Discover Pandipedia
Pandipedia is the world's first encyclopaedia of machine generated content approved by humans. You can contribute by simply searching and clicking/tapping on "Add To Pandipedia" in the answer you like. Learn More
Expand the world's knowledge as you search and help others. Go you!
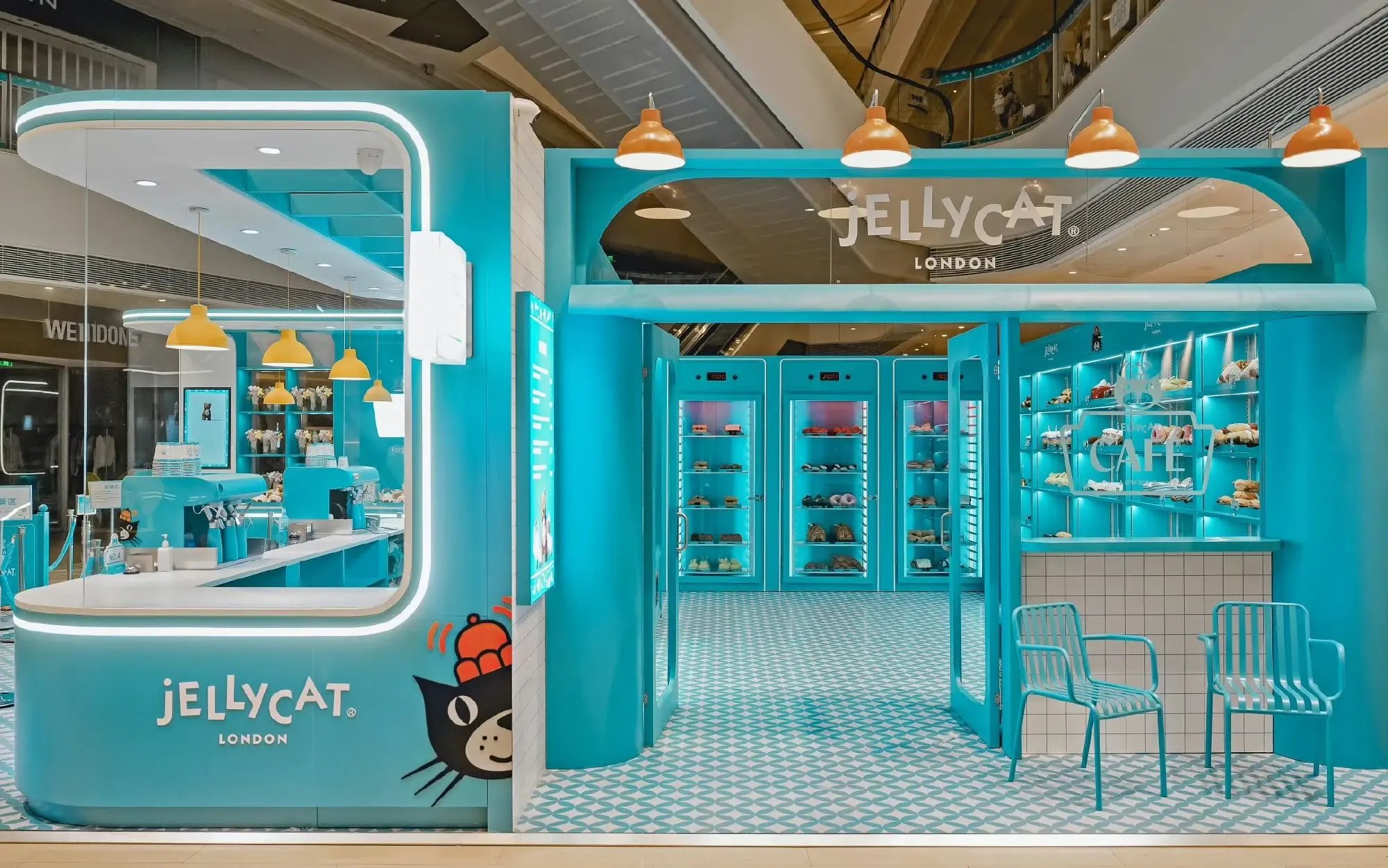

