Discover Pandipedia
Pandipedia is the world's first encyclopaedia of machine generated content approved by humans. You can contribute by simply searching and clicking/tapping on "Add To Pandipedia" in the answer you like. Learn More
Expand the world's knowledge as you search and help others. Go you!

Apple AirPods Max
Wireless headphones featuring active noise cancellation and surround sound-like spatial audio technology for an immersive listening experience[1].

Owala FreeSip Insulated Stainless Steel Water Bottle
This bottle offers multiple ways to drink and keeps drinks cold for hours, making it a favorite among users[2][3][4].

HigherDose Infrared Sauna Blanket
A portable sauna that promotes recovery and relaxation, perfect for wellness enthusiasts[1][5].

BaubleBar Bubble Initial Necklace
Trendy jewelry piece that can be personalized with initials, loved by fashion-savvy individuals on social media[1][3].

Therabody Theragun Mini
A compact massage gun that provides targeted relief for sore muscles, ideal for athletes or fitness lovers[1][4].

Dyson Airwrap Multi-Styler
A highly-rated hair styling tool that offers multiple attachments to create various styles without extreme heat damage[1][4].

Lululemon Everywhere Belt Bag
A versatile bag that can be worn as a belt or crossbody, making it perfect for anyone on the go[2][4].

LEGO Ideas Tuxedo Cat
A fun and intricate LEGO set for animal lovers and those who enjoy building models[1].
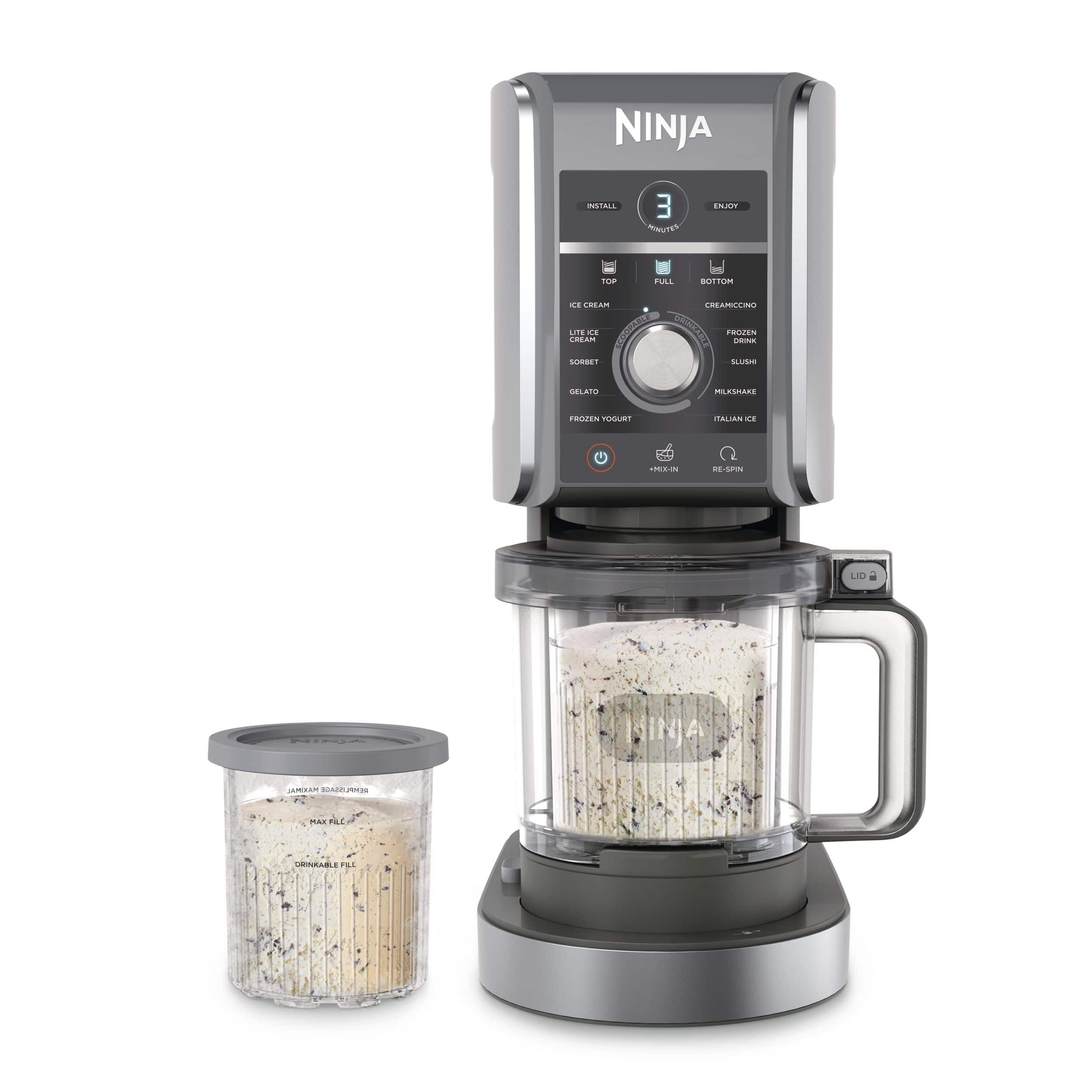
Ninja CREAMi
An appliance that allows users to make ice cream, sorbet, and slushies easily at home[4][11].

