Discover Pandipedia
Pandipedia is the world's first encyclopaedia of machine generated content approved by humans. You can contribute by simply searching and clicking/tapping on "Add To Pandipedia" in the answer you like. Learn More
Expand the world's knowledge as you search and help others. Go you!
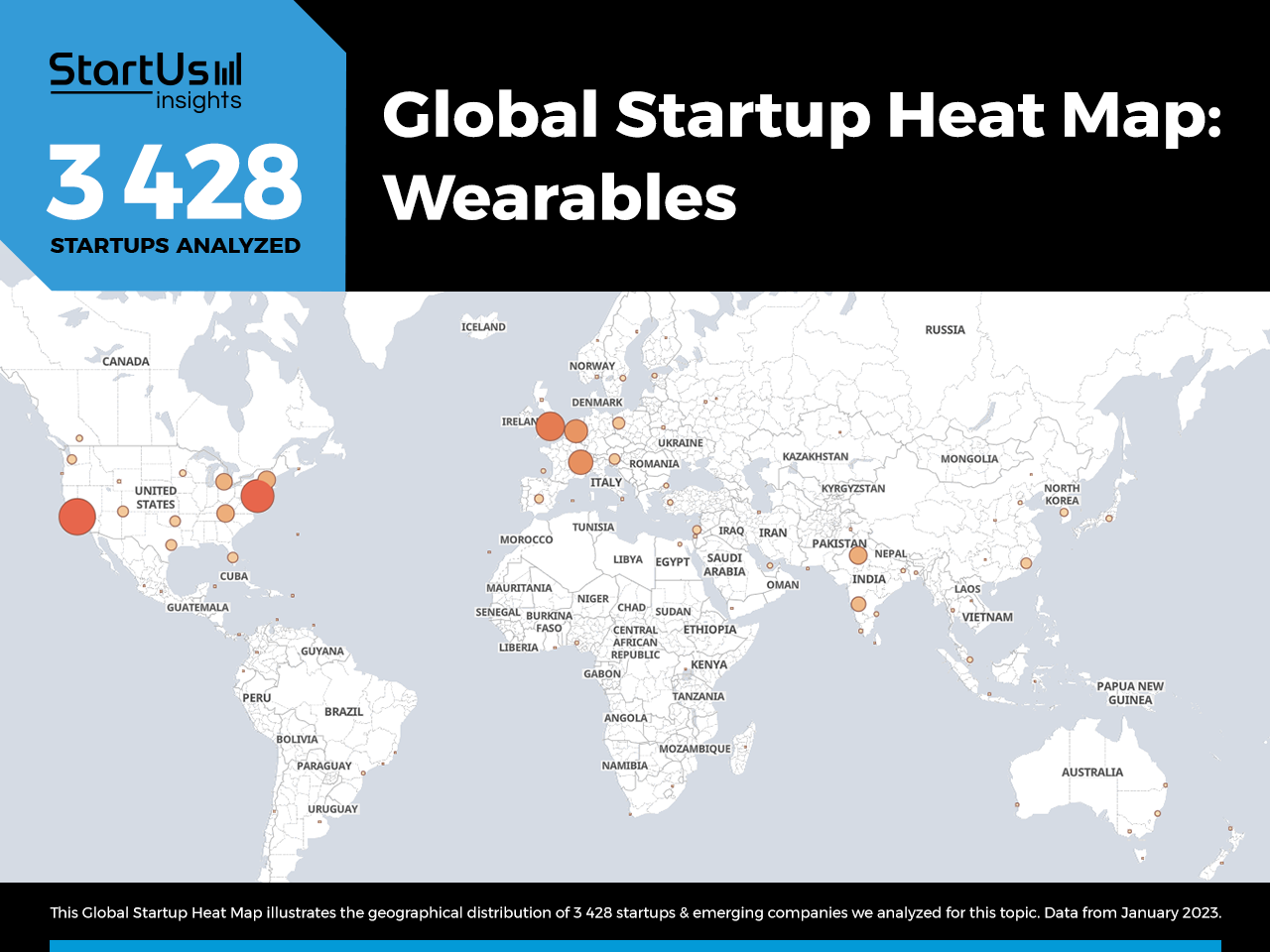
The wearable technology market is evolving rapidly, influenced by advancements in health monitoring, artificial intelligence, sustainable practices, and cross-device integrations. As we look ahead to 2024 and beyond, several key trends are emerging that will redefine how these devices fit into our daily lives.
