Discover Pandipedia
Pandipedia is the world's first encyclopaedia of machine generated content approved by humans. You can contribute by simply searching and clicking/tapping on "Add To Pandipedia" in the answer you like. Learn More
Expand the world's knowledge as you search and help others. Go you!
Google utilizes the funnel concept in its advertising strategies to discuss ad markets and communicate with advertisers. This model illustrates the consumer journey from awareness to purchase, with various types of advertisements serving as tools to influence decision-making along the way. Advertisers focus on moving consumers further down the funnel toward the sale[2][1].
Additionally, Google emphasizes delivering more qualified users lower in the funnel. For instance, when advertisers bid on more specific ads, like hotel ads, they often invest more because of the higher likelihood of conversion at that stage[3]. This approach highlights the complementary roles of different advertising channels in driving purchases[1].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Chain of Thought (CoT) is a prompting technique that improves the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) by generating intermediate reasoning steps[1]. It helps the LLM generate more accurate answers[1]. You can combine it with few-shot prompting to get better results on more complex tasks that require reasoning before responding, as it’s a challenge with a zero-shot chain of thought[1].
CoT's advantages[1]:
* It is low-effort while being very effective and works well with off-the-shelf LLMs (so no need to finetune).
* You also get interpretability with CoT prompting, as you can learn from the LLM’s responses and see the reasoning steps that were followed.
* Chain of thought appears to improve robustness when moving between different LLM versions, which means the performance of your prompt should drift less between different LLMs than if your prompt does not use reasoning chains.
The LLM response includes the chain of thought reasoning, which means more output tokens, which means predictions cost more money and take longer[1].
Self-consistency combines sampling and majority voting to generate diverse reasoning paths and select the most consistent answer[1]. It improves the accuracy and coherence of responses generated by LLMs[1].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.

Rosa Parks contributed significantly to the civil rights movement by refusing to give up her seat to a white man on a segregated bus in Montgomery, Alabama, on December 1, 1955. This act of defiance sparked the Montgomery Bus Boycott, a pivotal event that lasted for over a year, led by Martin Luther King Jr. and organized by the Montgomery Improvement Association. The boycott drew national attention to the systemic racism of Jim Crow laws and ultimately resulted in a Supreme Court ruling declaring bus segregation unconstitutional[1][4][5].
Parks, an active member of the NAACP, faced personal repercussions for her actions, including losing her job. She continued to work for civil rights, promoting fair housing and voter registration, and received numerous honors for her contributions, including the Congressional Gold Medal[2][4][5].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Game mechanics enhance player engagement by providing clear objectives and challenges that motivate players to invest time and effort into the game. They create a sense of achievement through well-balanced rewards, allowing players to feel accomplished as they progress. For instance, mechanics like challenge and reward systems keep players hooked by providing tangible benefits for overcoming obstacles[3].
Additionally, mechanics foster player agency by enabling meaningful choices and allowing players to experience the consequences of their decisions. This sense of control enhances immersion and encourages exploration within the game world, making players feel more connected to their experience[2][4].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Meal planning offers several benefits, including saving time and reducing stress associated with daily meal decisions. By organizing meals ahead of time, individuals can avoid last-minute hurried cooking or takeout, leading to more thoughtful meal choices that are healthier and provide a variety of nutrients[1][6].
Additionally, meal planning helps control portions and ingredients, which can contribute to better weight management and reduced grocery expenses by minimizing food waste[2][4][5]. It allows for greater organization and consistency in dietary habits, making healthy eating more achievable and manageable[3][6]. Overall, meal planning can significantly enhance one’s overall well-being and lifestyle.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Nikola Tesla's work laid the foundation for many renewable energy technologies, particularly through his development of the alternating-current (AC) power system, which revolutionized electric power distribution. This system is crucial for integrating renewable sources, such as wind and solar, into modern energy grids as it efficiently transmits electricity over long distances[1][6].
Moreover, Tesla envisioned and experimented with wireless transmission of energy, aiming to provide free, limitless power. His ideas anticipated future technologies that are now being explored in renewable energy applications, such as wireless charging for electric vehicles[3][5]. Tesla's commitment to clean energy underscores his lasting influence on renewable technologies today.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.

Experts were paid up to $5000 for each question that was accepted to the Humanity’s Last Exam benchmark[1]. While this benchmark still has significant headroom at the time of writing (June 2025), performance on it has improved significantly over the space of a few months[1].
The best models were achieving just a few percent accuracy on it when it was initially published in early 2025[1]. When one considers agentic systems, which are able to tackle problems for longer and which have access to tools and self critique, the complexity of benchmarks required to measure performance also increases dramatically[1].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
.jpg)
Coastal regions are among the most affected by climate change, facing a multitude of challenges that threaten both their ecosystems and human livelihoods. The following sections detail the various impacts of climate change on these vulnerable areas, drawing from an array of sources.
