Discover Pandipedia
Pandipedia is the world's first encyclopaedia of machine generated content approved by humans. You can contribute by simply searching and clicking/tapping on "Add To Pandipedia" in the answer you like. Learn More
Expand the world's knowledge as you search and help others. Go you!
The Transformative Impact of Emerging Technologies in Healthcare

The healthcare industry is currently undergoing a significant transformation driven by a range of emerging technologies. These advancements are reshaping how healthcare is delivered, enhancing patient outcomes, and improving operational efficiencies. Below, we explore some of the key technologies that are making a substantial impact.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)

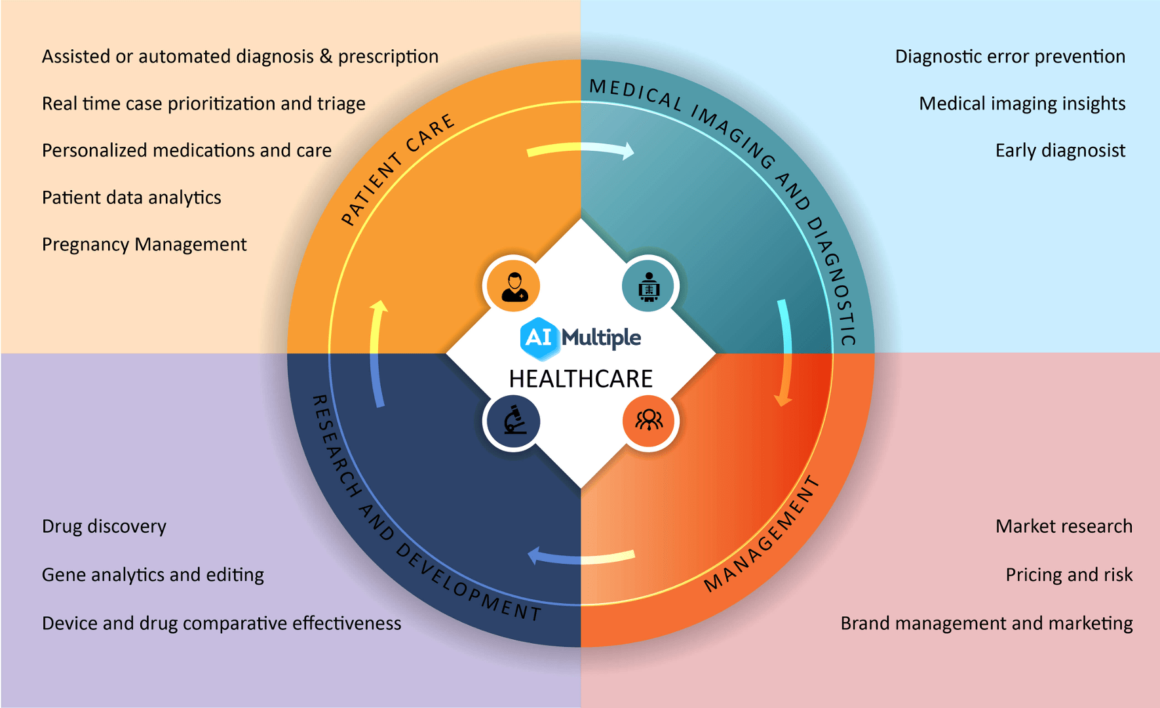
AI continues to revolutionize healthcare, offering solutions that enhance diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient management. The applications of AI are expanding rapidly, especially with generative AI, which is expected to democratize access to technology and facilitate personalized healthcare recommendations. AI algorithms are being utilized to analyze patient data, streamline operations, and augment clinical decision-making processes, thus improving the precision of diagnoses and treatment protocols[2][5][10].
For instance, AI-driven tools can help automate administrative tasks, which alleviates the burden on healthcare professionals, enabling them to focus more on complex patient care tasks[9]. The integration of AI in medical imaging has also improved the diagnostic capabilities of radiologists, allowing for faster and more accurate assessments[1][10].
Telehealth and Remote Monitoring
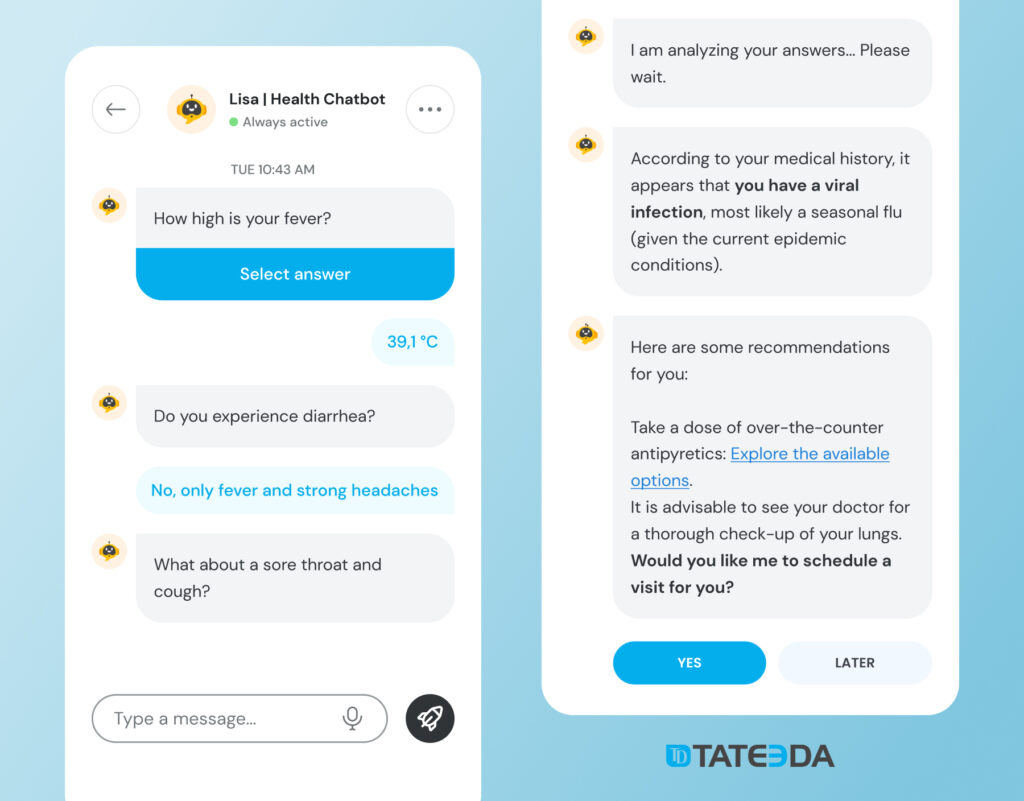
Telehealth has gained traction, particularly accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, allowing healthcare providers to extend services beyond physical facilities. This 'telemedicine 2.0' approach incorporates connected devices to monitor patients remotely, facilitating ongoing care and communication between providers and patients[4][7]. Technologies such as wearable devices and remote patient monitoring systems are making healthcare more proactive, especially in managing chronic conditions, thereby enhancing patient engagement and compliance with treatment[4][8][9].
Telehealth platforms are increasingly employing AI to enhance consultation services, such as symptom triage and preliminary diagnostics, which contribute to more informed decision-making for both patients and healthcare providers[11].
3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
3D printing technology is revolutionizing the production of medical devices and implants. This method enables the creation of customized medical products such as orthopedic implants and surgical tools, tailored specifically to individual patient needs. The growing need for personalized medicine is driving this trend, with predictions of significant growth in the market for 3D-printed medical devices[6][10]. Hospitals are utilizing this technology to streamline inventory management and reduce operational costs, particularly in outpatient settings that prioritize customized solutions[9][10].
Data Integration and Interoperability

The push for improved data integration and interoperability is crucial. As healthcare data proliferates from various sources, the need for systems that can communicate effectively becomes increasingly important. Enhanced interoperability enables healthcare providers to coordinate better and manage patient care seamlessly across different platforms and specialties. This integration not only improves patient outcomes but also supports health research and policy-making through comprehensive data analysis[4][11].
Healthcare leaders recognize that unified data systems are essential for successful care coordination, ultimately leading to more efficient and effective service delivery[9][10]. New technologies are emerging to facilitate the secure exchange of information among systems, which is fundamental in a digitally-driven healthcare landscape.
Sustainability and Decarbonization Efforts

Sustainability is becoming a hallmark of modern healthcare, with organizations implementing eco-friendly practices and focusing on reducing their carbon footprints. This includes not only the operational aspects but also the ethical integration of sustainable practices in decision-making and supply chain management[7][8]. Healthcare entities are now adopting strategies to mitigate climate change effects, recognizing the link between environmental health and patient care.
Healthcare technology firms are increasingly expected to commit to decarbonization goals and exhibit transparency in their environmental impacts, aligning their strategies with growing societal expectations around sustainability[9][10].
Enhanced Patient Engagement through Digital Platforms