Enhanced Health Monitoring Capabilities
One of the most significant trends in wearable technology is the continual improvement in health monitoring features. Devices are expected to advance in tracking metrics such as blood pressure, glucose levels, and stress levels. This transition is largely driven by demands for proactive health management, making wearables more like personal health assistants. For instance, smartwatches are anticipated to include non-invasive blood glucose monitoring, which allows diabetics to manage their condition without invasive procedures[4][7]. Additionally, features aimed at detecting sleep apnea and other health conditions are likely to become standard across various wearable devices, enhancing their utility in everyday health management[5][10].
Integration of Artificial Intelligence
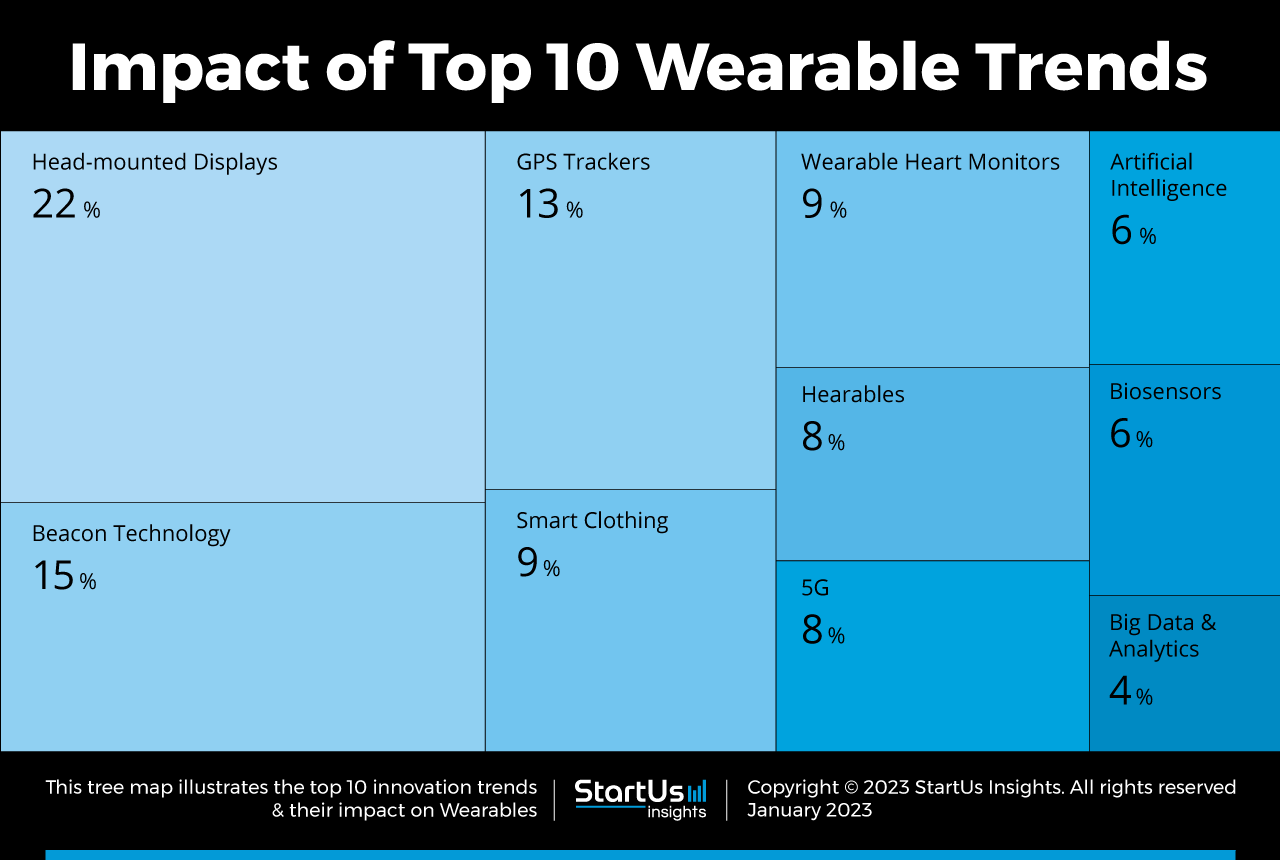
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are poised to play pivotal roles in the future of wearables. With AI-driven insights, wearables can analyze users' health data to provide personalized recommendations. For example, fitness trackers might adapt workout plans based on historical data from users' activity levels and health metrics[8]. AI capabilities will also enhance user experience by improving device interactivity and enabling voice commands, making devices more intuitive and user-friendly[2][7][11].
