism[11].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Understanding ASMR

The Autonomous Sensory Meridian Response (ASMR) is commonly described as a pleasant tingling sensation that begins in the scalp and neck and can spread throughout the body. This sensation is triggered by specific audio-visual stimuli, such as whispering, tapping, and gentle hand movements. Individuals who experience ASMR often report that it leads to feelings of relaxation, calmness, and overall positive affect[2][3].
Emotional and Psychological Responses
ASMR triggers a unique blend of emotional responses, characterized by both activation and relaxation. According to studies, ASMR experiences are associated with increased levels of calmness and excitement following exposure to ASMR videos. Specifically, research showed that ASMR participants reported significantly greater improvements in calmness and excitement compared to those who do not experience ASMR[6][10]. Interestingly, ASMR participants also experience reductions in negative emotions such as stress and sadness while watching ASMR videos, leading to a more favorable emotional state overall[8][10].
Furthermore, ASMR is not merely an entertaining phenomenon; it may serve as a therapeutic tool. A study highlighted that participants who experience ASMR often engage with these videos to manage stress and anxiety, showing significant decreases in both state and trait anxiety after viewing ASMR content. This reduction in anxiety is particularly pronounced in individuals already predisposed to higher levels of these emotional states[4][5][8].
Physiological Effects
In addition to psychological impacts, ASMR elicits measurable physiological responses. Research indicates that watching ASMR videos is linked to lower heart rates and increased skin conductance, which are indicators of relaxation and arousal, respectively[7][10]. These findings align with the idea that ASMR can be beneficial for regulating emotional states and may provide substantial therapeutic effects for individuals suffering from mood disorders, including anxiety and depression[6][9].
Individual Variability and Personality Traits
Notably, not everyone experiences ASMR. Only certain individuals are susceptible to this sensation, and studies have explored the personality traits associated with ASMR sensitivity. Research suggests that people who can experience ASMR often exhibit higher levels of neuroticism. This personality trait is linked to a predisposition to anxiety and negative emotional states[4][5]. ASMR experiences might amplify these emotional responses based on the individual's state of mind leading up to the exposure. For example, while ASMR is primarily associated with relaxation, misinterpretation of ASMR stimuli could lead to fear or disgust, particularly in those with high anxiety levels[9][10].
ASMR as a Therapeutic Intervention
Emerging literature supports the potential of ASMR as a non-pharmacological intervention for anxiety reduction. One study noted that all participants, regardless of their experience with ASMR, reported increased relaxation and improved mood after watching ASMR videos, with the most significant effects seen in individuals who regularly experience ASMR[6]. This suggests that ASMR may have therapeutic implications, particularly for individuals dealing with insomnia or depressive symptoms, potentially aiding sleep and reducing stress levels[8][9].
Furthermore, ASMR has been linked with mindfulness-like qualities, as the focused attention required to experience ASMR resembles mindfulness practices that have been shown to alleviate anxiety[6]. The possibility that ASMR can function similarly to mindfulness meditation could open new avenues for therapeutic application in psychological interventions.
Conclusion
The psychological effects of ASMR are diverse, combining emotional relief, physiological relaxation, and potential therapeutic benefits, particularly for those with anxiety disorders. Experiencers report significant improvements in mood, along with reductions in stress and anxiety levels after engaging with ASMR stimuli. Considering the growing popularity of ASMR videos, further research into this phenomenon could solidify its role as a viable method for improving mental health and emotional well-being, particularly for those high in neuroticism or suffering from anxiety disorders[2][4][6][9][10].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.

Lobbying plays a significant role in influencing government policy by advocating for specific interests. It involves both professional lobbyists, who may represent corporations and nonprofit organizations, and individual citizens who wish to address issues important to them. Lobbyists provide information, analysis, and advice to legislators, facilitating better-informed decision-making in areas like business and science[1][4][5][6].
However, the practice faces criticism for potential corruption and creating an unequal playing field where wealthy interests gain disproportionate access to policymakers. Regulatory measures exist to enhance transparency, such as registration requirements for lobbyists, but concerns about effectiveness and loopholes persist[2][3][5][6].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Mixed media art refers to artwork in which more than one medium or material has been employed. Common examples of mixed media include assemblages, collages, and sculptures. The materials used can encompass paint, cloth, paper, wood, and found objects among others[1].
Mixed media art differs from multimedia art, which combines visual elements with non-visual components such as sound and interactivity[1]. The genre gained popularity in the 20th century with modern artworks like Pablo Picasso's 1912 collage 'Still Life with Chair Caning' being notable examples[1]. Different forms within mixed media art include collage, assemblage, found object art, altered books, and the use of wet and dry media[1].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Introduction