Emerging technologies are enhancing patient engagement by creating more personalized experiences. Digital platforms are facilitating better communication and collaboration between patients and healthcare providers. As patients demand more convenience and control over their healthcare experiences, integrated health technology platforms are stepping up to provide streamlined processes for scheduling, billing, and care management[11]. This trend is not only improving the overall patient experience but also reducing inefficiencies within healthcare systems.
Conclusion
The intersection of technology and healthcare is paving the way for a more efficient, personalized, and patient-centric approach to care. AI, telehealth, 3D printing, interoperable systems, and sustainable practices are shaping the industry's future, driving significant improvements in patient outcomes and operational efficiencies. As these technologies continue to evolve, they promise to address some of the most pressing challenges in healthcare today. The commitment to leveraging innovative solutions to enhance patient care and service delivery will be crucial in the rapidly changing landscape of healthcare.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Lancôme Teint Idole Ultra Wear Foundation
This foundation is praised for providing an airbrushed effect while balancing skin tone, infused with hyaluronic acid, moringa, and vitamin E for hydration and comfort on the skin[1][9].
Estée Lauder Double Wear Stay-in-Place Makeup
Known for its long-lasting, full coverage that stays put throughout the day and comes in a broad range of shades, making it a favorite for those seeking durability and reliability[4][11].
Fenty Beauty Pro Filt’r Soft Matte Longwear Foundation
This award-winning formula offers a soft-matte finish and a vast shade range, designed for all skin types while staying comfortable throughout the day[4][11].
IT Cosmetics Your Skin But Better CC+ Oil-Free Matte Foundation
A buildable coverage foundation that offers a matte finish and includes skincare benefits and SPF, ideal for oily complexions[2][11].
NARS Soft Matte Complete Foundation
Provides buildable coverage with a satin finish that keeps skin looking natural while blurring imperfections[4][11].
Catrice HD Liquid Coverage Foundation
This weightless foundation offers a matte finish with high coverage that lasts all day without caking[12].
Make Up For Ever HD Skin Foundation
Features a lightweight yet matte finish that is both breathable and designed for enduring coverage, suitable for all skin types[11][12].
Maybelline Fit Me Matte + Poreless Foundation
A great drugstore option for oily skin, it effectively mattifies and minimizes pores while providing a natural finish[7][11].
e.l.f. Flawless Finish Foundation
Offers a lightweight, buildable coverage that leaves a semi-matte finish, making it suitable for everyday wear[7].
Tom Ford Traceless Soft Matte Foundation
This luxurious foundation provides a matte finish with high coverage and a long-wearing formula, ideal for special occasions[4].
NYX Can’t Stop Won’t Stop Foundation
A full-coverage, matte foundation that offers an extensive shade range and long-lasting performance[11].
Urban Decay Stay Naked Weightless Liquid Foundation
Delivers a real-skin matte finish that’s breathable and has excellent staying power[12].
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/charlotte-tilbury-airbrush-flawless-foundation-0449b5f6dd164de6999f984b2f40f687.jpg)
Charlotte Tilbury Airbrush Flawless Foundation
Known for full coverage with a natural, skin-like finish, this foundation can withstand heat and humidity[12].
Hourglass Vanish Seamless Finish Liquid Foundation
A weightless liquid foundation that provides full coverage with a soft-focus effect[12].
Laura Mercier Flawless Fusion Ultra-Longwear Foundation
Offers a natural matte finish with long-lasting coverage, suitable for all skin types[7].

Clinique Even Better Clinical Serum Foundation
Enriched with skincare benefits, it offers a natural finish while evening out skin tone and texture[4].