Smart Fabrics and Clothing
The trend towards smart clothing is gaining significance, with several companies integrating technology directly into apparel. These smart fabrics can monitor various vital signs and deliver real-time feedback, merging the functionalities of traditional wearables with the comfort and style of everyday clothing. Innovations in this area are expected to incorporate sensors that track health metrics unobtrusively, expanding the market for 'smart fashion' significantly in 2024 and beyond[9][11].
Sustainable Practices and Eco-Friendly Materials
5G Connectivity
The rollout of 5G technology is set to further revolutionize the wearables market by enabling faster data transfer and lower latency, facilitating real-time communication and remote monitoring for health management applications. This connectivity will allow wearables to seamlessly integrate with other smart devices within a user’s ecosystem, enhancing their functionality[2][8][11]. The integration of wearables into smart home systems could allow users to control their environments with greater ease, making technology more accessible and integrated into daily routines.
Expansion in the Pet Wearables Market
Alongside human application, the wearables trend is expanding into the pet market. Devices focused on health tracking for pets are set to become more prevalent, targeting owners who want to monitor their animals' health metrics in real time. This emerging segment showcases the versatility of wearable technology and its potential to cater to new demographics and market needs[5][11].
Growing Importance of Mental Health Tracking
As awareness of mental health issues increases, wearables are likely to incorporate features aimed at tracking mental well-being. Devices may soon offer functionalities such as stress tracking, sleep quality assessment, and even alerts for potential mental health issues, thereby broadening the scope of health metrics that these wearables can monitor[3][4]. This capability aligns with a growing consumer demand for holistic health management tools.
Legal and Regulatory Challenges
With the advancement of wearable technology comes the challenge of regulatory compliance. Companies will face scrutiny regarding data privacy and security as wearables increasingly collect sensitive personal health data. Legal disputes over technology rights and patents, such as those involving major players like Apple and other tech companies, are anticipated to shape the landscape of wearable tech in 2024 and beyond[8][9]. Compliance with regulations, such as FDA approvals for health-monitoring functionalities, will also become critical as wearables broaden their health applications.
Conclusion
The future of wearable technology promises significant advancements in health monitoring, sustainable practices, and smart integrations with daily life, emphasizing the importance of AI and user personalization. As trends continue to evolve, these devices are set to become even more integral to our health management and daily routines, contributing to improved quality of life and enhanced connectivity across various aspects of modern living.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.
The fediverse, short for 'federated universe,' is a decentralized network of interconnected social media platforms that communicate with each other using a common protocol called ActivityPub. It allows users to interact and share content across different platforms while retaining control over their data and identities. Essentially, users can have an account on one service and post on others, similar to how email works across different providers[3][5][6].
The fediverse aims to provide an alternative to traditional social media, which is dominated by large tech companies that control user data and privacy. In the fediverse, content is not locked into a single platform; instead, users can transfer their posts, likes, and comments between various apps[2][3]. For example, a user on Mastodon can interact with posts from other federated platforms like Pixelfed or PeerTube[1][3][4].