Jellycat was founded in 1999 in London by brothers Thomas and William Gatacre, originally targeting a niche in the plush toy market that combined quirky designs with premium quality. Their vision was to produce soft toys that stood out due to their unique style and luxurious materials. Initially starting with a small stall at trade shows, the brand quickly gained popularity and secured partnerships with prominent retailers such as John Lewis and Selfridges, which contributed to its early growth and recognition in the market[3][6].
By 2021, Jellycat expanded its operations internationally, opening a subsidiary in Minneapolis in 2001. This global reach has allowed the company to establish a presence across many markets, including the US, Europe, and Asia. As of the end of 2023, Jellycat reported revenue growth of 37%, reaching £200 million, largely attributed to its booming online presence and successful marketing strategies[1][9].
Unique Marketing Strategies

Jellycat's marketing strategy is centered around the emotional appeal of its products, focusing on comfort, nostalgia, and joy. The company has effectively tapped into broader consumer trends, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic, where demand for comforting products surged. As consumers shifted focus to online shopping, Jellycat's revenue saw an impressive increase, showcasing its ability to thrive under changing market conditions[4][9].
To further engage customers, Jellycat introduced experiential marketing initiatives like the 'Jellycat Diner' and various pop-up cafes in major cities worldwide. These immersive experiences not only heightened brand visibility but also fostered community engagement and excitement. The pop-up concepts, which included thematic elements like a fish and chips shop in London and a patisserie in Paris, have proven successful in attracting significant foot traffic and have often gone viral on social media, amplifying the brand's reach[1][8][9].
Emphasis on Quality and Design
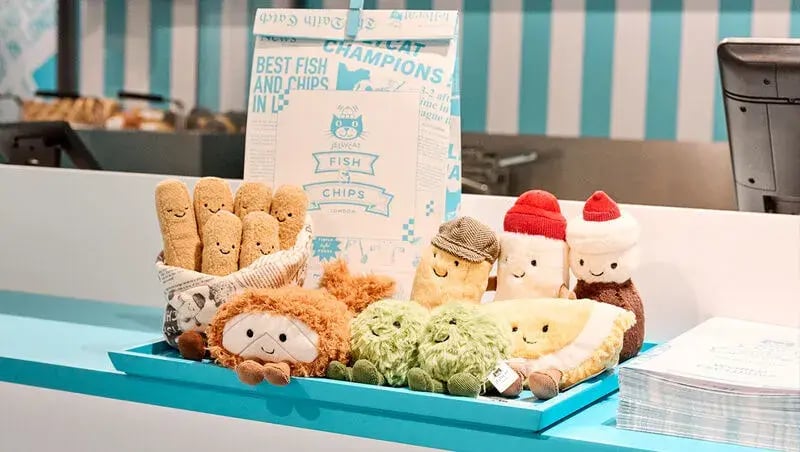

A cornerstone of Jellycat's appeal lies in its commitment to quality. The brand prioritizes the use of soft, luxurious fabrics and innovative designs that appeal to both children and adult collectors. This focus on high-quality materials has allowed Jellycat to differentiate itself from competitors in the plush toy market, leading to a strong following among both young and adult consumers. Jellycat's designs are often whimsical, featuring everything from plush animals to quirky objects like food items, further enhancing their collectability[6][7][9].
Moreover, Jellycat has effectively embraced the concept of anthropomorphism, giving their toys distinct personalities that resonate emotionally with consumers. This strategy not only helps forge strong connections with customers but also supports the brand's positioning within the lifestyle market, appealing to a wider age range than traditional toy companies[1][3].
Digital and Social Media Presence

In today's digital landscape, social media plays a vital role in Jellycat's marketing efforts. The company has cultivated a robust online presence, with extensive user-generated content from fans sharing their collections on platforms like TikTok and Instagram. This community-driven content has significantly enhanced brand visibility and engagement, creating a sense of urgency and collectability around Jellycat products. With over half a million followers on TikTok and a robust presence on Instagram, Jellycat has crafted a unique niche that allows customers to engage with the brand in personal and meaningful ways[9].
Jellycat's ability to adapt its marketing strategies to suit current trends has been crucial for its ongoing success. The brand continuously releases new collections, introducing around 200 new items each January and July, thereby maintaining excitement and interest among consumers[3][5]. Additionally, their focus on creating emotional connections through their products and marketing strategies has fostered lasting loyalty amongst customers.
Looking to the Future