Coach Tabby Shoulder Bag
A stylish bag with a vintage silhouette that has gained popularity this year[1][5].

Therabody TheraFace Depuffing Wand
A skincare device designed to reduce puffiness and promote skin health, favored by beauty enthusiasts[5].

CurrentBody Skin LED Light Therapy Mask
An innovative mask that offers red light therapy to improve skin texture and reduce fine lines[4][11].

Maison Margiela Replica Jazz Club Unisex Fragrance
A nostalgic scent inspired by nightlife, appealing to both men and women[1].

PlayStation Portal Remote Player
A handheld device that allows users to play PS5 games remotely, perfect for gamers[1].
Craft Coffee Subscription Box
A curated selection of specialty coffee delivered monthly, ideal for coffee lovers[12].
Glow Recipe Watermelon Glow Niacinamide Dew Drops
A hydrating product that enhances radiance and serves as a makeup base[12].

Bissell Little Green Multi-Purpose Portable Carpet Cleaner
An efficient cleaning device for upholstery and carpets, appreciated by pet owners[5].
Glossier You Rêve Perfume
A new version of the popular fragrance from Glossier, combining fruity and buttery scents[3].

Coach Motif Chain Bag Charm
A trendy accessory that adds personality to any bag, favored by fashionistas[3].

The Comfy Original Wearable Blanket
A cozy and oversized blanket that provides warmth and comfort[9][12].

Nightball Tangle Glow in the Dark Inflatable LED Football
A fun outdoor game that glows in the dark, great for kids and families[2].
Skinfix Barrier+ Triple Lipid Peptide Face Cream
A product focused on hydration and skin barrier support, trending among skincare experts[12].
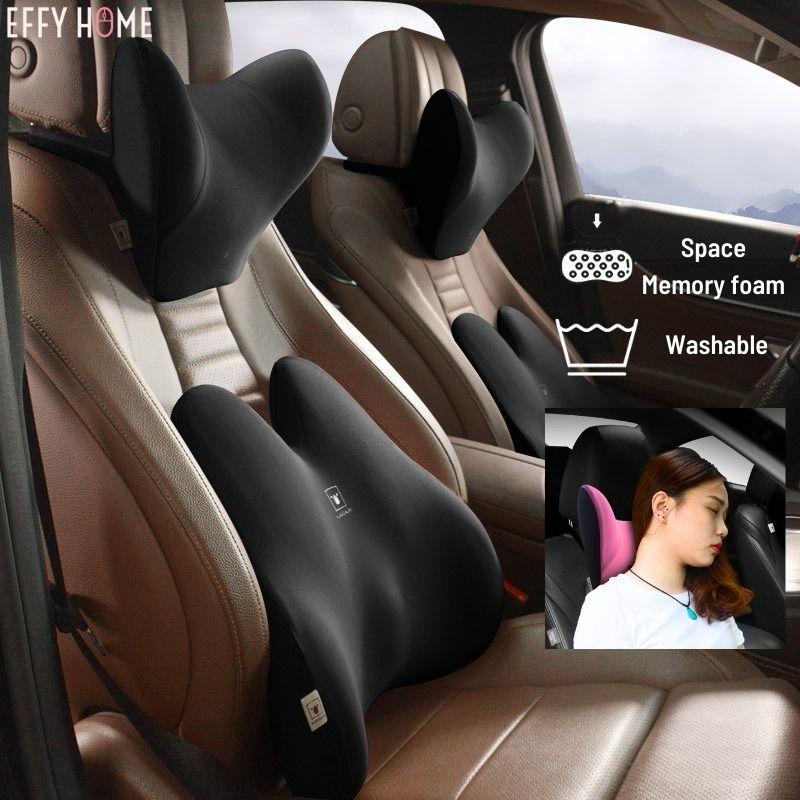
Ease Wear Lumbar Support Pillow
A supportive pillow designed to relieve back pain, perfect for home or office use[12].
Nike Killshot Glitter Swoosh Sneakers
Stylish and functional sneakers that combine comfort and fashionable design[12].

Cuyana Travel Case Set
A set of chic toiletry cases that help keep items organized while traveling, appealing to fashion-conscious travelers[12].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Religion plays a significant role in shaping culture by influencing individual beliefs, values, and social behaviors. It serves as a framework that helps individuals make sense of the world and navigate complex life questions, providing moral guidelines and community connection[2]. Moreover, cultural practices such as rituals and traditions are often rooted in religious beliefs, reinforcing group identity and social cohesion[6].
Research shows that individuals who share the same religious traditions exhibit cultural similarities regardless of geographic boundaries, suggesting that religious affiliation fosters distinct cultural traits[4]. Religion also impacts social issues, serving as a lens through which sociologists can examine cultural practices and societal changes[5][6].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.