bareMinerals BAREPRO Liquid Foundation
This lightweight foundation delivers a natural finish with long-wear benefits and explicit coverage capabilities[3].
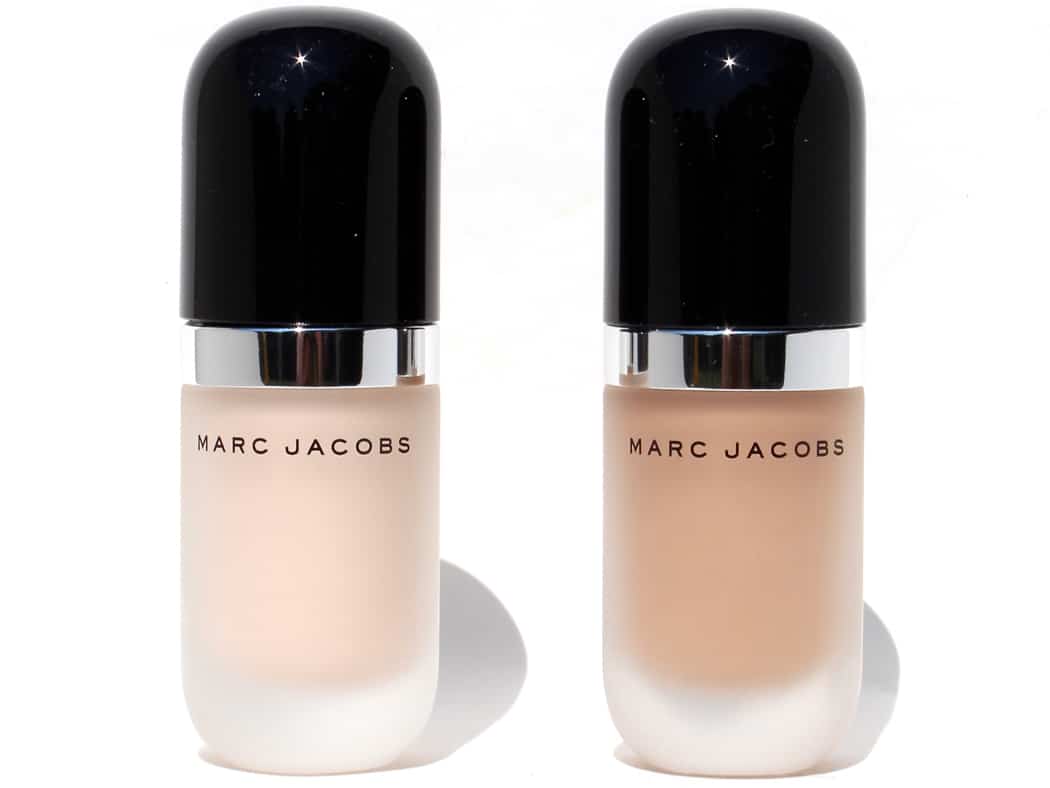
Marc Jacobs Beauty Re(marc)able Full Coverage Foundation Concentrate
Offers extraordinary coverage that’s lightweight and provides a matte finish, ideal for all-day wear[4].
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/giorgio-armani-luminous-silk-foundation-83bce890ae35470b8e3bc8c009a02952.jpg)
Giorgio Armani Luminous Silk Foundation
Known for its buildable, silky finish and lightweight feel, this foundation is a favorite among professionals[12].
Kosas Revealer Skin-Improving Foundation
Combines skincare benefits with coverage, offering a natural finish while remaining hydrating and lightweight[12].
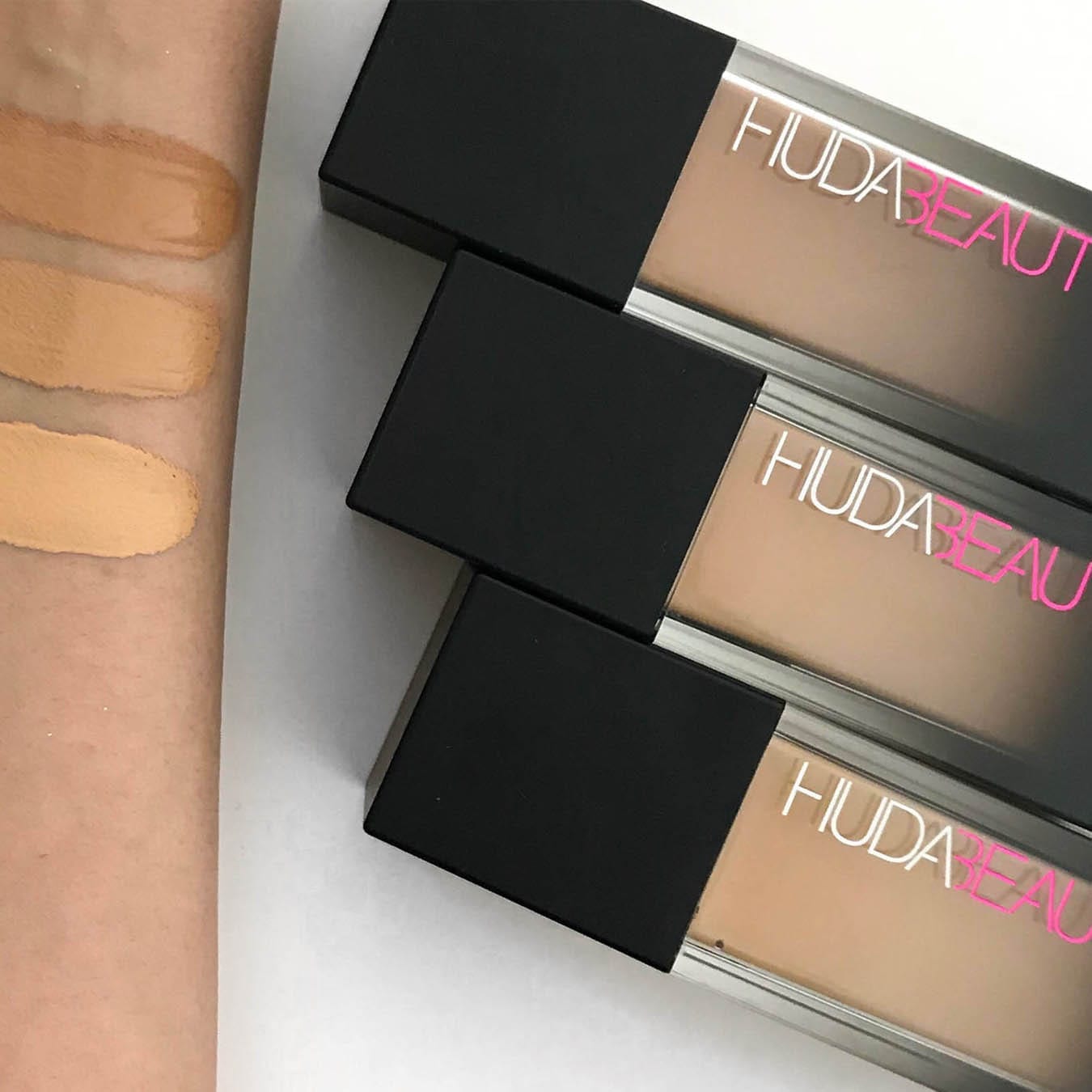
Huda Beauty Faux Filter Foundation
Known for its high coverage and matte finish, this foundation is ideal for those looking for full glam[4].
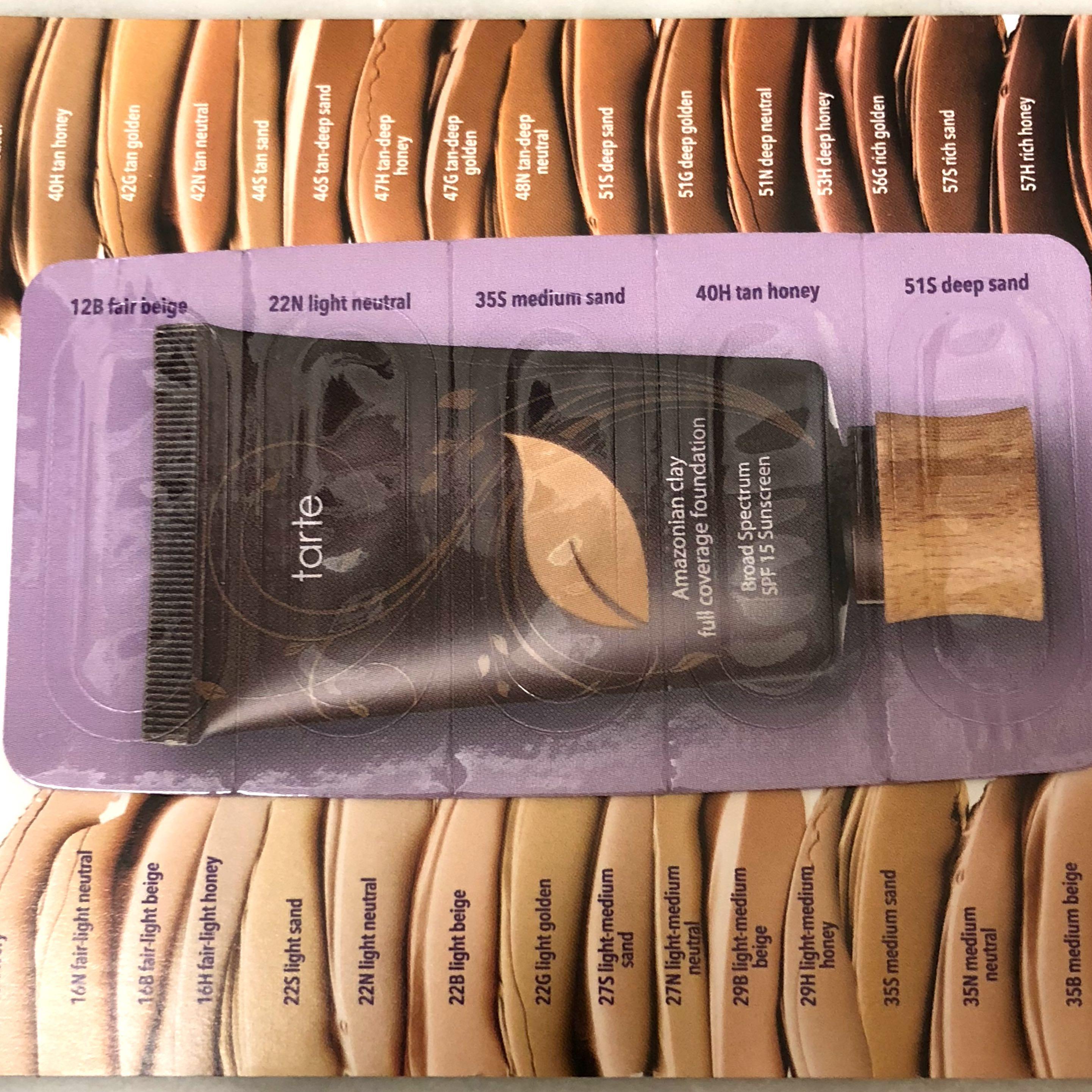
Tarte Amazonian Clay Full Coverage Foundation
A matte foundation formulated with clay to control oil production and provide buildable coverage[11].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.
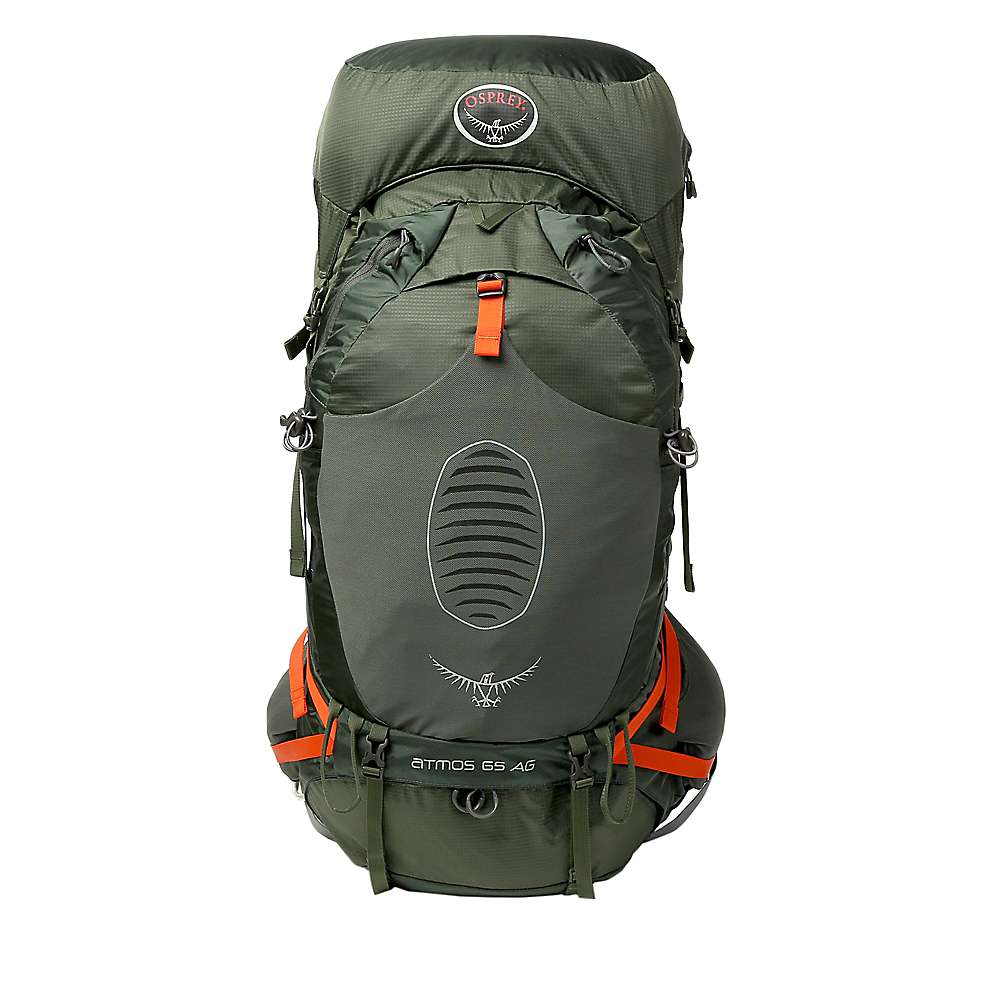
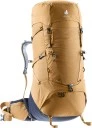
Osprey Atmos AG 65
Known for its anti-gravity suspension that provides excellent comfort and back ventilation, making it ideal for carrying heavy loads during fieldwork[2].
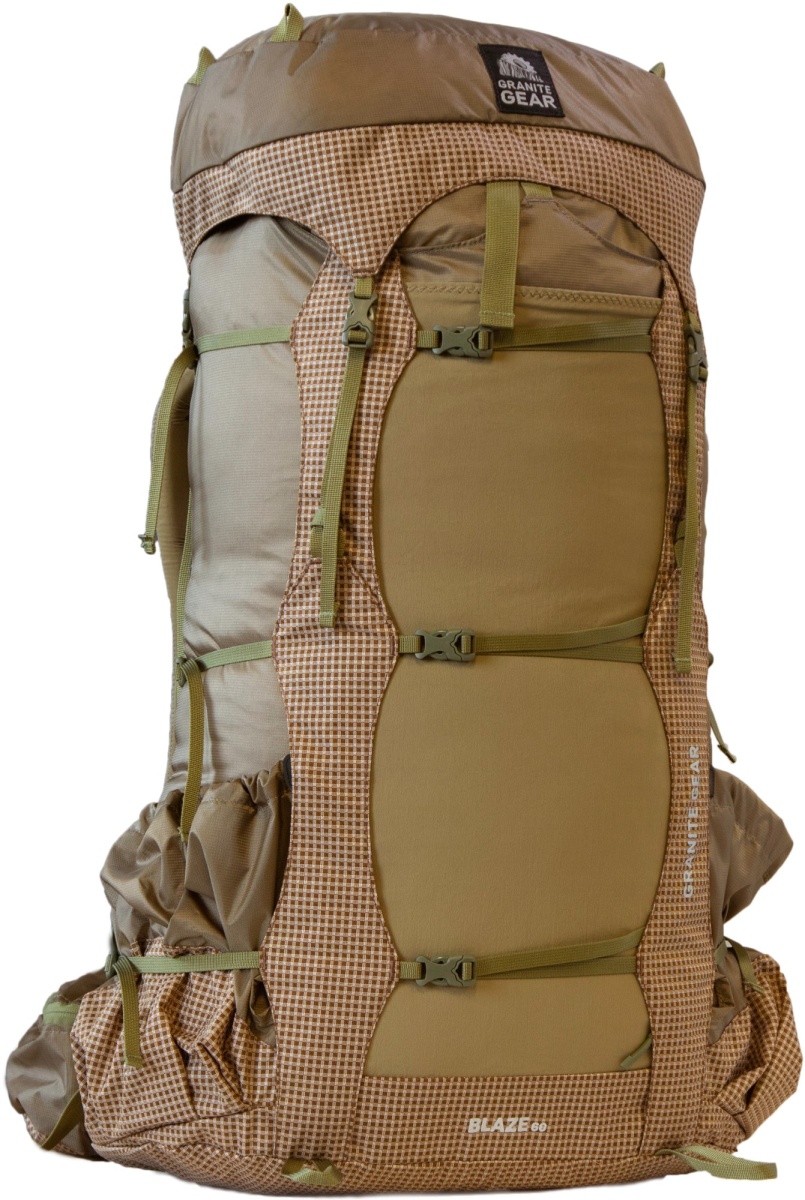