Future initiatives for Jellycat include a continued emphasis on sustainability, with plans to implement environmentally friendly practices and materials within their operations. This focus not only aligns with evolving consumer values but also helps solidify Jellycat's reputation as a responsible brand in a competitive market[3][8].
In conclusion, Jellycat's journey from a small stall at trade shows to a leading luxury plush toy brand is a testament to its innovative designs, effective marketing strategies, and dedication to quality. By emotionalizing its product experience and leveraging community engagement through digital platforms, Jellycat has successfully carved a unique space in the plush toy market, appealing to a diverse consumer base across generations.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.



Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.
The Scientific Method: A Foundation for Knowledge
The scientific method serves as a structured approach to investigating questions through observation and experimentation. This dynamic process is not merely a series of fixed steps; rather, it comprises a flexible set of principles that enables inquiry across multiple scientific disciplines. The scientific method is grounded in the formulation of a hypothesis—a testable prediction about the relationship between two or more variables—which is then subjected to systematic experiments that yield empirical data. Following experimentation, researchers analyze the data to ascertain whether the results support or contradict the initial hypothesis, and the findings are subsequently reported to contribute to the broader body of knowledge[3].
The importance of the scientific method cannot be overstated. It minimizes biases and encourages the reproducibility of results, making it vital in addressing societal challenges and advancing various fields. This rigorous process fosters objectivity and reduces the impact of subjective misconceptions, which is essential in producing valid and reliable conclusions[3][10]. Historically, the scientific method’s development traces back to ancient civilizations, evolving through contributions from figures such as Aristotle and later being codified by pioneers like Sir Francis Bacon, which laid the groundwork for future advancements in natural sciences[1][3].
Productivity Myths: What Research Shows
Several common beliefs exist around productivity, many of which have been debunked by research findings. These myths often stem from oversimplified notions of work efficiency, leading individuals to pursue strategies that may not yield the expected outcomes.
Myth 1: More Hours Equal More Output
One of the prevalent myths is that extending working hours directly correlates with increased productivity. Research compiled by the International Labour Organization illustrates that longer hours can lead to diminished results. In fact, individuals working flexible hours or part-time jobs tend to be more engaged and productive than those trapped in longer working schedules, with an optimal work week identified to be around 30 hours for maximizing quality and satisfaction[2][5].
Myth 2: Multitasking Enhances Efficiency
Another widespread misconception is that multitasking is essential for modern work environments. However, studies indicate that attempting to manage multiple tasks simultaneously often results in reduced efficiency and increased error rates. Researchers have found that people who believe they are adept multitaskers tend to underperform compared to those who focus on single tasks[2][8]. The recommendation, then, is to engage in 'flexible single-tasking,' where focus is maintained on one task until completion, followed by a deliberate transition to another task.
Myth 3: Clean Environments Are Necessary for Productivity
The belief that a tidy workspace equates to enhanced productivity is increasingly challenged by research. While some studies suggest clutter can distract and diminish focus, others indicate that a certain level of messiness may actually foster creativity and efficiency for individuals who thrive in less organized settings[2][4]. Individuals are encouraged to adopt organizational styles that feel intuitive to them rather than adhering strictly to conventional cleanliness.
Myth 4: Increased Happiness Leads Directly to Increased Productivity
While there is a general understanding that happier employees tend to be more productive, the relationship between happiness and productivity is more complex than one might assume. Studies reveal that sustained pressure to maintain a positive demeanor can backfire, causing stress and undermining productivity. Negative emotions, such as stress and urgency, can sometimes drive higher productivity in specific situations[2][8][10]. Thus, a nuanced approach that recognizes individuals’ need for emotional authenticity may enhance overall productivity more effectively than a simplistic focus on happiness alone.
Myth 5: Hard Work Guarantees Success
The notion that sheer hard work is the most reliable path to success overlooks the role of chance in achieving outstanding results. Evidence indicates that not all hard work yields equivalent outcomes and that factors beyond an individual's control, such as luck and external conditions, play significant roles. Therefore, emphasizing effective strategies and productive environments alongside hard work may be more beneficial than solely relying on effort[2][9].
Conclusion
In summary, while the scientific method remains fundamental to the advancement of knowledge, productivity myths often distort perceptions of what constitutes effective work practices. Debunking these myths is essential to cultivate a more informed understanding of productivity that aligns closely with empirical evidence. Acknowledging that productivity is influenced by numerous factors—including effective work schedules, collaboration strategies, emotional well-being, and adaptive work environments—can lead to improved outcomes for individuals and organizations alike[1][3][10]. To thrive in increasingly complex environments, individuals must move beyond these misconceptions and adopt practices grounded in scientific inquiry and evidence-based strategies for productivity.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Mental health issues among athletes have become increasingly recognized, yet remain a pressing concern in the competitive sports arena. Athletes may experience a range of mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety, and stress, often exacerbated by the unique demands of their environment. This report synthesizes findings regarding how mental health affects athletes, with an emphasis on prevalence, contributing factors, and potential interventions.
Prevalence of Mental Health Issues