One of the main benefits of the fediverse is that it offers stability, as users are not at the mercy of any single platform's policies or changes. This also addresses the issue of platform lock-in, allowing users to freely migrate their content and communities as needed[3][4][6]. With a variety of applications like Mastodon, Pixelfed, and PeerTube participating, the fediverse represents a move towards a more open and user-controlled social media landscape[1][5][6].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Historical Overview of Sleep Patterns

In the Middle Ages, sleep was commonly divided into two segments known as 'first sleep' and 'second sleep'. People typically went to bed shortly after dusk, around 9 PM, and each sleep phase lasted approximately four hours, followed by a natural waking period which often lasted about an hour. This waking time, referred to as 'the watch', allowed for various activities like prayer, socializing, or tending to household chores[1][7]. Historian Roger Ekirch, who researched these sleeping habits, discovered that this biphasic sleep pattern was not solely a medieval quirk; it was a widespread practice seen globally, from Europe to Africa and Asia, and has roots in prehistoric sleep behaviors[1][2][8].
Activities During the Watch

During the watch, individuals would engage in a variety of tasks. For many, this time was utilized for religious observance, such as reciting prayers. Medical texts from the time even advised that this interval was suitable for reflection and intimate activities between couples, suggesting that it was seen as a 'profitable hour'[5][8][10]. In addition to personal activities, practical tasks were commonplace; people often checked firewood supplies or shared moments of conversation with fellow bedmates, emphasizing the communal nature of sleeping arrangements[3][4][7].
Cultural Influence on Sleep Practices

Cultural factors greatly influenced sleeping habits during the Middle Ages. For instance, religious practices ingrained the idea of waking up to pray, particularly among monks who would rise for Matins around 2 AM[10]. The influence of solar patterns led to sleep strategies aligning with natural light cycles, which differed significantly in preindustrial societies compared to the later industrialized world[1][3]. Additionally, many medieval texts and literature, including Geoffrey Chaucer's "The Canterbury Tales", reflect the regularity of this biphasic sleep practice, indicating its acceptance in society[2][7].
Transition to Continuous Sleep Patterns
By the early 19th century, the Industrial Revolution marked a significant shift in societal sleep patterns. The introduction of artificial lighting, such as gas and later electric streetlights, led to people staying awake longer in the evening, thus condensing the traditional two-phase sleep into a single longer shift. This development gradually phased out the natural waking periods that had defined sleep for centuries[1][8]. The normalization of continuous sleep ultimately shaped modern perceptions of sleep, where uninterrupted rest is now deemed ideal, even amidst rising complaints of insomnia related to these changes[5][6].
Sleep and Social Status
Sleeping arrangements diverged significantly based on social status during the Middle Ages. Wealthier individuals were more likely to enjoy the comfort of feather-stuffed mattresses and private sleeping chambers, while the lower classes often shared beds with multiple family members or slept on less comfortable surfaces like straw[9]. The communal nature of sleeping not only facilitated social bonds but also illustrated the stark contrasts in living conditions based on wealth and social hierarchy[4][7].
Modern Reflections of Historical Sleep Patterns
Interestingly, remnants of biphasic sleep persist in some cultures today. Certain societies in the Mediterranean and Latin America maintain practices akin to "siestas" or daytime naps which share a conceptual lineage with the historical dual-sleep system[6][8]. Research continues to explore the relevance of these ancient sleeping patterns in addressing modern sleep disturbances, suggesting that a return to such natural rhythms could benefit contemporary society, especially for those suffering from insomnia[4][6][7].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Fog-signals may be produced by sound[1]. A number of methods for producing sound have been used, including bells, gongs, guns, rockets, whistles and sirenes. Bells and gongs are struck to create sound; guns and rockets make a sound via explosions[1]. Whistles and sirens use steam or compressed air to produce continuous sound[1]. Distinctions in sound can be created through differing notes or patterns of sound production[1].
''Automatic meter for producing Intermittent Lights hythe flow oftheGas[1].''
''Crymhals forpreserving theVerticality ofBuoy Light
Apparatus[1].''
''A
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Core Process Overview

AI humor models generate captions for images through a complex process that mimics human cognitive and creative skills[2]. This involves several key steps, often including visual detail extraction, humor ideation, narrative extrapolation, and caption ranking[2][3]. By integrating creative, social, and cognitive skills, AI-generated humor aims to produce communication that resonates with people[2].