Granite Gear Blaze 60
This lightweight pack can comfortably support up to 50 pounds, featuring a stretchy mesh front pocket and roomy hip belt pockets, enhancing its practicality for extensive field use[2][4].
Gregory Baltoro 65
Designed for heavy loads, this pack offers remarkable comfort and organization with multiple pockets and a suspension system built for stability[9][10].
Osprey Aether 65
Great for carrying sizable loads, it features intricate adjustability and a well-structured back panel for comfort over long treks[2][9].
Deuter Aircontact Core 65+10
This pack offers excellent organization options with multiple access points and a cushioned frame for comfort while carrying heavy gear[3][10].
ULA Circuit
A popular choice for long-distance hiking and backpacking, praised for its minimalist design and comfort in hauling heavy loads[9][10].
REI Co-op Flash 55
Known for its versatility, it can morph from a beginner to a sleek ultralight pack, perfect for both short and long trips[9][10].
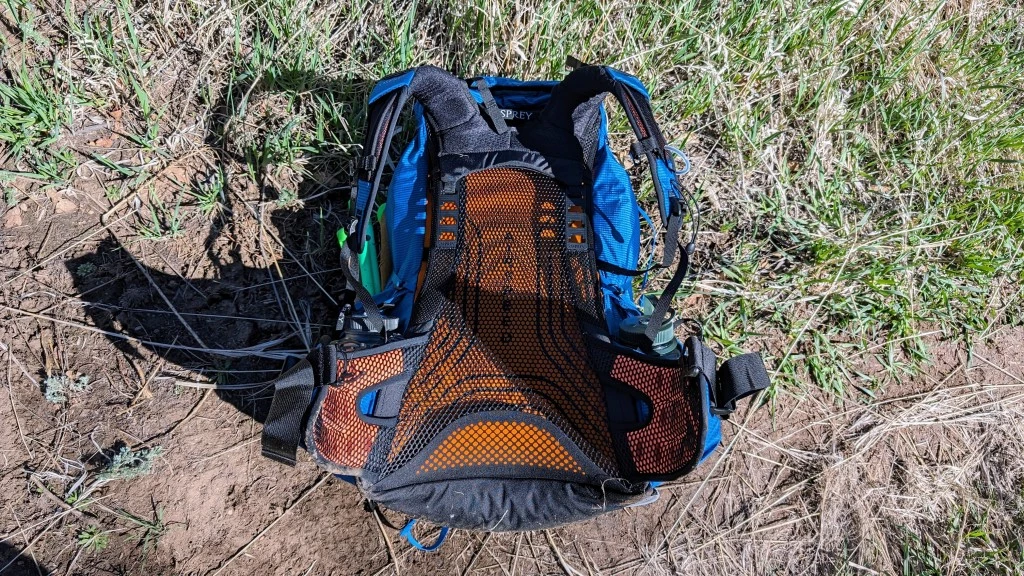

Osprey Exos 58
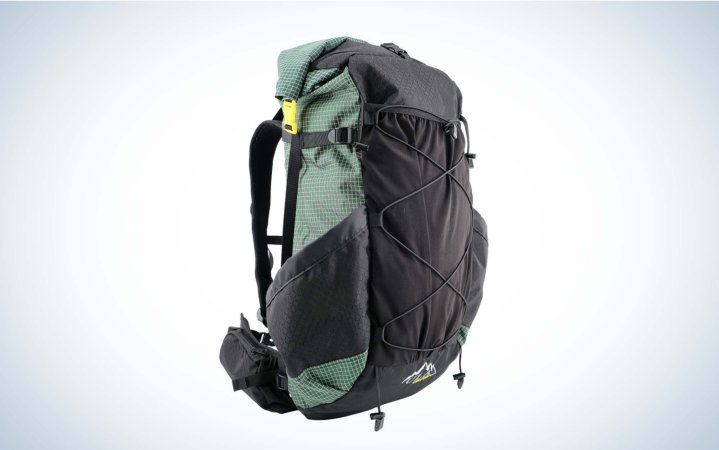
This ultralight pack excels in load-bearing while being breathable, making it suitable for extended fieldwork[2][9].
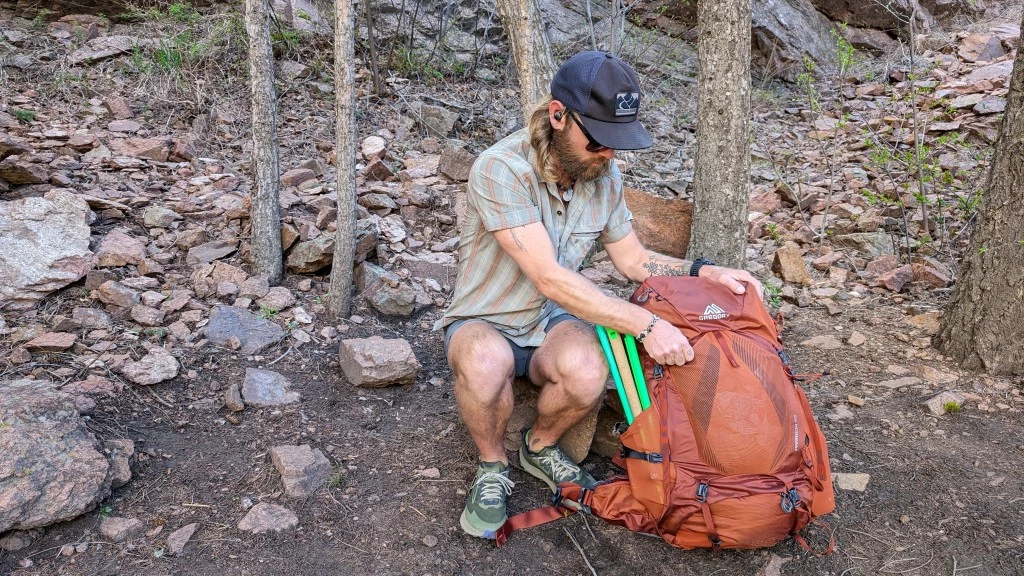

Gregory Paragon 58
With ample organizational features and great adjustability, it’s an excellent option for weekend trips and longer excursions[9][10].
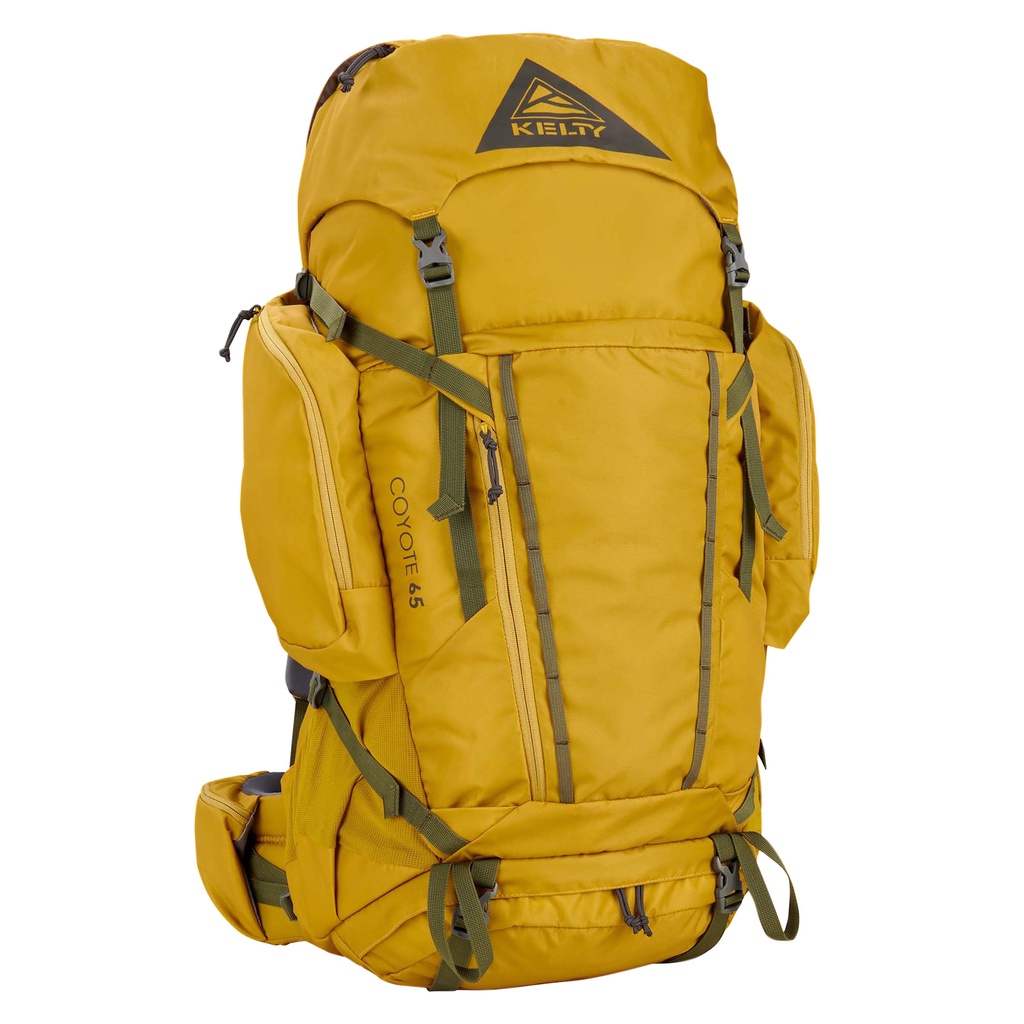
Kelty Coyote 65
A durable and affordable option with plenty of space and comfort, making it great for a variety of outdoor activities[4][10].
The North Face Recon 30L
This popular daypack offers good organization and is capable of holding a laptop securely, suitable for diverse fieldwork needs[3][7].

Patagonia Black Hole Pack 32L
A durable and waterproof backpack designed for rugged conditions, ideal for carrying gear in inclement weather[3].
Osprey Nebula 32
A versatile daypack that merges outdoor strength with urban styling, perfect for transitioning between fieldwork and daily use[3].
Volher Travel Backpack
A budget-friendly option with ample organizational pockets, making it suitable for everyday field use[3].
Timbuk2 Authority Deluxe
This offers excellent laptop protection along with spacious storage, making it suitable for professionals in the field[3].
North Face Borealis
Known for its comfort and organization, this pack works well as both a school and an outdoor bag[3].