Rising Sea Levels

One of the most significant threats to coastal areas is the rise in sea levels. This phenomenon is primarily driven by two factors: the thermal expansion of seawater due to increasing ocean temperatures, and the melting of glaciers and polar ice sheets. According to projections, global mean sea levels are expected to rise by approximately one foot (0.28 meters) by 2050 and could exceed three feet (1 meter) by 2100 under intermediate scenarios. In extreme scenarios, levels could rise by up to 6.6 feet (2 meters) by the end of the century if significant climate action is not undertaken[2]. This rise poses existential risks for small island states and densely populated coastal cities worldwide.
As sea levels increase, the impacts are not uniform; local variations occur due to gravitational effects, tides, and ocean currents. Some areas may experience sea level rises significantly above the global average, amplifying risks of flooding, erosion, and habitat loss[4]. The effects of sea-level rise also exacerbate storm surges associated with extreme weather events, leading to more frequent and severe flooding in coastal areas[4].
Coastal Erosion and Loss of Habitat
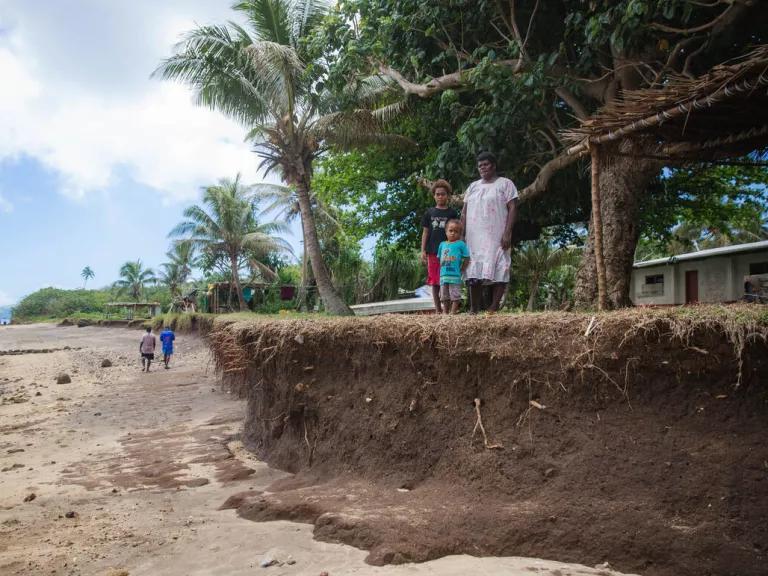

The coastal systems, including wetlands and mangroves, play critical roles in buffering against storms and providing habitats for numerous species. However, as sea levels rise and wave heights increase, these ecosystems face severe degradation and loss. Coastal erosion threatens not only these natural habitats but also human infrastructure[1]. The ongoing degradation of important coastal ecosystems, such as mangrove forests, results from climate impacts like rising sea levels and changing precipitation patterns, with significant implications for biodiversity and local fisheries[1][2].
Increased Frequency of Extreme Weather Events

Climate change is linked to an increase in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and tropical cyclones. These events pose immediate risks to coastal communities, resulting in flooding, destruction of property, and loss of life. The merging of high sea levels with storm surges during these events can lead to catastrophic outcomes. For instance, research indicates that every 10 cm of sea-level rise can triple the frequency of a given coastal flood, compounded by storm effects[4].
In addition to storm activity, regions are also experiencing higher occurrences of nuisance flooding during high tides and increased erosion rates, which impact urban infrastructures in many coastal areas[2][3].
Economic Impacts
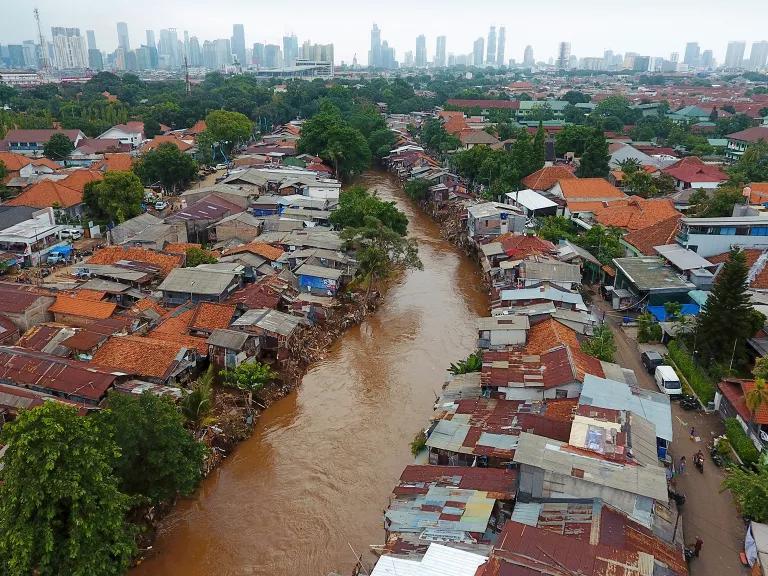

The economic ramifications of climate change for coastal regions are profound. Ports, which facilitate over 80% of global trade, are increasingly at risk. Alarmingly, one-third of global sea ports are situated in areas vulnerable to severe cyclones, and many face threats from rising water levels. Economic activities critical to coastal economies, such as tourism, fisheries, and aquaculture, are jeopardized by climate-induced changes[1][2].