Visual Detail Extraction
The initial stage involves a detailed analysis of the input image using visual language models (VLMs) such as GPT-4o[3]. This component extracts key visual elements, including objects, human expressions, and background settings[3]. The AI identifies the subject, main action, and background elements to build a foundation for humor[3]. For example, in an image of a demolition site, the system identifies a large industrial excavator and a person spraying the site with a hose[3].
Humor Ideation and Angle Selection
After extracting visual details, the system ideates on potential humorous elements[3]. This involves identifying funny facial expressions or analogous elements within the image[3]. The system analyzes the image and proposes humorous angles, considering both direct and indirect humorous aspects[3]. For instance, the visual contrast between an excavator and a person might be interpreted as a David versus Goliath scenario, providing a foundational metaphor for generating humorous captions[3].
Narrative and Conflict Extrapolation
To add depth and relatability, AI models often extrapolate narratives and conflicts that draw upon common and relatable experiences[3]. This step connects the visual elements with broader life experiences, making the humor more accessible[3]. The system chains together the results of the previous steps into a new prompt sent to GPT-4o[3]. The prompt contains the visual details, the visual humor ideation, and a list of common Gen Z experiences, and the instruction to 'generate narratives that reflect the essence of the image that is set within the framework of the Gen Z experience'[3]. These narratives are generated based on common experiences such as work, school, family, and relationships[3]. For example, a demolition site image might generate narratives like 'Tackling student loans' or 'Group Project Disaster,' which are common among Gen Z[3].
Caption Generation
In this stage, the system generates humorous captions using a fine-tuned language model[3]. A fine-tuned version of GPT-3.5 trained on humorous Instagram comments is often employed[3]. The captions are generated through two distinct strategies: focusing on the visual humor of the image and incorporating external narratives[3]. Image-focused captions comment directly on the image content, while narrative-driven captions introduce external references to add humor[3]. For example, an image-focused caption might be, "bro out here getting paid $8 an hour to spray some water on some bricks," while a narrative-driven caption could be, "The entitled bro you tried to make the group presentation with"[3]. Caption generation is segmented into two separate prompts utilizing the fine-tuned GPT-3.5 model[3].
Caption Ranking and Filtering
The generated captions are then ranked and filtered to select the most effective ones[3]. A GPT-4o-based agent, fine-tuned to evaluate humor from a Gen Z perspective, assesses the captions based on humor, relatability, and alignment with the image and narrative[3]. This agent filters out captions that do not meet the humor threshold, ensuring that only the most relevant and relatable captions are presented[3]. For example, captions like 'Me mopping up my last relationship' might be favored over less relatable ones[3].
Fine-Tuning and Training Data
Fine-tuning is crucial for tailoring the AI model to generate relevant and engaging humor[3]. This involves training the model on datasets of humorous comments and captions[3]. For example, a GPT-3.5 model can be fine-tuned using a dataset of humorous Instagram comments to better capture Gen Z humor[3]. The quality and quantity of the training data play a significant role in the performance of the model[1].
Specific AI Techniques
Several AI techniques are utilized in this process, including prompt engineering, fine-tuning, and chain-of-thought processing[2]. Prompt engineering involves crafting prompts that clearly define the problem and expected output[2]. Fine-tuning allows the model to learn specific patterns of a target output type[2]. Implicit in this is the tone, the style, and the vocabulary expected in the humor[2]. Chain-of-thought processing helps models by explicitly detailing the steps[2]. Chains are used to separate stages of the humor generation process[2]. An observation stage makes implicit information in images explicit, similar to the spirit of chain-of-thought and thought experiments[2].
Utilizing User Preferences & Cultural Nuance

AI models can analyze user preferences, interests, and even their sense of humor to generate tailored jokes[1]. One approach to achieving this personalization is by leveraging collaborative filtering techniques, which are commonly used in recommendation systems[1]. This involves identifying users with similar tastes and recommending jokes that have been enjoyed by those users[1]. By combining state-of-the-art AI techniques with a deep understanding of human psychology and humor, AI-generated comedy is revolutionizing the way we create and consume humor[1]. Cultural context also plays a significant role with Wu et al. (2024) revealing significant differences in humor perception between Western and Eastern cultures[3].