Herschel Heritage
A versatile and stylish backpack that combines functionality with a classic look, useful for casual fieldwork[1].
Aqua Quest Defender 50L Backpack
Waterproof and rugged, designed for outdoor activities where moisture and durability are a concern[9].
Mammut Lithium Pro
Its robust construction and strategic pocketing make it suitable for demanding outdoor work[9].
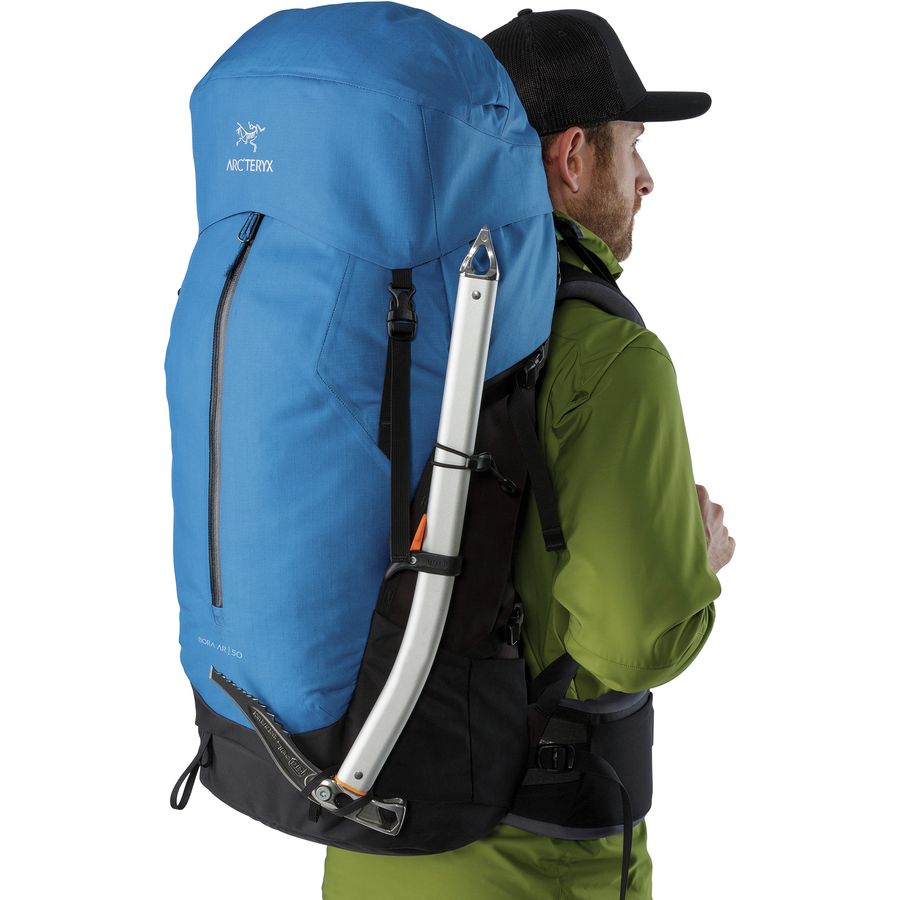
Arc’teryx Bora AR 63
This backpack integrates advanced materials and design, providing a weather-resistant option for extensive fieldwork[10].
Mystery Ranch Glacier
Built for heavy loads, it excels in durability and comfort, ideal for extended trips into the backcountry[10].
CamelBak Cloud Walker 18
A lightweight and compact option providing hydration capability, suitable for day outings in the field[8].
Deuter Speed Lite 24
Great for light and fast movement, this pack features a sleek profile, ideal for active fieldwork[9].
Black Diamond Speed 30
Designed for climbing and other intense activities, offering a streamlined design and durability in rugged conditions[9][10].
Arc’teryx Futura 50
This is a durable and practical choice for wet conditions, built for professional use in challenging environments[8].

Quechua MH500
An affordable and fully-featured daypack, performing well on hikes and outdoor adventures, suitable for new users[10].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
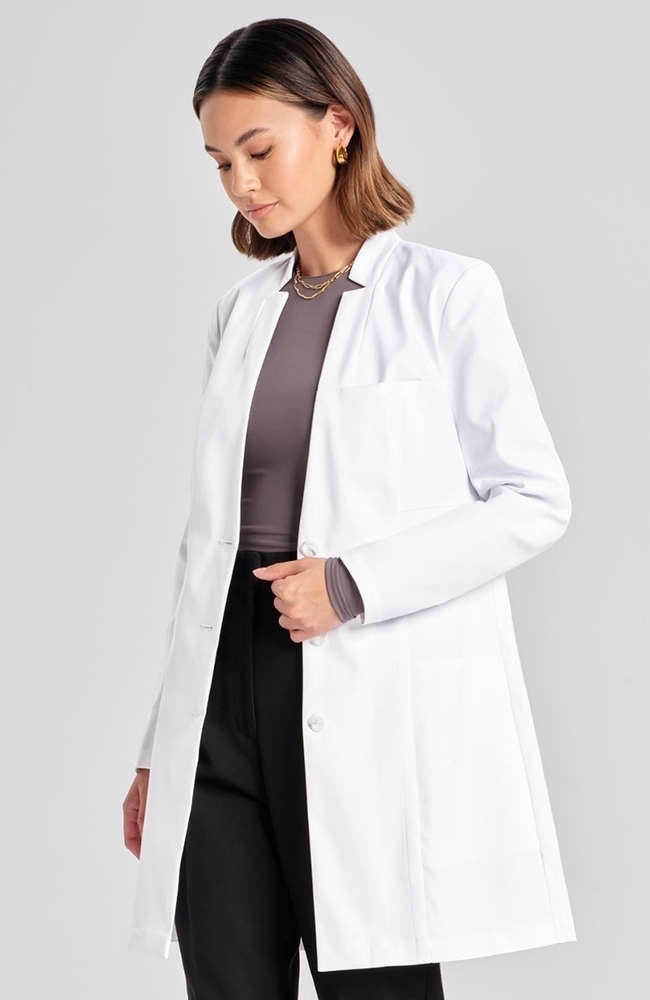
Dr. James 100% Cotton Lab Coat
A solid all-around chemistry lab coat for students featuring strong metal snaps for quick removal in emergencies and extra pockets for convenience, although it has some shortcomings with neck coverage and wrist protection.
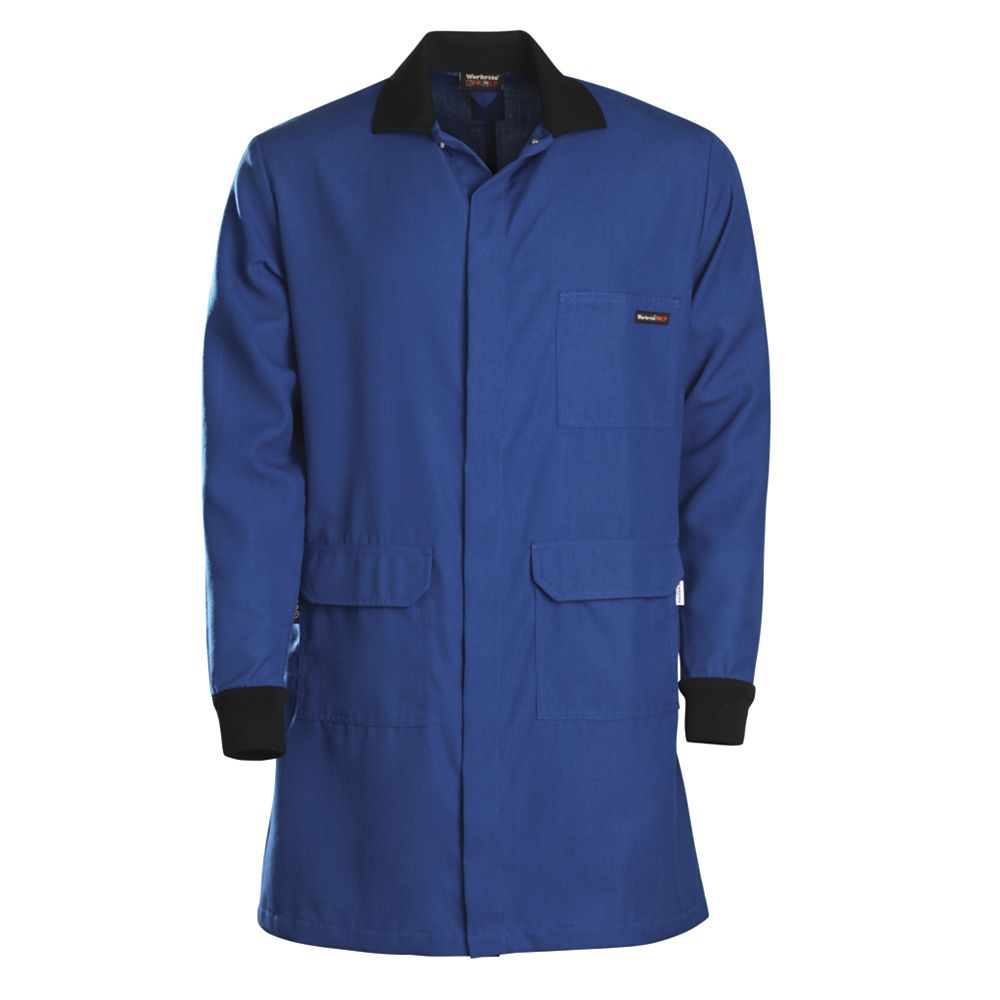
Workrite FR/CP Lab Coat
A top-of-the-line lab coat for chemists working with dangerous chemicals, flame-resistant and liquid splash resistant, made from heavy Nomex IIIA fabric, ideal for high-hazard environments.
Red Kap Lab Coat
An affordable option made from 80% polyester and 20% combed cotton; suitable for less hazardous chemical work, featuring knit cuffs, although it should not be used around open flames or high heat sources.

Worklon Lab Coat
Designed for biologists prioritizing comfort, with a blend of 80% polyester and 20% cotton, offering ease of movement with side slits for pocket access and knit cuffs, though not recommended for flammable materials.
Thermo Fisher Scientific Fisherbrand™ Unisex Lab Coat
Made of a 65/35 polycotton blend, suitable for biological materials with added comfort from the higher cotton content and includes standard pockets for utility.
Med Couture Women’s 37″ Lab Coat
A stylish lab coat for female medical professionals with a blend of polyester and cotton, providing comfort and functionality with a tailored fit and multiple pockets.
Adar Universal Unisex Lab Coat
A longer 39-inch lab coat featuring larger pockets and a buttoned adjustable back belt, designed to cater to various body types while remaining functional and professional.
Grey’s Anatomy 35″ Full-Length Lab Coat by BARCO
This women’s lab coat offers a modern slim fit with lightweight polyester-rayon fabric, perfect for healthcare environments without sacrificing style or comfort.
Cherokee Women’s 33″ Lab Coat
Tailored for women, this coat has a stylish design with princess seams and multiple pockets, made from a comfortable cotton-polyester blend for durability and ease of movement.