Earthquakes are natural seismic events resulting from the sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust, primarily due to the movement of tectonic plates along fault lines. These movements generate seismic waves that can cause significant ground shaking and various forms of damage.
Tectonic Plates and Faults
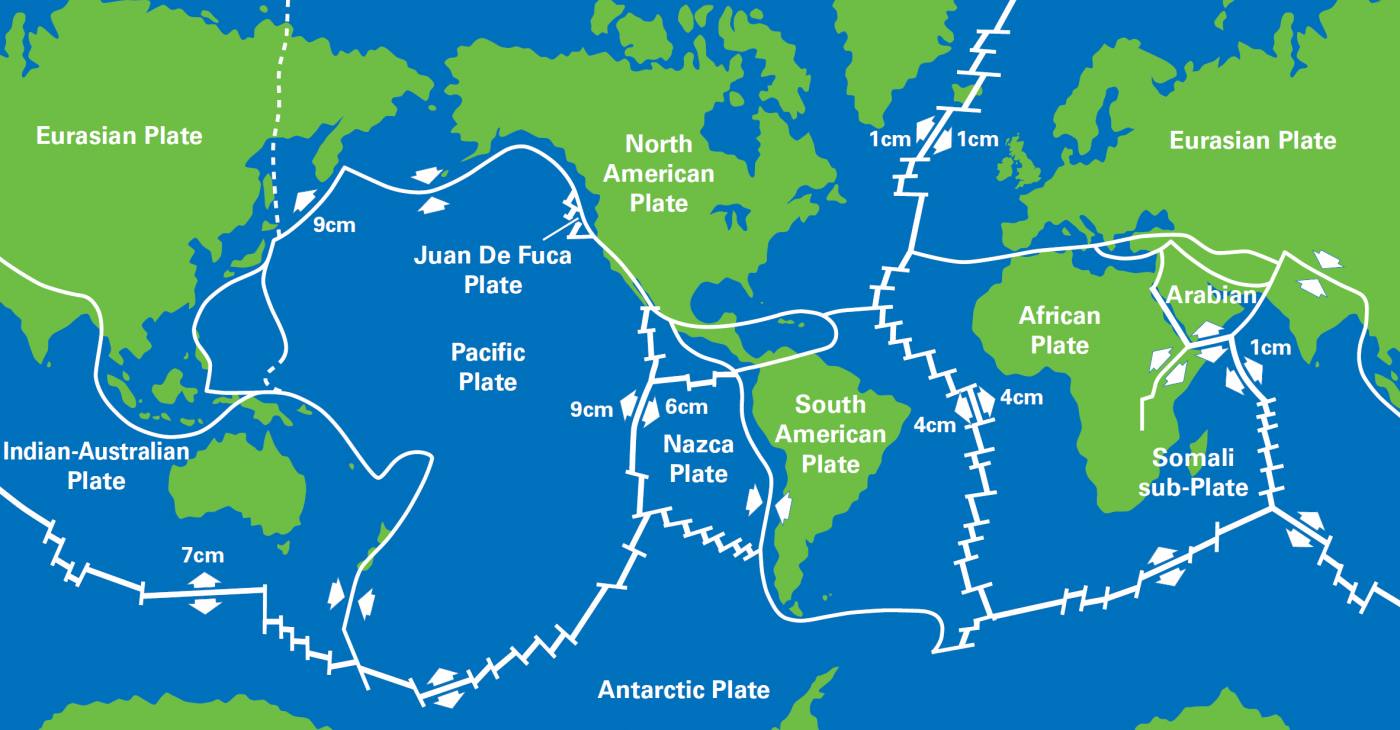
The Earth's lithosphere, which is its outer layer, is divided into approximately 15 major tectonic plates. These plates float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere beneath them and interact at their boundaries, where stress can accumulate over time[3]. As tectonic plates continuously move—albeit slowly, typically just a few centimeters per year—they can become 'stuck' at their edges due to friction. This friction prevents the plates from sliding smoothly past one another, leading to an increase in stress along the fault lines[1][2][5].
When the accumulated stress overcomes the frictional forces holding the plates together, a sudden slip occurs, resulting in an earthquake. This violent release of energy propagates in waves through the Earth's crust, manifesting as the shaking we feel during an earthquake[2][7]. The exact point within the Earth where the rupture begins is referred to as the hypocenter (or focus), while the point directly above it on the Earth's surface is known as the epicenter[8].
The Elastic Rebound Theory

The mechanism behind the sudden release of energy in earthquakes is explained by the elastic rebound theory. This theory describes how stress builds up in rocks along a fault line due to continuous tectonic movement. Over time, as stress accumulates, the rocks undergo deformation (bending or stretching). Once the stress exceeds the strength of the rocks, they fracture and snap back to their original shape, resulting in an earthquake[3][9]. This snapping motion produces seismic waves that travel outward from the fault, causing the ground to shake.
Types of Faults
There are three primary types of faults that contribute to seismic activity:
Normal Faults: Occur when the crust is extended, causing one block of rock to drop relative to another. This type of fault is often found in regions experiencing rifting, where tectonic plates pull apart[12].
Reverse (Thrust) Faults: These faults occur when the crust is compressed, pushing one block of rock over another. This is commonly seen in subduction zones where an oceanic plate is forced beneath a continental plate[12].
Strike-Slip Faults: Characterized by horizontal movement, where blocks of crust slide past each other without much vertical movement. The San Andreas Fault in California is a well-known example[12].
Induced Earthquakes

