Discover Pandipedia
Pandipedia is the world's first encyclopaedia of machine generated content approved by humans. You can contribute by simply searching and clicking/tapping on "Add To Pandipedia" in the answer you like. Learn More
Expand the world's knowledge as you search and help others. Go you!
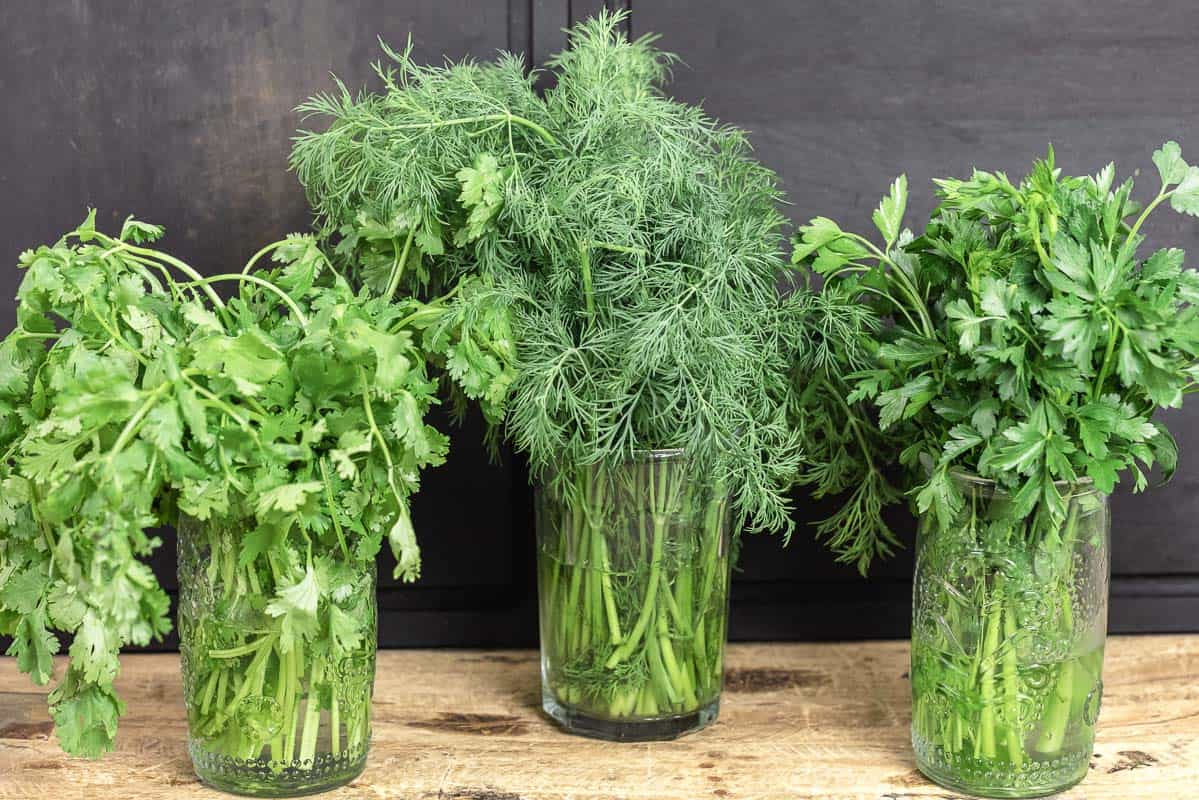

The best way to store fresh herbs depends on whether they are soft or hardy. For soft herbs like parsley and cilantro, wash them in cool water, dry thoroughly, trim the stems, place them upright in a glass of water, cover the leaves with a bag, and refrigerate. Change the water every few days for optimal freshness[1].
Hardy herbs like rosemary and thyme should be washed, dried, then wrapped in damp paper towels and stored in a ziplock bag in the fridge. Properly stored soft herbs can last from 10 days to 2 weeks, while hardy herbs may last up to 3 weeks[2].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Apple MacBook Air M3
Lightweight, durable laptop ideal for remote work, featuring the powerful M3 chip, ensuring reliability on-the-go[1].