Magnus Care Professional Unisex Lab Coat
A comfortable polyester-cotton blend lab coat offering durability and ease of maintenance, featuring a unisex design with ample pockets for tools.

NY Threads Professional Lab Coat for Men
Constructed from a durable blend of polyester and cotton, this lab coat combines style and functionality with a classic design and multiple pockets for essentials.
Medelita Lab Coat
A stylish and functional lab coat ideal for modern medical professionals, made from a breathable fabric with ample storage space for instruments and tools, priced higher for premium quality.
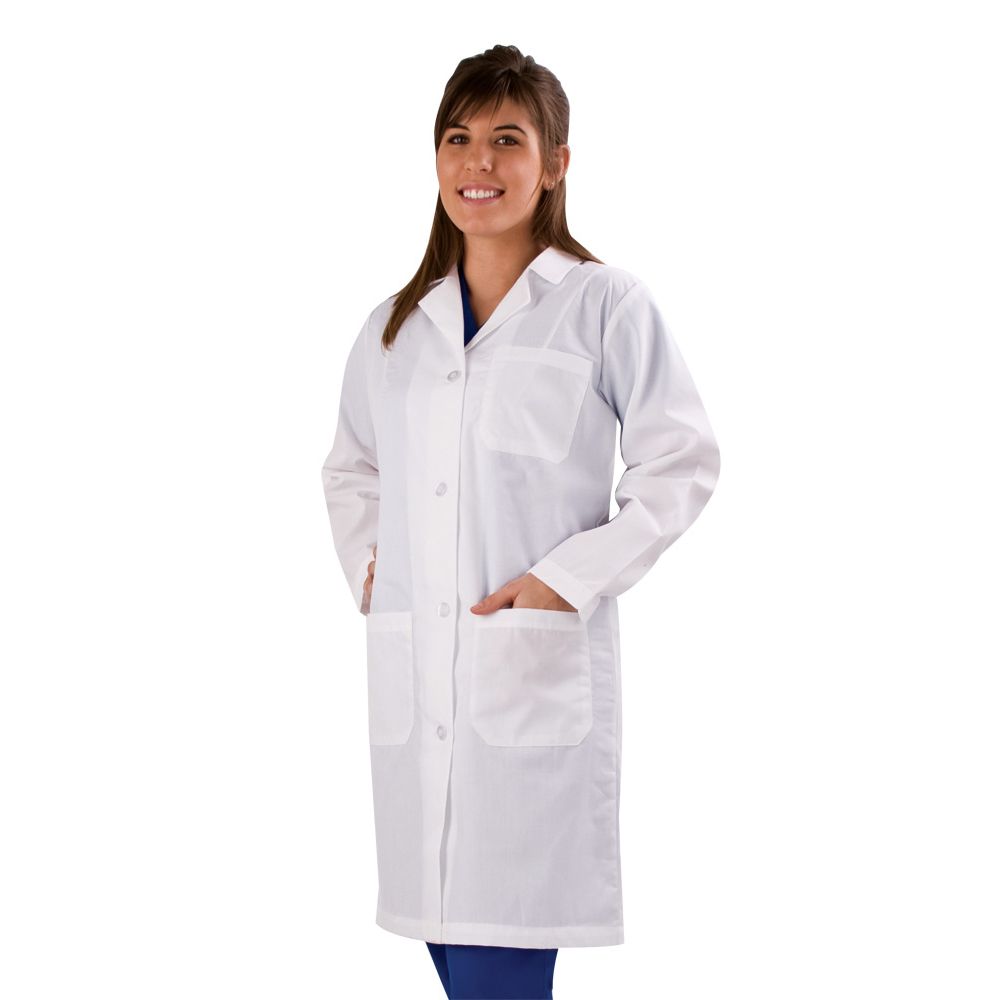
Natural Uniforms Unisex Lab Coat
An affordable and simple lab coat, designed with practicality in mind but lacks style options and only available in white, made from lightweight materials for comfort.
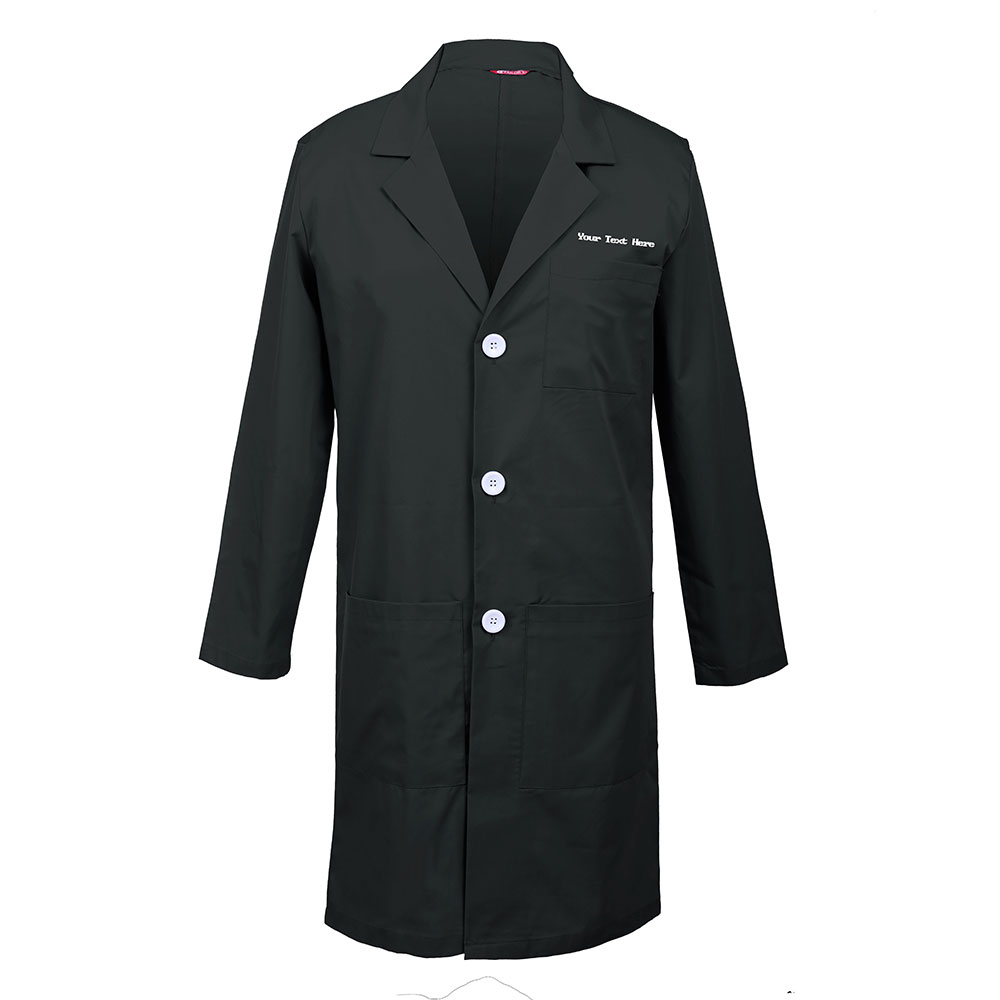
TAILOR’S Personalized Customizable Embroidered Men’s Lab Coat
Offers color choices and customization with embroidered text, made of a polycotton blend that's lightweight and comfortable, although fabric quality may vary.
Vogrye’s Professional Lab Coat
A cost-effective choice for costumes or casual lab wear, priced low but made with thinner materials and may have sizing inconsistencies.

Natural Uniforms’ Unisex Lab Coat
A sturdy and inexpensive lab coat perfect for Halloween costumes, featuring a comfortable fit and various practical features.
3M Virtua CCS Safety Glasses
Lightweight and versatile safety glasses suitable for daily use, featuring a removable foam gasket and attachment points for ear protection, ideal for versatile work environments.
NoCry Clear Anti Fog Safety Glasses
Lightweight protective glasses focused on comfort with an adjustable fit, offering impact resistance and minimal distortion for clear vision.
Pyramex I-Force Safety Glasses
Versatile eye protection that can convert from goggles to glasses, providing durability and adjustable features for different work settings.
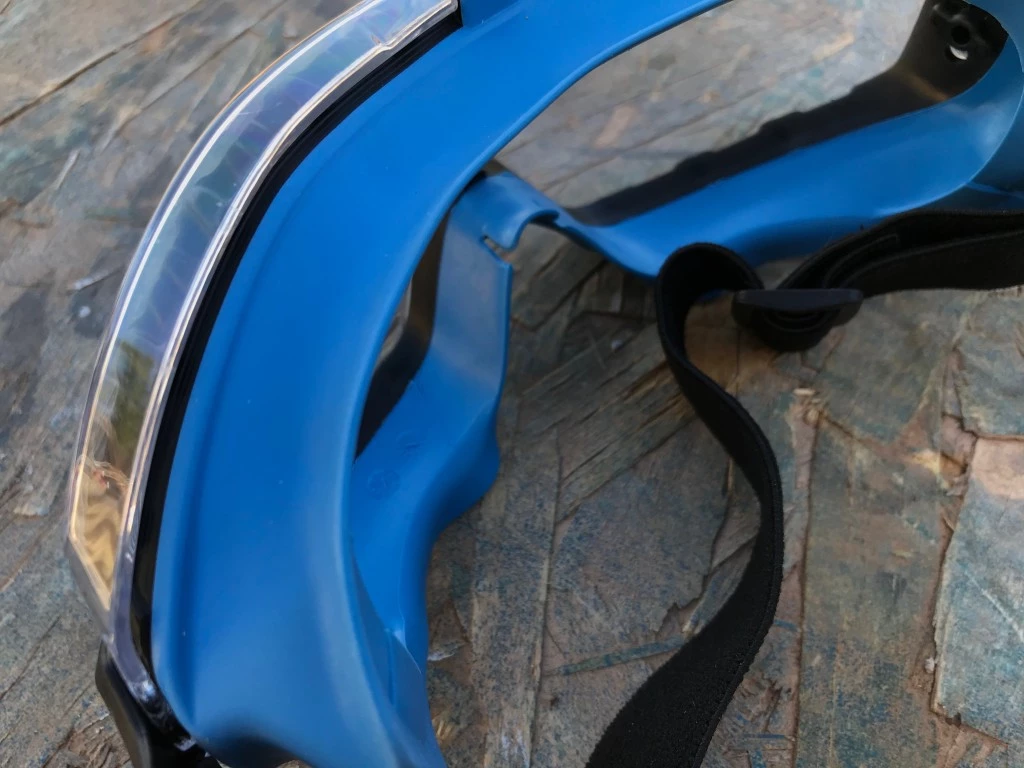