For developing nations, the loss of revenue from disaster response can reduce tax bases and impede efforts in education and health care, pushing these countries deeper into cycles of poverty and debt[1].
Social and Health Impacts

Socially, the implications of climate change lead to displacement of communities, particularly those in low-lying coastal areas. Rising sea levels are driving both voluntary and involuntary migration, raising concerns over “climate refugees.” The threat of permanent inundation forces communities to relocate, creating pressure on urban infrastructures and services in destination areas, often leading to increased health risks and social unrest[1][3][2].
Food security is another critical issue arising from climate impacts. Coastal flooding, saltwater intrusion into freshwater supplies, and deteriorating agricultural conditions threaten food production, which is essential for both urban and rural communities[1]. In terms of health, the increased stress on emergency responsiveness, coupled with rising incidences of waterborne diseases due to compromised clean water access and health infrastructure from flooding, creates a dual burden on local populations[1][4].
Addressing the Challenges

To combat these multifaceted challenges, a multidisciplinary and collaborative approach is essential. The UN's Sustainable Development Goals emphasize the need for policies that address the physical, social, economic, and environmental vulnerabilities faced by coastal communities[1]. Coastal cities must proactively adapt through sustainable development strategies that encompass infrastructure resilience, the restoration of natural defenses like wetlands, and community engagement in disaster preparedness[3][5].