While most earthquakes are natural occurrences related to tectonic activity, human activities can also induce seismic events. For instance, the injection of wastewater from oil production into underground wells has been linked to increased seismic activity. This occurs when the high-pressure fluid alters the stress distribution in the surrounding rocks, potentially triggering earthquakes[4][6]. Although rare, hydraulic fracturing (fracking) can cause earthquakes directly, but it is more common for significant seismic events to be associated with wastewater disposal practices[4][9].
Seismic Waves and Their Impact

The energy released during an earthquake travels through the Earth as seismic waves, which include various types:
P-waves (Primary waves): These are compressional waves that are the fastest and can travel through solids, liquids, and gases.
S-waves (Secondary waves): Slower than P-waves, they can only travel through solids and move by causing particles to oscillate perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
Surface waves: These waves travel along the Earth's surface and tend to cause the most significant damage due to their larger amplitude and longer duration[3][7].
The complex interactions of these waves can result in various impacts ranging from minor tremors to catastrophic damage, especially in densely populated areas near the epicenter. Additionally, aftershocks—smaller quakes that follow the main event—can continue to occur for days or even months as the Earth's crust adjusts to the new conditions[12].
Conclusion
In summary, earthquakes arise from the intricate movements of tectonic plates and the sudden release of built-up stress along faults. Understanding the mechanisms of earthquakes, including the types of faults and the role of tectonic plate movements, is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate their impacts. Both natural processes and human activities can influence seismic activity, highlighting the need for continued research and monitoring in earthquake-prone regions.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

COSRX Advanced Snail 96 Mucin Power Essence
Contains 96% snail secretion filtrate, excellent for hydration and skin repair while reducing the appearance of dark spots[1].

SK-II Facial Treatment Essence
Infused with Pitera, this essence nourishes, conditions, and hydrates the skin, making it a favorite in the beauty community for promoting a youthful appearance[2][5][8].

Tatcha The Essence
A blend of ingredients including Akita rice and green tea, this essence hydrates and preps the skin while supporting its microbiome[1][6].

Peach & Lily Wild Dew Treatment Essence
Combines skin-loving ingredients like niacinamide and hyaluronic acid to provide long-lasting hydration and improve skin texture[1][5][8][10].

Caudalie Vinoperfect Brightening Glycolic Essence
This essence employs glycolic acid to gently exfoliate and hydrate, aiding in skin brightening and evening out tone[1][3].
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Fresh-Kombucha-Facial-Treatment-Essence-b83cde0adf964e68938a0c5bddf1b212.jpg)
Fresh Kombucha Facial Treatment Essence
Enriched with kombucha and hyaluronic acid, this essence helps to refine skin texture and boost hydration levels[3][4].
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/neogen-real-ferment-micro-essence-3d8b8fb5afda4f739ecc9fa33e774a7a.jpg)
Neogen Real Ferment Micro Essence
This product features a high concentration of fermented ingredients, effectively hydrating while also offering brightening benefits[2].

Dickinson’s Enhanced Witch Hazel Hydrating Toner with Rosewater
A budget-friendly option that hydrates and soothes skin, making it suitable for sensitive skin types[1].
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/bioderma-b82eb9a6a76948788d2453b75d36ee75.jpg)
Bioderma Hydrabio Essence Lotion
Celebrated for its instant hydrating capabilities while being suitable for various skin types, particularly beneficial for dry skin[2][5].

Rhode Glazing Milk
A milky essence known for its lightweight hydration and beneficial ingredients that leave the skin feeling soothed and smooth[3][4].

Sunday Riley Pink Drink Skin Firming Resurfacing Essence Face Mist
Ideal for enhancing skin elasticity and hydration with peptides and botanical extracts[1].

Tata Harper Hydrating & Plumping Hyaluronic Acid Floral Essence
This essence refreshes and hydrates the skin while providing a light, floral scent[1][3].

ILIA The Base Face Milk
Targets compromised skin by providing active hydration and soothing benefits, designed for a variety of skin types[5].
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Kiehls-Iris-Extract-Activating-Treatment-Essence-801c71e0908940a0800725ad00341e7f.jpg)
Kiehl’s Iris Extract Activating Treatment
Infused with sodium hyaluronate, this essence helps improve skin texture and hydration levels while being suitable for all skin types[2].
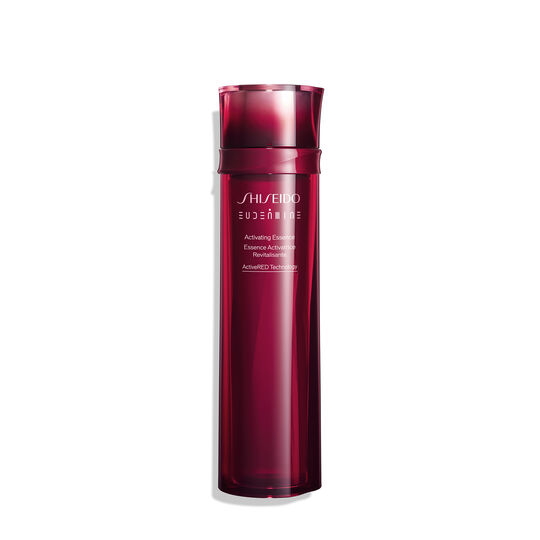
SHISEIDO Eudermine Activating Essence Lotion
This product boasts hydrating properties and aims to improve overall skin texture and moisture retention[7][10].
MISSHA Time Revolution The First Treatment Essence RX
Known for its fermented ingredients, it enhances moisture and supports overall skin clarity[2].
Clayton Shagal Moisture Plus Essence
Provides intense hydration and supports skin elasticity, ideal for those looking to restore moisture balance[5].