Recent studies indicate that mental health problems in athletes are comparable to those in the general population. Reports suggest that between 5% and 35% of elite athletes experience mental health disorders, with the prevalence often mirroring that of the general community, particularly during critical periods such as training peaks, performance failures, and transitions in their careers[2][6][9]. A notable survey highlighted that nearly half of elite athletes acknowledged symptoms of mental health issues, with rates of depression, anxiety, and eating disorders being particularly significant[9].
In elite sports settings, female athletes tend to report higher levels of anxiety and specific mental health concerns compared to their male counterparts, although both sexes experience symptoms related to depression and stress at alarming rates[5][6]. The intense pressures of competition, coupled with injuries and public scrutiny, contribute to these elevated rates of mental health issues[3][6].
Factors Contributing to Mental Health Challenges
Several factors contribute to the mental health challenges faced by athletes. The culture of competitive sports often emphasizes toughness and resilience, which can stigmatize mental health discussions and discourage seeking help. This misconception creates barriers, leading many athletes to internalize their struggles rather than address them openly[2][4][9].
Stressors unique to the sporting environment—such as performance expectations, public scrutiny, and the risks associated with injuries—can exacerbate mental health issues. Athletes frequently face pressures from various sources, including coaches, sponsors, and the media, all while managing the responsibility of maintaining their performance and public persona[3][6][9]. This pressure can create a cycle where mental health problems—like anxiety and depression—compound the stress of competition and training, further impairing performance and well-being[2][6].
Impact of Mental Health on Performance
Mental health issues can severely impact an athlete's performance. Anxiety and depression can lead to decreased concentration, motivation, and overall athletic functionality. Athletes who experience mental health issues may struggle with emotional regulation, impacting their ability to perform under pressure, which is critical in competitive sports[5][8]. Overtraining syndrome, characterized by prolonged fatigue and mental exhaustion, can emerge when athletes are unable to balance the demands of their sport with their mental health, resulting in not just physical, but also psychological distress[9].
Moreover, disengagement from the sport, burnout, or even long-term career-threatening injuries may result when mental health is compromised. This is particularly evident in elite athletes facing unplanned retirement or transitions out of sport, which are often accompanied by identity crises and heightened feelings of isolation and depression[3][7]. Transitioning to retirement exposes athletes to risk factors such as loss of identity and social connections, making mental health support crucial during this period[1][3].
Strategies for Support and Intervention