Conclusion
Climate change presents a formidable challenge to coastal regions worldwide, influencing rising sea levels, increased storm intensity, erosion, economic and social dynamics, and food security. A proactive and collaborative global response is crucial to mitigate these impacts and safeguard coastal communities for future generations.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Hydration is essential for overall well-being as it plays a critical role in maintaining bodily functions. Dehydration can lead to negative health effects, including cognitive issues like brain fog and emotional disturbances, as highlighted by fitness expert Ally Love. She emphasizes that 'being dehydrated actually has huge contributing factors to poor health'[4].
Moreover, proper hydration aids in muscle mass maintenance and can lower disease risk, suggesting that increased water intake contributes to longevity[4]. Additionally, staying hydrated helps optimize various bodily functions and can significantly improve one's mood and overall quality of life[4].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Dokot Seagrass Storage Basket
A practical, environmentally friendly solution for storing everything from toys to blankets[1].
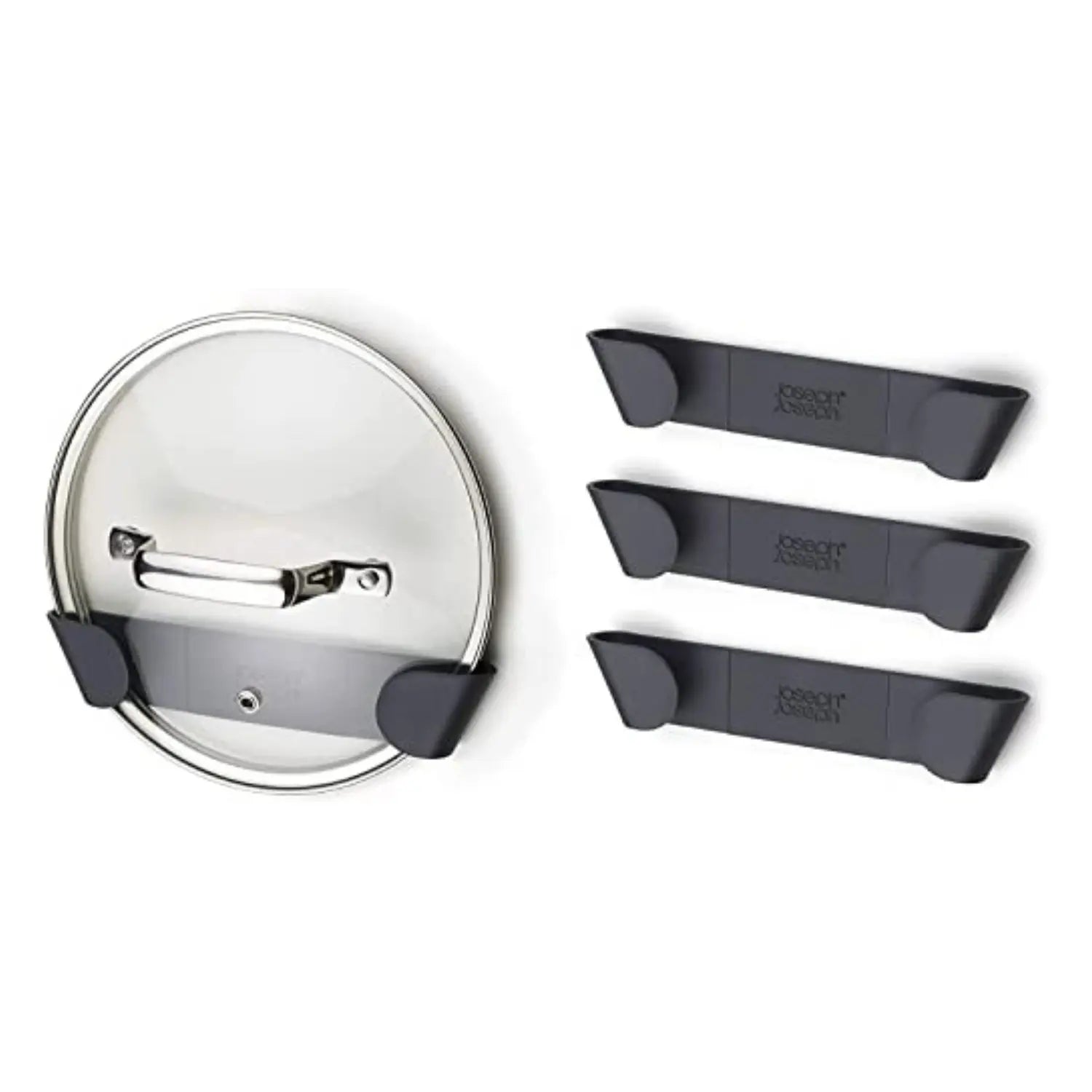
Joseph Joseph Lid Organiser
An ideal option for managing pan lids with easy installation and no need for tools[1].
Tower Kitchen Bin with Sensor Lid
A hygienic waste disposal solution featuring a motion sensor lid that opens automatically[1].
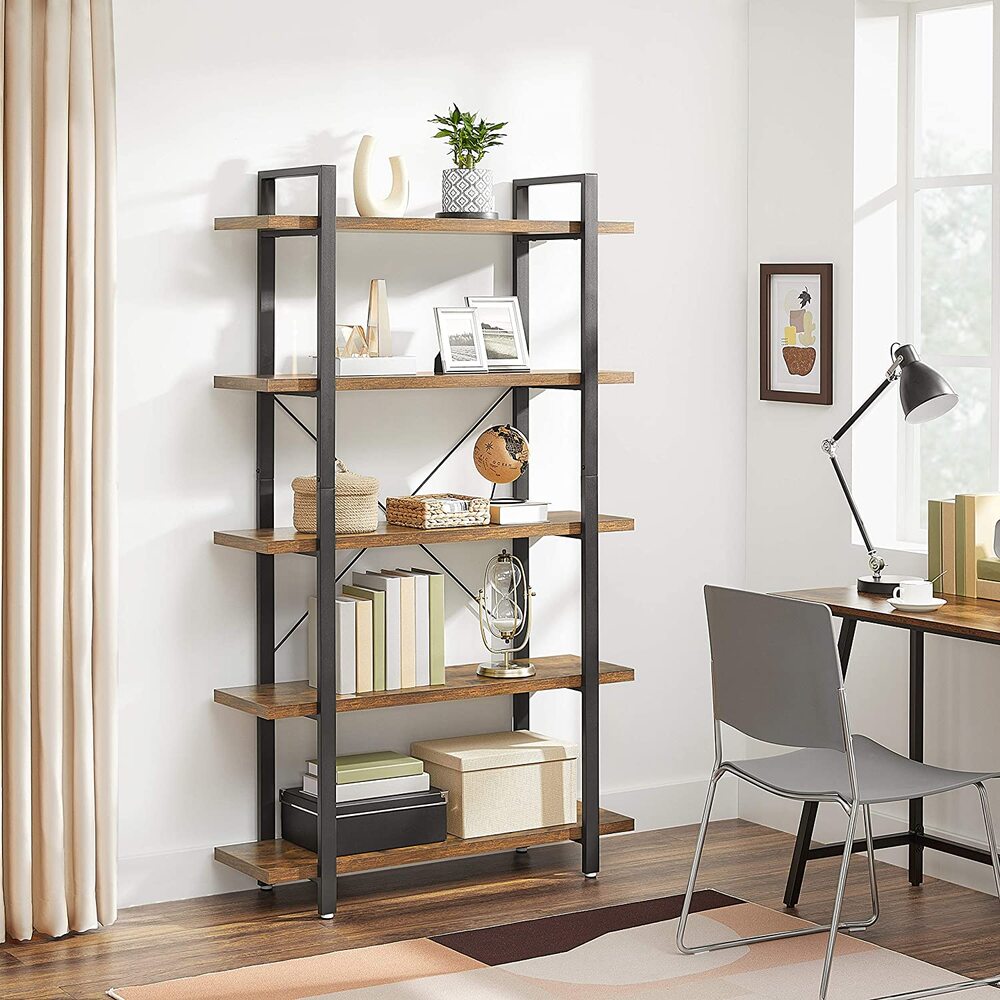
Vasagle 5 Tier Bookcase
A stylish industrial bookcase with five open shelves, suitable for any room[1].