SolidWork Safety Goggles
Excellent for serious eye protection, these goggles feature a thick rubber gasket for a tight seal against fumes and dust while maintaining comfort.
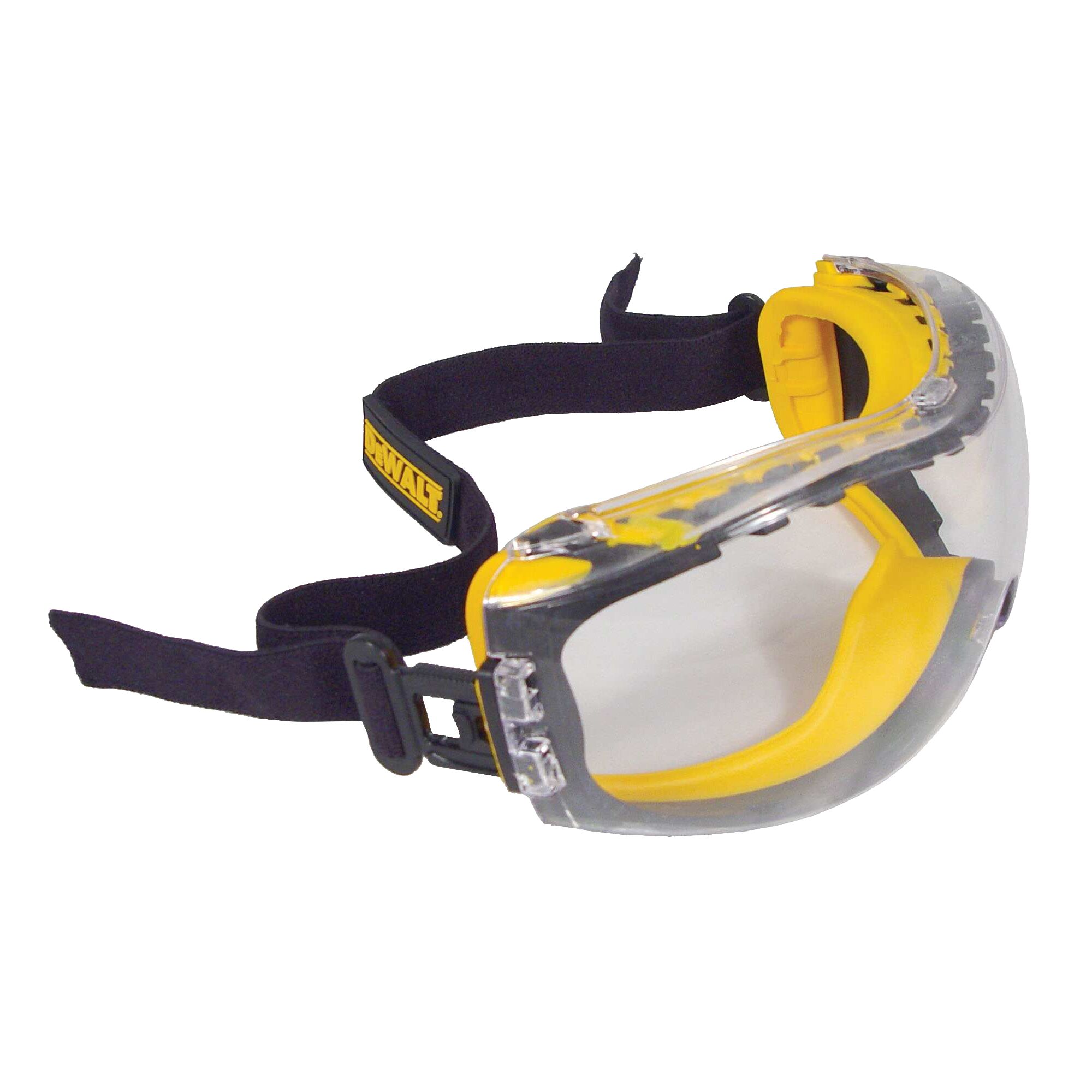
Dewalt Concealer Safety Goggles
Designed for heavy-duty protection with a snug fit and elastic headband, ensuring multiple hazard barriers without compromising comfort and usability.
Radians Mirage Safety Glasses
An affordable option for light usage, offering decent coverage and a snug fit, noted for flexibility but not highly durable in demanding environments.
Kleenguard Maverick Safety Glasses
Standard protective eyewear offering good coverage with side protection, suitable for everyday lab tasks while allowing good peripheral vision.
Pyramex Fortress Safety Glasses
Features an adjustable nose bridge and durable construction, providing adequate protection against impacts but may leave gaps for dust or debris.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
AI as a Complement, Not a Replacement, for Human Therapists
AI in therapy is not designed to replace human counseling or in-person treatment offered by certified therapists but to effectively supplement traditional therapy[4]. AI has numerous benefits that can supplement the work of human therapists and other professionals[4]. The quality of the therapeutic relationship and recovery outcomes for patients are significantly affected by humanistic care[9]. AI is envisioned not as a replacement for human therapists but as a powerful tool that extends the reach of mental health services[2]. By augmenting traditional mental health care, AI can offer scalable and cost-effective solutions that reduce barriers such as cost, stigma, and logistical challenges[2]. The integration of AI in Psychotherapy promises transformative advancements in mental health care, each highlighted by recent research; however, it emphasizes the need for stringent ethical standards[2]. Ethical and practical considerations underscore the importance of using AI responsibly in mental health care[6]. While AI offers exciting possibilities, it must be implemented with caution, guided by comprehensive ethical standards and regulatory oversight to protect users and uphold the integrity of mental health care[6].
The Strengths of AI in Mental Health Support
AI offers strengths in mental health care, including accessible, data-driven support[6]. One of AI's advantages is its 24/7 availability[6]. AI-driven therapy leverages advanced algorithms and data analysis to provide mental health support[1]. Platforms utilize mood tracking, journaling, and AI-powered chatbots to offer guidance and support[1]. Some of the boons of AI include data-driven insights, non-judgmental support, convenience, affordability, and immediate support[1]. AI algorithms can analyze large amounts of data, including patient history, symptoms, and other relevant information, to identify patterns that may not be evident to a human clinician[7].
AI-driven interventions can reduce healthcare costs, making mental health care more affordable and accessible[2]. Studies have shown that individuals are sometimes more willing to disclose sensitive information to AI systems due to the perceived non-judgmental nature of machines[2]. This phenomenon can lead to more honest exchanges during therapy sessions, allowing for more accurate assessments and potentially more effective treatment[2]. Also, AI systems offer a level of consistency in mental health care delivery that human practitioners can find challenging to achieve due to natural variations in mood, fatigue, and personal bias[2]. These systems can be programmed to ignore irrelevant factors such as race, gender, or socio-economic status, promoting a more equitable healthcare environment[2].
Limitations Preventing AI from Replacing Human Therapists
AI has significant limitations that prevent it from fully replacing human therapists[6]. One major limitation is AI's lack of genuine empathy, cultural sensitivity, and deep understanding[6]. AI systems lack genuine empathy and the ability to form deep emotional connections with patients[2]. Human therapists use their own emotional understanding to build trust and rapport, which is fundamental in therapy[2]. AI cannot authentically replicate this emotional resonance, as it does not experience emotions[2]. The design and implementation of AI in healthcare must prioritize ethical considerations, including strategies to mitigate bias, ensure transparency, and maintain patient trust[2]. Algorithmic bias is a critical concern in the application of AI to mental health care[2].
AI systems still face significant challenges with long-term memory retention and integration[2]. Algorithmic bias is a critical concern in the application of AI to mental health care[2]. Studies have indicated that the initial benefits of AI-driven interventions often diminish over time, with no significant long-term improvements observed[2]. Moreover, AI may not fully grasp cultural nuances, potentially leading to misunderstandings[2].
Ethical Considerations and the Future of AI in Mental Health
Integrating AI into mental health care brings about ethical and practical considerations. As AI tools play a more active role, issues around informed consent, data use, and boundary-setting become crucial[6]. Users may not fully understand the extent to which their personal information is collected, analyzed, or shared by AI systems[6]. There is a pressing need for regulation, transparency, and standardized guidelines to govern the use of AI in mental health care[6]. The development and deployment of AI technologies in mental health must adhere to ethical principles that respect the dignity and autonomy of patients[7].
As AI becomes integrated into mental health care, it is essential to recognize and address its limitations[2]. Challenges related to memory retention, algorithmic bias, and ethical considerations underscore the need for a balanced approach[2]. The integration of AI into mental health services offers promising avenues for enhancing care delivery and improving treatment efficacy and efficiency[2]. By augmenting traditional mental health care, AI can offer scalable and cost-effective solutions that reduce barriers such as cost, stigma, and logistical challenges[2]. Ethical concerns include potential harm to the public, perpetuating bias, data protection and privacy concerns, and questions around transparency, accountability, and liability[5]. Integration of AI into mental healthcare and mental health therapy represents a promising frontier in healthcare[3]. While AI holds the potential to revolutionize mental healthcare, responsible and ethical implementation is essential[3].
Blending AI and Human Expertise for Enhanced Care
AI may play an important role in supporting psychotherapy, particularly in addressing the global mental health service gap where access to trained professionals is limited[2]. AI is envisioned not as a replacement for human therapists but as a powerful tool that extends the reach of mental health services[2]. Ultimately, AI has an important role in the future of mental health, but it’s a complementary one[6]. By working alongside therapists, AI can serve as a valuable tool to enhance mental health support[6]. AI brings an element of anonymity and safety, and it can act like a stepping stone for patients who are perhaps uneasy about getting traditional therapy[8].
In this emerging paradigm, AI is envisioned not as a replacement for human therapists but as a powerful tool that extends the reach of mental health services[2]. In this way, AI has immense potential as a supportive tool in mental health, offering accessible resources and data-driven insights to complement traditional therapy[6]. Authentic empathy, relational dynamics, and the deep personal connection between client and therapist are at the heart of effective therapy, which AI cannot replicate[6].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Building an Inclusive Classroom Environment