The recognition of mental health issues in athletics calls for comprehensive support systems and interventions. The adoption of early intervention frameworks tailored for athletes is essential in order to enhance mental health literacy and promote help-seeking behaviors[3][7]. Sports organizations and governing bodies are beginning to implement programs focused on mental health awareness, aiming to create cultures of openness and support[2][4].
Interventions can include targeted mental health literacy programs for athletes and coaching staff, promoting understanding of mental health challenges and available resources[7][9]. Screening athletes for mental health symptoms regularly alongside physical assessments is another critical step. This approach can facilitate early identification of mental health struggles, allowing for appropriate and timely interventions[9].
Additionally, fostering an environment where athletes feel supported to discuss their mental health without stigma is vital. This can involve training coaches and support staff to recognize signs of mental distress and respond appropriately[7][9]. Such initiatives can normalize the conversation around mental health in sports, enabling athletes to seek help without fear of judgment[4][6].
Conclusion
In summary, mental health issues significantly affect athletes, presenting challenges that can hinder performance and overall well-being. With mental health conditions being prevalent and often overlooked, it is essential to implement effective support systems and interventions within sports organizations. By addressing the stigma surrounding mental health and promoting a culture of openness, the sports community can begin to prioritize mental health on par with physical health, facilitating better outcomes for athletes across all levels of competition.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have gained significant attention in the field of deep learning, recognized for their ability to generate realistic data. This blog post simplifies the core concepts of GANs, their architecture, and their applications based on the insights from the foundational paper on the subject.
What Are GANs?
GANs propose a novel framework for estimating generative models through an adversarial process. This involves training two models simultaneously: a generator (G) that learns to capture the data distribution and a discriminator (D) that assesses whether a sample is from the training data or generated by G. The training goal for G is to maximize the probability of D making a mistake, effectively engaging both models in a two-player minimax game[1].
The Architecture
In GANs, the generator produces samples that mimic the real data, and the discriminator evaluates these samples. The training process can be described mathematically as:
[
\min_G \max_D V(D, G) = \mathbb{E}{x \sim p(x)}[\log D(x)] + \mathbb{E}_{z \sim p_z(z)}[\log(1 - D(G(z)))]
]
This equation reveals that the discriminator's role is to distinguish real from generated samples while the generator aims to improve its output to fool the discriminator[1].
Training Process
The authors discuss a systematic approach to training both models effectively. They detail how alternating between updating D and G is crucial for optimal performance. D is trained to differentiate between real and fake samples, while G is updated to generate samples that can deceive D[1].
Early in the training, if G produces poor samples, D can easily reject them, leading to saturation of the training signal. As training progresses, the authors emphasize that D must be kept at near-optimal performance so that G can learn from meaningful feedback, thus enhancing its ability to generate realistic samples[1].
Theoretical Foundations
The paper delves into the theoretical basis of GANs, establishing that under certain conditions, the generator can learn to approximate the true data distribution effectively. The theoretical underpinnings focus on the interplay between the two networks, highlighting how their competitive nature drives the entire generation process[1].
The authors also present algorithms for implementing GANs, focusing on refining the generator and discriminator steps. They advise that during training, one must be cautious of how updates to G and D might affect the stability of the overall system[1].
Challenges and Advantages

Despite their innovative approach, GANs face specific challenges. For instance, they may struggle with convergence and mode collapse, where the generator produces limited variations of outputs. Moreover, the framework requires careful synchronization between G and D during training to ensure that they contribute effectively to the learning process[1].
However, the advantages of GANs are compelling. They enable the generation of high-dimensional samples without the need for explicit probabilistic modeling. The flexibility of the architecture also allows it to be applied in various contexts, from image generation to data augmentation in machine learning tasks[1].
Applications
GANs have far-reaching applications across numerous domains. They are utilized in generating images, enabling artistic creation, enhancing training datasets, and even creating synthetic data for privacy-preserving purposes. The paper illustrates their efficacy by comparing generated samples from GANs against traditional models, showcasing the high quality achieved through this framework[1].
Furthermore, GANs have sparked interest in research areas such as semi-supervised learning, where they help in improving classifier performance when labeled data is scarce. The ability of GANs to learn from unlabelled data demonstrates their versatility and potential for future advancements in machine learning[1].
Conclusion
Generative Adversarial Networks represent a significant leap forward in data generation techniques, combining a competitive learning process with the power of deep learning architectures. The insights provided in the foundational paper outline not only the mechanics of GANs but also their practical implications and the myriad of challenges they present. As research continues to evolve, GANs are likely to play a pivotal role in the future of artificial intelligence and data science, ushering in new techniques and applications that we have yet to fully explore[1].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.