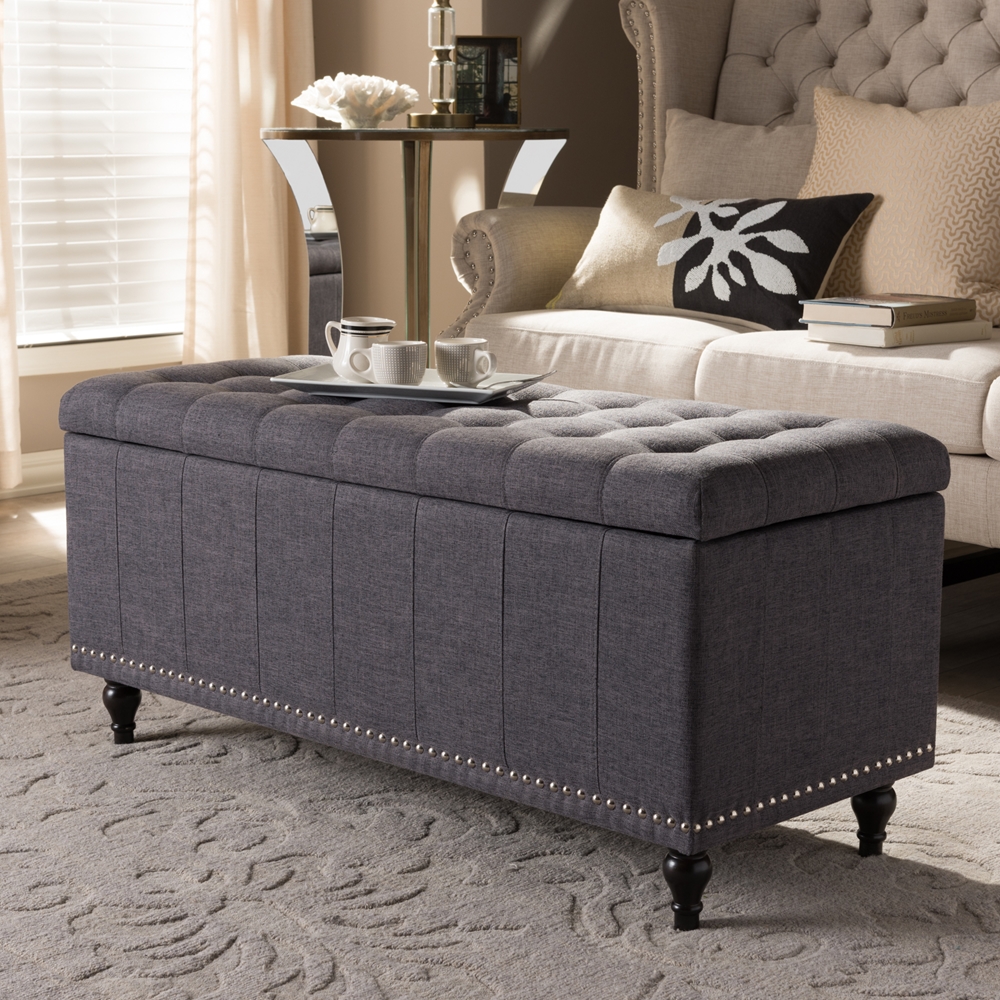
Grey Storage Ottoman Padded Bench
An elegant storage solution that combines seating and a generous storage capacity of 120L[1].
Collapsable Clothes Drawer Organisers
Efficient storage for clothes and accessories, easily folded away when not in use[1].