Creating an inclusive classroom environment is essential for promoting equity in education and ensuring that all students, regardless of their backgrounds, abilities, or learning styles, can succeed. This report synthesizes effective strategies and practices derived from a variety of educational sources.
Understanding Inclusivity
Inclusive education values each student's uniqueness and recognizes the diversity they bring to the learning environment. The aim is to ensure that all learners feel respected, valued, and supported. As highlighted in various sources, this involves not just integrating students with disabilities or those from marginalized backgrounds, but also addressing and reflecting the varied identities of all learners in the curriculum and classroom interactions[8].
Designing a Diverse Curriculum
A culturally responsive curriculum is at the heart of inclusivity. Educators should incorporate materials and perspectives from a wide range of cultures and experiences into their teaching methods. This approach allows students to see themselves represented, which enhances their engagement and sense of belonging. For instance, featuring authors and historical figures from diverse backgrounds in the curriculum can help students appreciate the significance of varied narratives[7][8][10]. Regularly reviewing curricular materials to eliminate biases and incorporating community insights are also critical steps in developing an inclusive curriculum[2][3].
Establishing a Supportive Environment

Creating a classroom culture that fosters collaboration and respect is vital. Teachers should focus on building positive relationships with their students, showing an interest in their lives, and encouraging peer interactions[4][5]. According to research, students thrive in environments where they feel safe and respected, allowing them to engage in discussions and activities confidently[7]
Ground rules for respectful interaction and zero tolerance for discrimination should be well-established to nurture a safe space for expression. Encouraging students to share their experiences and respecting diverse viewpoints can foster empathy and understanding among classmates[6][10].
Differentiated Teaching Approaches

To address the diverse learning needs of students, educators should employ differentiated instructional strategies that cater to various learning styles. This can involve providing multiple ways for students to engage with content—such as discussions, projects, or hands-on activities—and allowing them to demonstrate understanding in various formats[2][4][9]. For example, utilizing technology can help personalize learning experiences and make content more accessible[8].
Furthermore, using formative assessments to identify each student’s strengths and needs allows teachers to adjust their teaching methods accordingly. Offering alternative means of participation and demonstrating flexible teaching practices can support students who may struggle with traditional assessment methods[7][9].
Professional Development and Training
Continuous professional development focused on inclusive teaching practices is crucial for educators. Many teachers express a need for more training in this area to effectively address the diverse needs of their classrooms[8][10]. Equipping teachers with the skills and knowledge to implement inclusive strategies will enhance their confidence and competency in this critical area of education.
Training should encompass understanding diverse cultural backgrounds, strategies for engaging every student, and techniques for modifying assessments to ensure all students can demonstrate their knowledge effectively[5][9].
Family and Community Engagement

Involving families and the wider community in the educational process is a cornerstone of effective inclusive practices. Building open, two-way communication channels with parents can provide insights into their children's needs and experiences[4][8]. Hosting community events and engaging with local organizations can also provide additional resources and support for students and families, fostering a more connected educational environment[8][10].
Addressing Bias and Stereotypes
Educators must be proactive in recognizing and addressing their own biases as well as those that may exist within the learning materials they use. Acknowledging and discussing microaggressions and stereotypes can help create a more inclusive atmosphere where all students feel valued and respected[2][4][6].
Teachers should encourage open dialogue about diverse cultures and identities, allowing students to challenge biases and develop a deeper understanding of inclusion[4][7][8].
Conclusion
An inclusive classroom environment is built on the principles of respect, understanding, and support for all students. By embracing diverse curricula, fostering supportive relationships, employing differentiated approaches, and engaging the community, educators can ensure that every student feels like a valued member of the learning experience. As the landscape of education continues to evolve, the commitment to inclusivity remains a vital goal for teaching leaders in 2024 and beyond.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.

The urgent need for effective conservation strategies stems from the alarming rate of biodiversity loss, with over 44,000 species documented as being at risk of extinction. The consequences of these declines threaten the stability of ecosystems that are essential for human well-being, providing services like clean water, livelihoods, and cultural preservation. This report delves into the key challenges surrounding conservation efforts aimed at safeguarding endangered species.
The Declining State of Biodiversity

A significant challenge in conservation is the ongoing decline in biodiversity, which is occurring at a pace 100 to 1,000 times faster than what scientists would expect under natural circumstances. This rate of extinction signifies a dire need for effective conservation measures amidst overwhelming evidence that many efforts are insufficiently funded. Despite considerable conservation actions, researchers argue these measures are not currently funded at the scale necessary to reverse global declines in biodiversity[1][5].
Challenges in Implementation and Scale
A comprehensive meta-analysis of 665 conservation trials revealed that conservation actions are effective in improving biodiversity in approximately two-thirds of cases[5]. However, many conservation strategies often suffer from a lack of representation, particularly from regions rich in biodiversity such as sub-Saharan Africa and parts of South America and Southeast Asia. This imbalance in representation means that conservation efforts may not adequately address the specific needs of endangered species in these hotspots[5].
Additionally, while established conservation methods such as protected areas and management of invasive species are shown to be successful, insufficient investment and support hinder their scalability. For instance, effective management of protected areas remains a cornerstone for conservation actions, yet inadequate resources often prevent these areas from operating optimally[1][4].
Overcoming Systemic Drivers of Biodiversity Loss

The systemic drivers contributing to biodiversity loss present another major challenge. Factors such as unsustainable consumption and production practices exacerbate the situation. Penny Langhammer, a lead author of a pivotal study, highlighted that meaningful conservation must include addressing these underlying causes rather than merely focusing on treating the symptoms[1]. Effective advocacy for policy changes and sustainable practices is crucial, as existing laws may not offer the protections needed for many endangered species while failing to account for the impacts of human activities on their habitats.
Knowledge and Learning from Failures
Interestingly, the same meta-analysis indicated that in cases where conservation actions did not yield the intended benefits for target species, valuable lessons were still learned. Conservationists were able to adapt and refine their methods based on these experiences. For example, a conservation attempt in India to remove invasive algae inadvertently led to its spread, providing insights for implementing more effective strategies in the future. The continuous learning and adaptation process within conservation practices is essential in a rapidly evolving environmental landscape[1][4].
The Role of Individual Actions in Conservation

While institutional efforts are paramount, individuals also play a crucial role in conservation. Simple actions taken by the public, such as purchasing sustainable products, advocating for conservation, and participating in habitat protection initiatives, contribute significantly toward safeguarding endangered species[2]. Engaging with local conservation organizations, educating oneself about local wildlife, and volunteering at wildlife rehabilitation centers all empower individuals to impact biodiversity positively. Ultimately, collective grassroots actions complement larger conservation strategies and foster a culture of responsibility toward endangered species.
Emerging Issues in Conservation
Another layer of complexity lies in emerging conservation challenges outlined by experts. Recent discussions highlight the potential threats posed by environmental issues such as climate change, invasive species, and diseases that can rapidly impact marine and terrestrial ecosystems. For example, mass mortality events concerning sea urchins in the Caribbean have raised alarms about the potential for future outbreaks of marine disease, which could further destabilize tropical ecosystems[3].
Moreover, the exploration of new technologies, such as hydrogen energy production and ocean-based carbon removal, presents both opportunities and risks. These innovative approaches may help combat climate change but could inadvertently harm existing ecosystems if not carefully managed[3]. Effectively navigating the balance between advancement and ecological integrity is vital for future conservation success.
Conclusion
The challenges facing endangered species conservation are vast and multifaceted. They require a concerted effort from both institutions and individuals to develop innovative and adequately resourced strategies. The evidence highlights that while many conservation actions are working, the urgency to scale these efforts and address systemic drivers of biodiversity loss is more critical than ever. By enhancing collaborative efforts and ensuring that conservation strategies are evidence-based and well-equipped, we can work towards a more sustainable future for the planet's biodiversity.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
The first ASMR video is attributed to a YouTube channel named WhisperingLife, which was created in 2009. The channel featured whispering, and the first video titled 'Whisper 1-Hello!' was notably aimed at triggering the ASMR sensation in viewers, marking the beginning of ASMR as a genre on the platform[1][4].
Before the term 'ASMR' was coined in 2010 by Jennifer Allen, the phenomenon was discussed in various online forums, with users referring to it informally[5][6]. Allen's creation of the term helped consolidate this community, which had been growing since these early discussions began around 2007[2][6].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Artificial intelligence (AI) is powered by several key technologies and concepts. At its core, AI utilizes machine learning and deep learning technologies, which involve training algorithms to make predictions or decisions based on data. These algorithms learn from the data using various techniques, such as supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning[5][6].
Machine learning involves creating models by training an algorithm on data to enable computers to learn from and make decisions without being explicitly programmed for tasks. This includes algorithms like neural networks, which are modeled after the human brain's structure and process complex data[5][6]. Neural networks are especially effective in recognizing patterns and relationships in large datasets.
Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, uses multilayered neural networks called deep neural networks. These networks automate feature extraction from large datasets, enabling machines to learn from unstructured data and make accurate predictions[5][6].
Additionally, artificial intelligence systems incorporate technologies for natural language processing (NLP) and computer vision, allowing machines to understand and respond to human language and identify objects in images and videos[5].
Overall, the development of AI relies on combining these technologies to enable systems to simulate human learning, comprehension, problem-solving, decision-making, and creativity[5][6].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/fenty-beauty-by-rihanna-pro-filtr-soft-matte-longwear-liquid-foundation-7b340ba8713d4a54ab5a5957ff62ff1c.jpg)




























































-3050.jpg?resizeid=3&resizeh=800&resizew=800)