AmorePacific Vintage Single Extract Essence
Formulated with green tea extract, this essence helps provide a lot of hydration while offering protective benefits against environmental damage[4].
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/neogen-real-ferment-micro-essence-3d8b8fb5afda4f739ecc9fa33e774a7a.jpg)
Neogen Dermalogy Real Ferment Micro Essence
Rich in naturally fermented ingredients, this essence enhances moisture retention and overall skin hydration[1].
La Roche-Posay Hydraphase Intense Serum
Known for its ability to deliver deep hydration while maintaining skin moisture levels throughout the day[8].
Omorovicza Queen of Hungary Mist
This essence acts as a toner and hydrator, using mineral-rich waters and extracts to gently refresh the skin[9].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
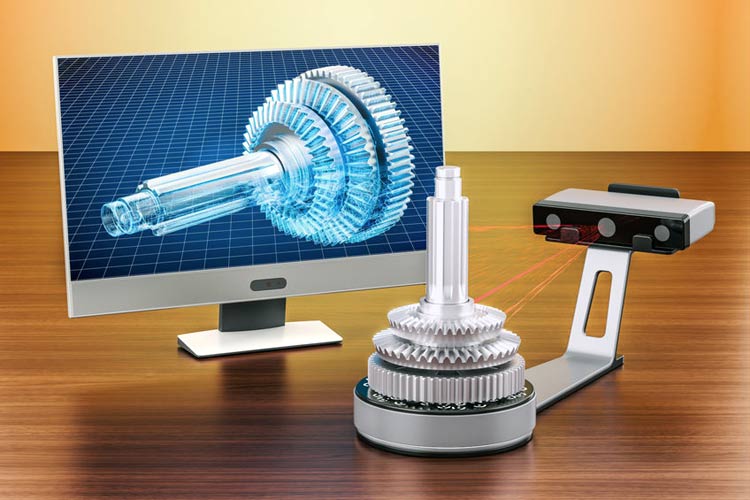

3D scanning technology has emerged as a transformative tool across various industries, offering unique capabilities for measuring and digitizing physical objects. This report outlines the importance of 3D scanning, its functionalities, applications, and future potential.
Defining 3D Scanning
3D scanning involves capturing an object's shape and appearance to create digital 3D models. This technology utilizes sensors such as lasers or structured light to obtain precise measurements from the object, forming a 'point cloud' that represents its surface. Following this, the point cloud data is processed to create a mesh model, which can then be textured for realism. The entire process enhances the accuracy and efficiency of creating 3D representations of physical items and is essential for tasks requiring detailed geometric data[1][4].
Versatile Applications Across Industries

3D scanning has found applications in numerous fields, including entertainment, medicine, architecture, and engineering. In the movie and video game industries, 3D scanning allows artists to create lifelike characters and props efficiently compared to traditional modeling techniques[1][5]. It is similarly beneficial in the medical sector, where it aids in the design of prosthetics and implants, enhancing the fit and comfort for patients while accelerating production processes through 3D printing technologies[1].
In architecture, 3D scanning provides accurate measurements and visualizations of buildings, allowing architects to create detailed designs and perform reverse engineering to improve existing structures[1][2]. The technology also plays a crucial role in the construction and engineering sectors for site modeling and quality control, enabling iterative improvements in design and craftsmanship[2][5].
Technological Advancements and Integration

Modern advancements in technology have significantly enhanced the functionality and ease of use of 3D scanning equipment. Contemporary scanners can deliver high-quality data with minimal operator expertise, transforming 3D scanning from a specialized task into an integral part of the design and manufacturing workflow[2]. The integration of 3D scanning data into generative design processes helps engineers to optimize creations from the outset, ultimately improving the quality of the final parts while reducing rework and material waste[2].
Moreover, with the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI), 3D scanning can facilitate real-time data analysis and decision-making, significantly augmenting manufacturing processes. AI systems can leverage intricate data provided by 3D scans to refine algorithms used in production, enhancing accuracy and efficiency[2][5].
Historical Context and Evolution
The journey of 3D scanning technology began in the late 1980s when the first imaging triangulation systems were installed for industrial applications. Early systems primarily focused on surface inspection and comparative measurements but required significant manual intervention. Over time, the technology has matured into a user-friendly solution capable of adapting to various industrial needs[3]. The rise of high-definition 3D scanners has revolutionized cultural heritage conservation, archaeology, and paleontology, enabling the detailed documentation of artifacts and structures without physical contact[3].
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its advantages, there are challenges associated with 3D scanning technology. Environmental factors, such as lighting conditions, can significantly impact the quality of scans. Additionally, there is a need for adequate training to utilize the technology effectively, which ensures accurate results[5]. While 3D scanning systems have become more portable and easier to use, they still face constraints regarding size, scanning time, and the costs associated with high-performance devices[5].
Looking Ahead
The future of 3D scanning appears promising as the technology continues to evolve. With projections indicating consistent growth in the market, more sectors are likely to realize the benefits of incorporating 3D scanning into their processes. The integration of advanced AI with 3D scanning systems holds the potential to enhance data accuracy further, facilitate better inspection processes, and ultimately streamline production workflows[4][5].
In conclusion, 3D scanning technology is not merely a tool for creating digital models; it is a catalyst for innovation across multiple industries. Its ability to provide precise measurements, facilitate rapid prototyping, and inform design decisions underscores its significance in today's technological landscape. As the technology advances, its applications will undoubtedly expand, offering even greater efficiency and accuracy in capturing the physical world.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Cordless 12V Drill
Essential for drilling and driving screws, perfect for hanging shelves and assembling furniture[1].