The IndexNow protocol is an open-source initiative developed by Microsoft Bing in collaboration with Yandex, designed to help website owners notify search engines about changes made to their site instantly. This includes updates such as newly published content, modifications, or deletions of web pages. By using IndexNow, website owners can send a notification (or 'ping') to participating search engines, prompting them to crawl and update their indexes more efficiently, thereby reducing the time it takes for new content to appear in search results[1][3][5][6].
Traditionally, search engines rely on crawlers to discover new content, which can be a slow process, sometimes taking days or weeks. IndexNow changes this by introducing a 'push' model in contrast to the traditional 'pull' model, allowing website publishers to proactively alert search engines about changes, thus speeding up indexing and improving overall search engine efficiency[2][4].
Current participating search engines include Microsoft Bing, Yandex, and Seznam, with Google testing the protocol but not fully implementing it yet. The protocol is particularly beneficial for sites with frequent updates, as it minimizes unnecessary crawls and reduces server load[3][5][6]. Overall, IndexNow aims to create a more efficient web by ensuring that changes are promptly reflected in search engine results, helping improve visibility and potentially enhancing SEO performance[1][2][6].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Manmachine Solutions offers professional housekeeping services tailored to your needs. They provide expert cleaning and maintenance solutions for both homes and offices, ensuring a spotless environment. Their focus on facility management showcases their commitment to quality, and they serve multiple niches including industrial, commercial, and corporate sectors[1].
The company's structured approach and dedicated audit team ensure the best service and customer satisfaction. Their integrated facility management programs include corrective and predictive maintenance, guaranteeing that they meet your specific demands[1].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Tyree Island was a challenging location due to multiple factors[1]. It lacked any shelter for shipping and most of its surface was composed of sand[1].
Because of these issues, everything needed to be brought to Tyree Island including; fuel, craftsmen, building materials, and tools[1]. The island was also remote from markets, had inaccessible shores, and stormy seas[1].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Gardening can be a rewarding activity, especially when planned effectively for each season. Understanding the best practices for layout, plant selection, and maintenance can significantly enhance the yield and health of your garden. Here’s how to plan a seasonal garden, particularly for the fall and transition into winter.
Understanding Your Growing Environment
The first step in planning a seasonal garden is assessing your local growing conditions. This includes identifying your hardiness zone, which helps determine what plants will thrive in your area, especially during the colder months. Research your area’s frost dates; knowing when the first frost is expected allows you to time your planting effectively. For instance, if your first frost date is November 5, you may need to start your fall garden preparations around mid-August to ensure your crops mature before the cold arrives[8].
Plant Selection for the Season
Choosing the right plants is crucial. For fall gardening, cold-hardy vegetables work best, as they can tolerate cooler temperatures and even light frosts. Great options include:
Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and lettuce flourish in cooler weather, often tasting sweeter after a frost[5][8].
Brassicas: Broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts are excellent choices, as they thrive in the milder autumn conditions[1][4][5].
Root Vegetables: Carrots, beets, and radishes are other ideal candidates due to their resilience to cold weather[4][8].
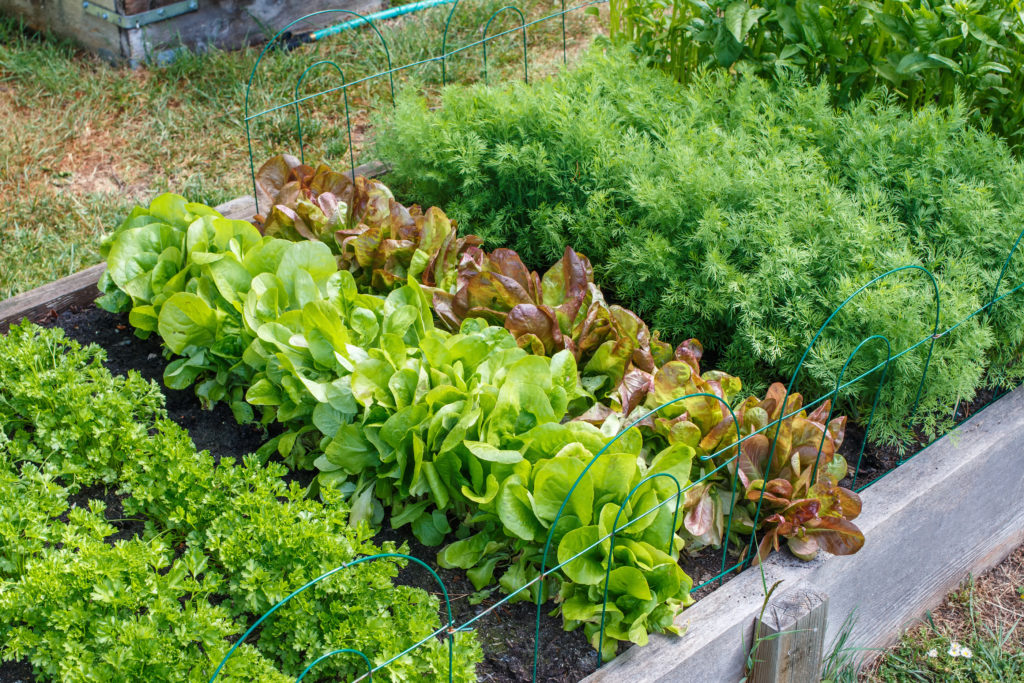