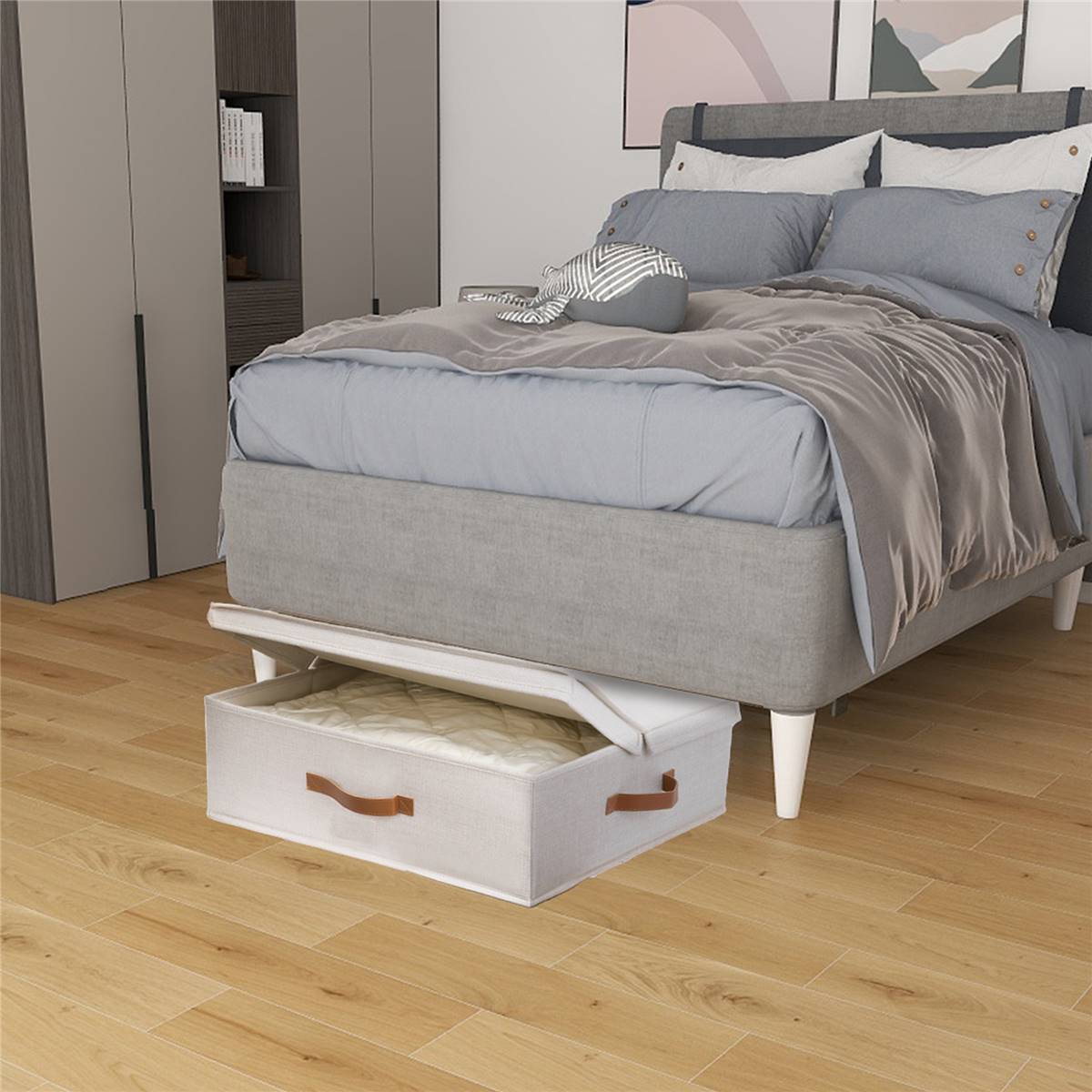
Foldable Under Bed Storage Box
A durable, waterproof storage solution designed to maximize space beneath the bed[1].
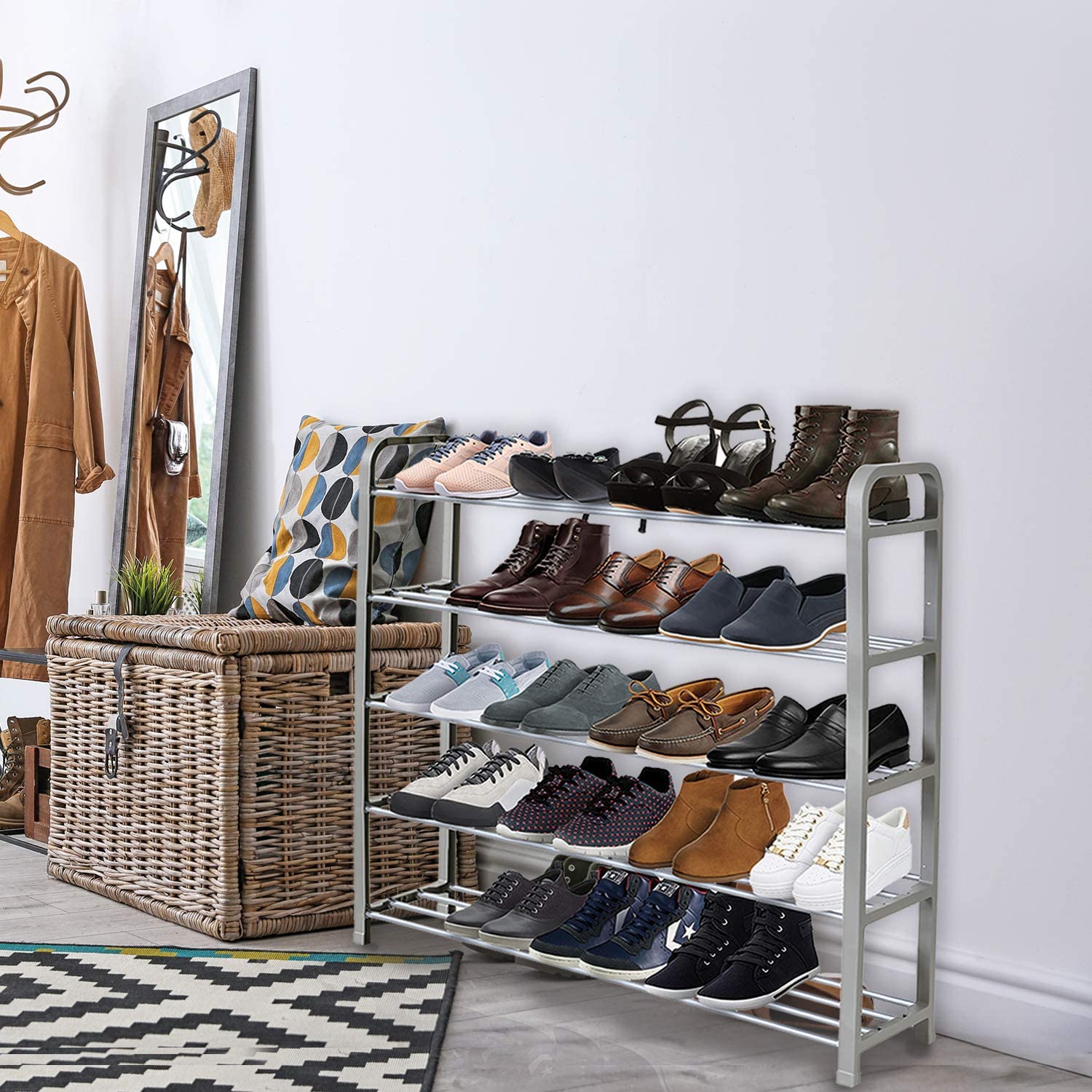
Keplin 5 Tier Shoe Rack
A sturdy shoe rack that holds up to 20 pairs of shoes, with no-tools assembly[1].
Joseph Joseph Under-Shelf Spice Rack
A space-saving solution for spices that mounts under shelves, maintaining a neat kitchen[1].
Fanhao Stainless Steel Hanging Clothes Rack
A strong and stylish hanging rack with two tiers and additional hooks for versatile storage[1].
Joseph Joseph Compact Cutlery Drawer Organiser
A compact drawer organiser with five compartments for easy kitchen utensil storage[1].
32 Piece Food Storage Containers Set
An airtight set that keeps food fresh and organized, perfect for pantry management[1].
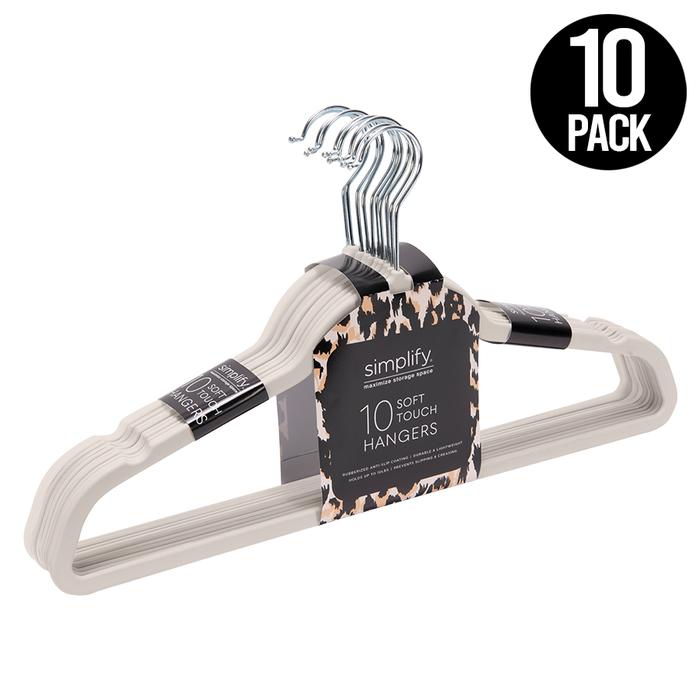
Marissa Hagmeyer Recommended Slim Rubberized Hangers
Space-saving hangers in various sizes and colors to keep your closet organized[3].
Acacia Wood Turntable
An elevated lazy Susan perfect for organizing kitchen items in upper cabinets and awkward spaces[3].
Handmade Storage Baskets
Aesthetically pleasing options for storing items like blankets or children's toys discreetly[3].
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/neat-methods-grid-baskets-61e78d40763c4892b283dfecb7efaaa8.jpg)
Grid Basket
A versatile storage solution that can be used in multiple rooms, including the pantry and laundry[3].
Adjustable Utensil Organizer
Expands to fill drawer space and organizes utensils, reducing clutter on countertops[8].
Storage System for Garages
A thorough Rubbermaid system that organizes tools and outdoor equipment[8].
:strip_icc():format(webp)/niimbot-label-maker-machine-e2d50b972ea54b30a44068e977489b00.jpg)
Label Maker
Provides clear labels to help everyone in the household know where items belong, maintaining organization[8].