Challenges and Considerations
Despite advancements, AI-generated humor faces challenges, including the need for ethical considerations and the difficulties in replicating human-like social skills[2][1]. Ensuring inclusive and non-offensive humor is critical, as AI models are trained on large datasets that may contain biased or offensive content[1]. Intellectual property and joke ownership also become complex as AI-generated humor gains prominence[1]. As AI models improve, they may have the potential to both disingenuously create human bonding and to augment human’s ability to bond, carrying the potential to change the nature of human trust and communication[2].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Introduction to Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) are a powerful class of neural networks designed to handle sequential data, achieving state-of-the-art performance in tasks such as language modeling, speech recognition, and machine translation. However, RNNs face challenges with overfitting, particularly during training on limited datasets. This led researchers Wojciech Zaremba, Ilya Sutskever, and Oriol Vinyals to explore effective regularization strategies tailored for RNNs, specifically those using Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) units.
The Problem of Overfitting in RNNs
Overfitting occurs when a model learns not only the underlying patterns in the training data but also the noise, leading to poor generalization on new, unseen data. Traditional regularization methods like dropout have proven effective for feedforward networks but are less effective for RNNs due to their unique architecture. The paper highlights that standard dropout techniques do not appropriately address the recurrent nature of LSTMs[1].
Introducing Dropout for LSTM Regularization
The authors propose a new way to implement dropout specifically for LSTMs. The key idea is to apply dropout only to the non-recurrent connections in the LSTM units, while keeping the recurrent connections intact. This approach helps preserve the long-term dependencies crucial for RNN performance. The dropout operator function, denoted as D, is implemented to randomly set a subset of its inputs to zero, effectively allowing the model to generalize better during training[1].
In mathematical terms, the proposed model maintains the essential structure of LSTMs while introducing the modified dropout strategy, which prevents the model from discarding vital information over multiple time steps[1].
Experimental Setup
The research incorporates extensive experimentation across different domains such as language modeling and image caption generation. For language modeling, the authors utilized the Penn Tree Bank (PTB) dataset, which consists of roughly 929k training words. They experimented with various LSTM configurations, ranging from non-regularized to several levels of regularized LSTMs. Results showed significant improvements in performance metrics, particularly in the validation and test sets, when applying their proposed dropout method[1].

In speech recognition tasks, the paper documented the effectiveness of regularized LSTMs in reducing the Word Error Rate (WER), thereby demonstrating the advantages of their approach in practical applications[1].
Results and Findings
The paper's results are telling. For instance, they found that regularized LSTMs outperformed non-regularized models on key performance indicators like validation and test perplexity scores. Specifically, the medium regularized LSTM achieved a validation set perplexity of 86.2 and a test set score of 82.7, highlighting the capacity of the proposed dropout method to enhance model robustness[1].
Further, in tasks involving image caption generation and machine translation, the regularized models exhibited improved translation quality and caption accuracy. This suggests that applying dropout effectively can lead to better long-term memory retention, crucial for tasks requiring context and understanding over extended sequences[1].


Conclusion
The exploration of dropout as a regularization technique specifically tailored for LSTMs underscores its potential to improve performance across various tasks involving sequential data. The findings validate that applying dropout only to non-recurrent connections preserves essential memory states while reducing overfitting. As a result, RNNs can achieve better generalization on unseen datasets, ultimately leading to enhanced capabilities in language modeling, speech recognition, and machine translation. This research not only addresses a critical gap in the application of regularization techniques but also offers practical implementation insights for future advancements in deep learning frameworks involving RNNs[1].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Oxytocin, often referred to as the 'love hormone,' has gained attention for its potential therapeutic effects, particularly when delivered via a nasal spray. This report synthesizes current research into the benefits and drawbacks associated with the use of oxytocin nasal spray.