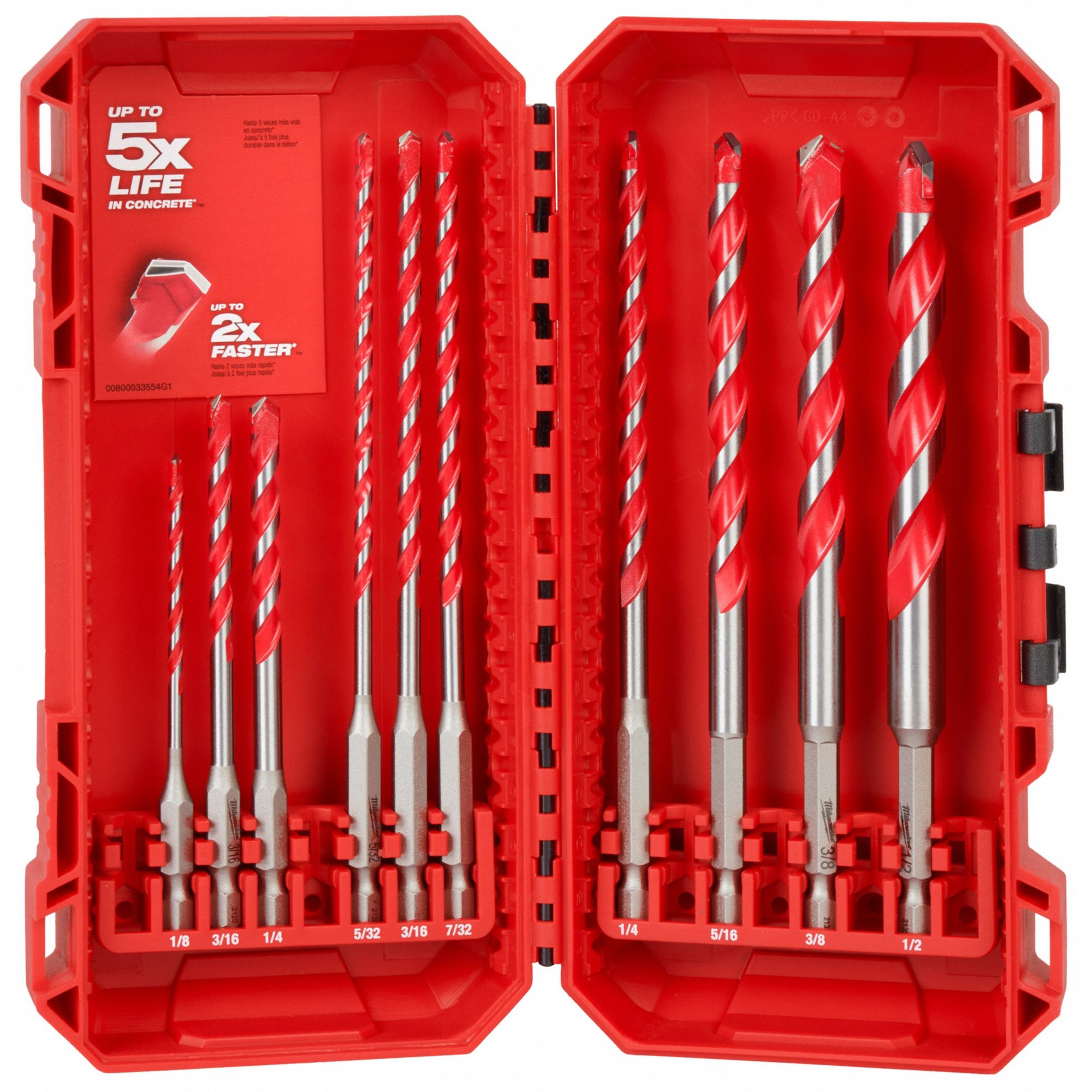
Drill Bit Set
Provides various sizes for different drilling needs, enhancing the capabilities of the drill[3].
Rechargeable Batteries
Necessary for powering cordless tools, ensuring they're always ready to use[1].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.