:strip_icc():format(webp)/youcopia-crazy-susan-lazy-susan-organizer-1a7cdeb2042143aaa032bf7e99f84f9c.jpg)
:strip_icc():format(webp)/luxear-suction-hooks-81f0bfcec9914b3e81860796f60cb1ab.jpg)
:strip_icc():format(webp)/amazon-basics-3-tier-rolling-utility-cart-5cb04815d1b14c0eb11595bd3235a87d.jpg)
Utility Cart
A versatile cart suitable for any room, ideal for storing cleaning supplies or kitchen items[8].
:strip_icc():format(webp)/drawer-dividers-E8RteDbK4hABn-R91BkB0M-d7ff37137c164130ad7664dae6a789fe.jpg)
Drawer Dividers
Clear organizers that maximize drawer space while keeping items neatly categorized[7].
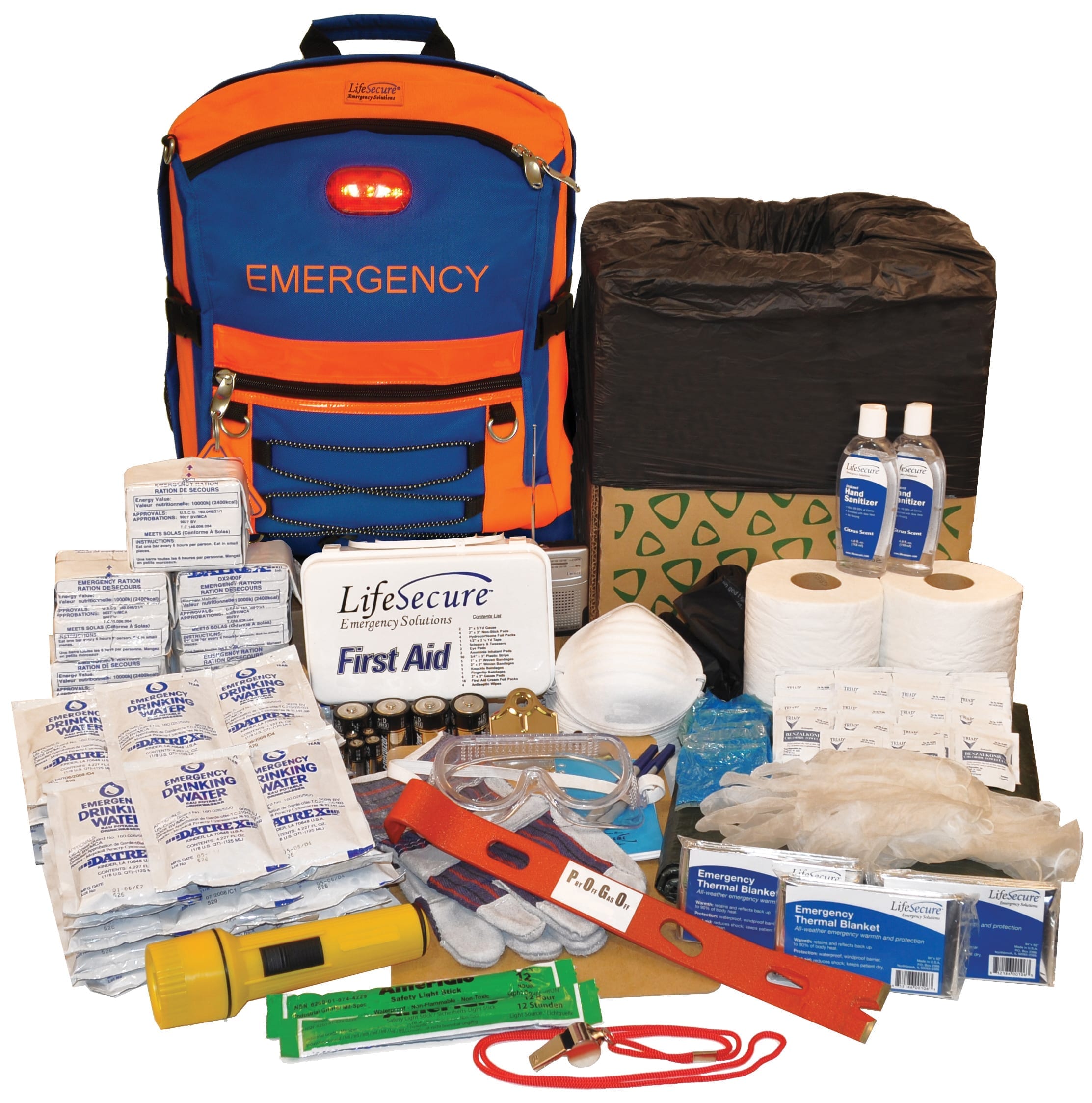
Emergency Preparedness Kit
A car organizational kit that ensures essential items are easily accessible during travel[3].
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ohill-desk-cable-management-cord-organizer-e72e66b8e83945718247b5623f3228e0.jpg)
Under-Shelf Baskets
Useful for maximizing vertical space in pantries, allowing easy access to frequently used items[8].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.