Potential Benefits
Improvements in Social Interaction

The administration of oxytocin nasal spray has been linked to enhancements in social behaviors. Studies indicate that oxytocin can facilitate trust, bonding, and empathy, which are crucial for interpersonal relationships. For instance, it has been found to increase positive social interactions, helping individuals become more generous and willing to trust others, even strangers[3][4]. This hormone may also promote fidelity within monogamous relationships by reducing attraction to others[1].
Therapeutic Effects in Specific Populations
There is some evidence suggesting oxytocin's effectiveness in treating social deficiencies, particularly in children with autism. Studies have shown that young children receiving oxytocin demonstrated significant improvements in social responsiveness after treatment[1][2]. Furthermore, it has been noted that children with lower baseline oxytocin levels may benefit the most from the nasal spray[7].
Stress and Anxiety Reduction
Oxytocin nasal spray may possess anxiolytic properties, potentially reducing anxiety and stress levels during social interactions. Some studies revealed that it helps in decreasing defensive behaviors associated with anxiety, thus fostering a more positive communication atmosphere, especially in romantic relationships[4][5]. The spray’s effects on stress reduction have been primarily noted in couples during conflicts, leading to improved communication dynamics[4].
Neurocognitive Enhancements
The nasal spray may improve social cognitive abilities by facilitating the recognition and processing of social cues. Research shows that oxytocin enhances attention toward social stimuli, thereby increasing the ability to correctly appraise social contexts and emotional expressions[3][6]. This action may be particularly beneficial for individuals experiencing social cognition deficits due to conditions like autism or PTSD[11].
Overall Safety Profile
Initial findings indicate that oxytocin nasal spray does not have a significant number of adverse effects when compared to placebo treatments in clinical settings[5][3]. This relative safety profile can make it an attractive alternative to traditional medications for mental health issues, which often come with a broader range of side effects[3].
Drawbacks and Concerns
Variable Individual Responses
One of the significant drawbacks of oxytocin nasal spray is the variability in response among individuals. The effects of oxytocin can differ markedly from one person to another, influenced by personality traits and situational variables. In some instances, the administration of oxytocin has been associated with negative behaviors such as increased envy or reduced cooperation[4][1]. This variability complicates the predictability of treatment outcomes.
Limited and Inconsistent Research
While preliminary studies suggest benefits, extensive research on oxytocin's efficacy is limited, and findings can be inconsistent. Many studies tend to focus on specific conditions like social anxiety or postpartum depression, which may not encompass a wider range of anxiety disorders or psychiatric conditions[3][5]. Additionally, some investigations report minimal or no significant benefits, emphasizing the need for more robust and comprehensive clinical trials to establish definitive efficacy[3][11].
Short-Term Effects and Methodological Issues
Research often focuses on the acute effects of a single-dose administration of oxytocin, leading to concerns that long-term benefits may be limited or non-existent. Studies have also revealed problems with methodological designs, such as small sample sizes and reliance on subjective measures of social responsiveness, which may skew results and affect reproducibility[2][3].
Possible Negative Social Effects
Emerging literature suggests that oxytocin could inadvertently cause adverse outcomes in certain contexts. For example, it has the potential to decrease the ability to identify risks in trusting relationships, which could lead to negative interpersonal dynamics if used without careful consideration[4][3]. Furthermore, there are reports suggesting that long-term use may cause impairments in behavioral patterns associated with social interactions in animal studies, raising concern for human applications[8].
Ethical Considerations
The administration of oxytocin nasal spray raises ethical questions regarding informed consent and autonomy, particularly in relationship dynamics. Individuals must independently agree to treatment without any coercion, as imbalances in autonomy could lead to misuse or unwanted pressure to engage in the treatment[4].
Conclusion

Oxytocin nasal spray holds promise as a therapeutic agent for enhancing social behavior and reducing anxiety, especially in specific populations such as children with autism. However, its variable effects, limited research foundation, and potential for adverse social consequences necessitate caution. More comprehensive studies are crucial to ascertain the long-term efficacy and safety of oxytocin nasal spray, while also addressing the ethical implications related to its use. As research progresses, the hope is that a clearer understanding of oxytocin’s effects will emerge, guiding its application in clinical practice.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25270802/247011_Fediverse_Explainer_final_CVirginia.jpg)