A novel is considered a classic if it demonstrates a level of quality that allows it to endure through time and remain relevant across generations. Classics often address universal themes—such as love, morality, and human struggle—providing insight that continues to resonate with readers[2][5][6]. Italo Calvino posits that a classic is a book that never exhausts what it has to say to its readers, continually offering fresh perspectives upon each reading[1][6].
Additionally, classics frequently reflect the cultural backdrop of their time, influencing and being influenced by societal norms and values[3][5]. Their ability to evoke deep emotional responses and inspire critical discourse contributes to their lasting significance in literature[4][6].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/TermDefinitions_crypto_final-940e93a6cb5341999a5d735fbf04fbfe.png)
Cryptocurrencies are digital or virtual currencies that utilize cryptography for security, making them difficult to counterfeit or double-spend. They primarily operate on decentralized networks based on blockchain technology—a distributed ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers. This decentralization means that cryptocurrencies are generally not issued by any central authority, which offers a level of immunity from government interference or manipulation[1][3].
Bitcoin, introduced in 2009, is the first and most well-known cryptocurrency. It operates through peer-to-peer transactions, which means that transactions occur directly between users without intermediary banks[2][5]. In essence, every cryptocurrency transaction is recorded on a blockchain, ensuring the integrity and security of the transaction data[1][2].
Although cryptocurrencies were initially envisioned as a medium of exchange similar to fiat currencies, they are now mostly treated as investment vehicles due to their price volatility and potential for appreciation[3][5]. They can be bought and sold on exchanges, or obtained through mining, which involves solving complex mathematical problems to validate and record transactions on the blockchain. In this process, miners can earn new cryptocurrency as a reward for their efforts[2][5].
While there is growing interest in using cryptocurrencies for everyday transactions, their adoption as a common payment method remains limited, with many retailers still not accepting them directly as payment[3][4]. As a result, cryptocurrencies are often viewed as speculative investments rather than functional currencies[4][5].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Globalization, defined as the growing interconnectedness among nations through trade, investment, technology, and cultural exchanges, significantly affects local economies. This interaction intricately weaves together opportunities and challenges that shape economic landscapes worldwide.
Economic Growth and Job Creation
One of the most prominent impacts of globalization on local economies is the potential for economic growth and job creation. As access to international markets expands, local businesses can increase their customer base. This can lead to significant growth opportunities, allowing them to scale operations and hire more employees. For instance, the European Union has highlighted that 'the number of jobs supported directly or indirectly by EU exports outside the union is continuously growing,' demonstrating how trade can undergird local employment levels[4]. Specifically, the increased demand for goods and services from local businesses provides a substantial boost to economic activity, enhancing overall employment rates.
Additionally, globalization encourages the establishment of new industries and improved infrastructure. This is particularly evident in developing countries, where the influx of foreign investments fosters job opportunities and strengthens economic sectors like manufacturing and technology. For instance, companies relocating their operations to lower-cost countries can stimulate employment in those regions, leading to better labor market conditions overall[1][8].
Increased Competition and Innovation

While globalization opens doors for local economies, it also intensifies competition. Local businesses now face rivals from around the globe, necessitating improvements in innovation and efficiency. This dual effect—pressure to innovate alongside expansive market opportunities—forces local businesses to evolve continuously. Firms that adapt to global standards can thrive, while those that cannot may struggle to survive[3].
For example, many local businesses are leveraging technology to enhance transactional efficiency and customer engagement. By adopting new technologies, from supply chain management systems to e-commerce platforms, local enterprises can optimize their operations, reducing costs and increasing customer satisfaction. This digital transformation allows local businesses to compete more effectively against larger multinationals, which frequently dominate global markets[3].
Challenges of Outsourcing and Offshoring
Despite the opportunities presented, globalization can lead to job displacement due to outsourcing and offshoring practices. Local businesses may shift production to countries with lower labor costs, causing employment losses in higher-wage economies. The negative impacts are typically observed in sectors characterized by low-skilled labor, such as textiles and manufacturing, as these industries are more susceptible to competition from cheaper imports[1][4].
These shifts can create regional economic disparities, particularly affecting areas reliant on industries that have relocated. The European Globalization Adjustment Fund was established to help counteract these negative effects, providing support to workers displaced due to globalization-induced changes[4]. Such initiatives underscore the need for targeted policies to navigate the adverse consequences while maximizing the benefits of economic integration.
Wage Dynamics and Inequality

Globalization can exert downward pressure on wages across various sectors. As businesses outsource jobs to countries with lower wage thresholds, local workers may face stagnant or declining wages[1][8]. This has led to increasing income inequality within nations, with a notable wage gap widening between highly-skilled and low-skilled workers. For example, globalization has created significant wage disparities that challenge middle-income, middle-skilled workers in developed economies as they compete with lower-wage workers from emerging markets[2].
Furthermore, while skilled labor tends to benefit from the dynamics of globalization through higher wages, unskilled laborers often find themselves at a disadvantage. The increase in competition from foreign markets can lead to wage stagnation and job insecurity for workers in less competitive sectors, exacerbating financial instability and inequality[1][5].
Cultural Impact and Local Identity
Globalization also has a profound impact on local cultures and identities. As international brands and products infiltrate local markets, there is a risk of cultural homogenization, where local traditions and business practices may become overshadowed by global standards. This cultural shift can dilute local customs and consumer preferences, leading to a loss of local identity[3][9].
However, globalization can also foster a richer exchange of ideas and cultural practices, promoting diversity and inclusivity. Local businesses can leverage unique cultural attributes to differentiate themselves in a crowded market, offering products that reflect local heritage and values, thus creating a niche in the global landscape[3].
Conclusion