During the planning phase, consider the days to maturity for each crop. For example, radishes can be harvested in as little as 25 days, while carrots may take 70 to 80 days, so plan your planting schedule accordingly to ensure they are ready before the frost[4][8].
Garden Layout and Design
The layout of your garden is pivotal in maximizing sunlight exposure and space. Start by selecting a site that receives ample sunlight. For limited spaces, raised beds or container gardening can be effective solutions[1][3].
When designing your garden, consider the following tips:
Position taller plants like kale or broccoli to the north side of your garden to prevent them from shading shorter crops.
Use narrow pathways between planting areas to make it easier to access your plants[1].
Implement succession planting by sowing new seeds as soon as previous crops are harvested, ensuring a continuous yield[1][3].

For instance, after you harvest quicker-growing crops like radishes or salad greens, you can plant frost-tolerant varieties like spinach or kale in their place for a late-season harvest[1].
Soil Preparation and Maintenance
Before planting, prepare your soil by enriching it with organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure. This enriches soil fertility and improves its structure, setting a solid foundation for your plants[5][7]. It’s also vital to test the soil's pH and amend it as necessary to create the best environment for growth.
Maintenance practices will change as temperatures drop. During fall and winter:
Watering should be adjusted to monitor soil moisture levels, as cooler temperatures lead to reduced evaporation rates. Deep watering sessions are more beneficial than frequent shallow ones[1].
Applying a layer of mulch can help conserve moisture, suppress weeds, and insulate roots during freezing nights[4][7].
Harvesting and Storing Produce
Knowing when and how to harvest is essential for enjoying the fruits of your labor. Most vegetables have specific indicators of readiness:
Leafy Greens: Harvest outer leaves as they grow, allowing the inner leaves to continue developing[4][5].
Root Vegetables: Check the size and color of the shoulders at the soil level for indicators of readiness[5].
Brassicas: For broccoli, harvest the main head before it flowers, while Brussels sprouts are ready when they reach 1 to 2 inches in diameter[5].
Storage after harvest is equally important. Clean the produce properly, keeping them cool and in a dark place. Vegetables like carrots and beets do well in root cellars or the refrigerator. Ensuring good airflow around stored items helps prevent rot, thus prolonging their shelf life[1].
Conclusion
Successfully planning a seasonal garden involves a number of factors, including understanding your environment, selecting suitable plants, creating an efficient layout, preparing your soil, and employing effective maintenance and harvesting strategies. By following these guidelines, you can maximize your garden's productivity, especially during the fall and winter months. Happy gardening!
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.











/samsung-ha-ref-rf56k9540sr-family-hub-overview-5aa18f0e18ba010037c023a5.jpg)






