Nestled in the heart of Bihar near Rajgir and Patna, Nalanda is one of the most celebrated sites of ancient learning and Buddhist heritage. Once known as the world’s first international residential university, this historic center was a place where scholars from Asia converged to pursue knowledge in a variety of disciplines. Renowned as a great Buddhist mahavihara, Nalanda has been revered for its intellectual rigor and cultural impact over centuries[1][4].
Historical Significance
Founded in the 5th century CE by Emperor Kumaragupta I of the Gupta dynasty, Nalanda quickly rose to prominence in ancient Magadha. It served as a major center of higher learning under the patronage of various rulers, flourishing during the Gupta era and later under Harsha and the Pala Empire. Historical accounts indicate that the mahavihara attracted scholars from as far-flung regions as China, Korea, and Central Asia. Xuanzang and Yijing, two famed Chinese pilgrims, spent years studying at Nalanda and carried precious Sanskrit texts and relics back to their homelands, cementing the institution’s reputation as a global hub of scholarly exchange[1][4][7].
Academic and Cultural Legacy

The academic curriculum at Nalanda was as diverse as it was comprehensive. Subjects taught ranged from Buddhist philosophy—a discipline that gave rise to influential schools of thought like Madhyamaka and Yogachara—to subjects such as logic, mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and Sanskrit grammar. The institution was unique in its approach to education, with rigorous debates and discussions forming the cornerstone of its teaching methodology. This emphasis on holistic learning and inquiry allowed students to explore ancient texts and scientific subjects alike. Nalanda’s legacy is also enriched by its association with great scholars such as Nagarjuna, Dharmakirti, and the mathematician Aryabhata, whose contributions laid important foundations for future intellectual achievements[4][9][11].
Architectural Heritage and Ruins
Today, Nalanda’s ruins offer a glimpse into the grandeur of its past. Spread over an area that originally covered several hectares, the site contains remnants of 11 monasteries and multiple brick temples arranged in a methodical layout. The stupas, including the famous Sariputra Stupa built to honor one of the Buddha’s chief disciples, stand as testimony to the architectural excellence of the period. Intricate sculptures, inscriptions, and restored sculptures such as those depicting scenes from the Jataka tales add to the cultural richness of the site. The existence of a vast library, known as Dharmaganja, underscores the institution’s commitment to knowledge and the preservation of precious manuscripts[1][7][9].
Modern Revival and International Impact
After centuries of decline following its destruction by invaders, interest in Nalanda was revived in the 21st century. The Government of India, recognizing its unparalleled legacy, passed an act in 2010 to re-establish a modern center of higher education near the ancient ruins. The new Nalanda University, inaugurated in 2014, has been designed with state-of-the-art sustainable infrastructure while paying tribute to its historical roots. With a sprawling campus that integrates eco-friendly features such as rainwater harvesting and solar power, the modern institution strives to become a global knowledge hub. Its interdisciplinary programs and international collaborations reflect the spirit of the original Nalanda, inviting students and scholars worldwide to engage in meaningful academic and cultural exchanges[6][9][10].
Tourism and Cultural Experience

Visitors to Nalanda not only appreciate its historical and academic significance but also enjoy a rich cultural experience. The site is an important stop on India’s Buddhist tourism circuit and offers a blend of archaeological exploration and local flavor. The Nalanda Archaeological Museum, established in the early 20th century, houses a captivating collection of artefacts such as sculptures, coins, and inscriptions that narrate the university’s illustrious past. Complementing the historical journey is the taste of local Bihari cuisine, which reflects centuries of culinary traditions influenced by Buddhist practices. With well-connected transport options from Patna and Rajgir, the area provides an accessible and immersive experience that brings the ancient heritage of Nalanda to life for modern travelers[2][3][5][8].
Conclusion
Nalanda has long been an emblem of India’s rich educational and cultural heritage—a place where learning was interwoven with philosophy, art, and science. Today, the revival of Nalanda University stands as a testament to the enduring legacy of this ancient institution, bridging the vast expanse of time between its storied past and its promising future. As scholars and tourists alike continue to explore its ruins and modern campus, Nalanda remains a beacon of intellectual exchange and a reminder that knowledge knows no boundaries[1][4][9].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
