In summary, globalization exerts a multifaceted impact on local economies. It provides significant opportunities for economic growth, innovation, and cultural exchange while concurrently posing challenges related to competition, labor displacement, and wage disparities. The dual nature of globalization underscores the importance of comprehensive policies that maximize benefits while mitigating adverse effects. By navigating these complexities effectively, local economies can adapt and thrive in an interconnected world.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Transportation safety is a critical area of governance, involving multiple modes of transport such as aviation, maritime, and road vehicles. Each mode has specific regulatory frameworks to ensure safety standards are met and maintained.
Aviation Safety Regulation
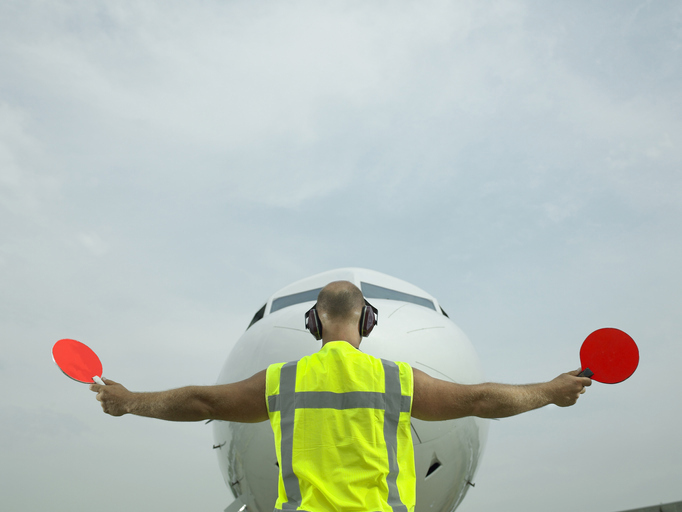

In the aviation sector, safety regulation is primarily overseen by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the United States. The FAA is responsible for establishing and enforcing regulations that govern air travel, including safety standards for aircraft operations, airport safety, and pilot certification. The International Air Transport Association (IATA) emphasizes the importance of sustainability and safety within the industry, indicating that groups such as IATA act as advocates for best practices and standardized safety measures across airlines globally. Their guidelines help airlines implement safety management systems and enhance operational safety, including preparing for emergencies and managing risks associated with air travel[1].
The IATA Annual Safety Report plays a significant role by uncovering aviation safety concerns and developing prevention strategies, ensuring the ongoing enhancement of safety measures in the industry. Statistics illustrate the relative safety of air travel; between 2000 and 2010, the death rate per passenger-mile in commercial aviation was about 0.2 deaths per 10 billion passenger-miles, significantly lower than that of road vehicles, which was approximately 150 deaths per 10 billion vehicle-miles[2].
Road Transportation Safety Regulation

Road transportation safety in the United States is not governed by a singular federal authority but involves various agencies at both federal and state levels. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) oversees vehicle safety regulations, while the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) is charged with regulating commercial vehicle safety. Each state manages its road safety regulations, which can lead to variations in safety standards across the country[2].
In addition to the federal oversight, several organizations contribute to road safety initiatives. The National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) investigates accidents and makes recommendations aimed at improving safety across all modes of transportation. These combined efforts aim to reduce fatalities, which have been a persistent issue, with annual road traffic deaths fluctuating significantly over the years; for instance, there were over 42,000 fatalities in 2022[2]. The disparity in regulations stems from the different risks associated with road versus air travel, making tailored regulatory approaches necessary.
Maritime Safety Regulation
Maritime safety is regulated internationally, primarily through the International Maritime Organization (IMO), which was established to enhance safety standards across global shipping industries. Its first important task was to adopt the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS), which remains one of the most significant treaties addressing maritime safety. The IMO's Maritime Safety Committee oversees the development of regulations and standards relevant to ship safety, the training of seafarers, and protocols for search and rescue operations. The committee's work is supported by sub-committees that focus on specialized areas, such as the carriage of dangerous goods and compliance with international collision regulations[3].
These international regulations are crucial in improving safety at sea, recognizing that shipping is inherently dangerous and requires communal efforts to mitigate risks involved with maritime operations.
Developing Safety Standards Across Modes

Across air, road, and maritime transportation, safety regulation is underscored by adherence to established guidelines and the adoption of modern safety measures. For aviation, the emphasis is on rigorous standards enforced by the FAA and IATA, which promote best practices and operational transparency. In the context of road safety, regulatory frameworks are varied due to state-level governance, but aim at reducing fatalities through strict traffic management and safety oversight. Maritime safety, under the aegis of the IMO, highlights the necessity of international standards in a globally interconnected industry.
The overall trend in transportation safety showcases improvements driven by data collection, accident investigations, and the implementation of technology to enhance safety measures. As standards evolve and adapt to emerging challenges in transportation, the primary focus remains to minimize risks and protect lives across all modes of transportation.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
















:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/MISSHA-Time-Revolution-The-First-Treatment-Essence-RX-da5bb693a0ee46f5ba65d521b9ab4dcb.jpg)

































