Portable Wi-Fi Hotspot
Essential for reliable internet access anywhere. The Simo Solis Lite is compact and offers multiple functionalities[1].
Sony WH-1000XM5 Headphones
Industry-leading noise-canceling headphones, exceptional sound quality, and battery life, perfect for blocking distractions while working remotely[1].
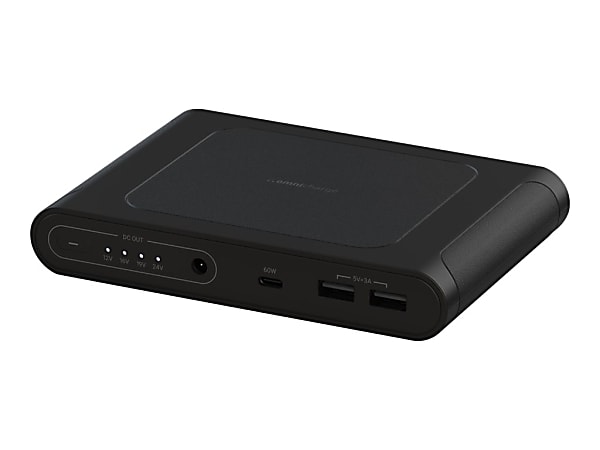
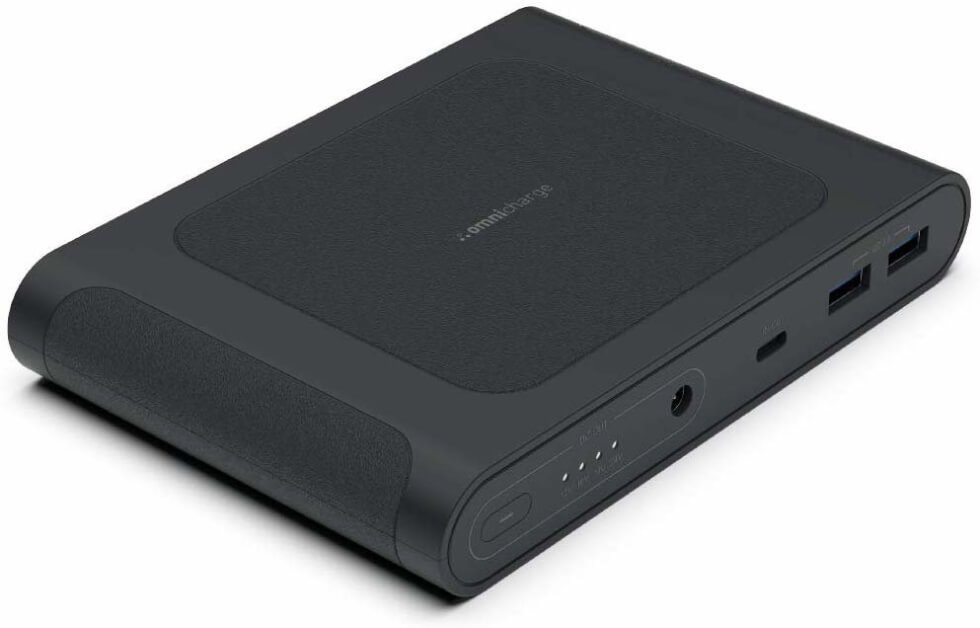
Omni Mobile 25600 Power Bank
High-capacity portable charger for devices, supports multiple outputs and wireless charging, ideal for digital nomads[1].
MOGICS Bagel Travel Adapter
Universal travel adapter with multiple outlet types and built-in fuse, perfect for charging devices worldwide[1].
Asus ProArt Display PA148CTV1
14” portable laptop monitor that offers a dual-screen setup for enhanced productivity while traveling[1].
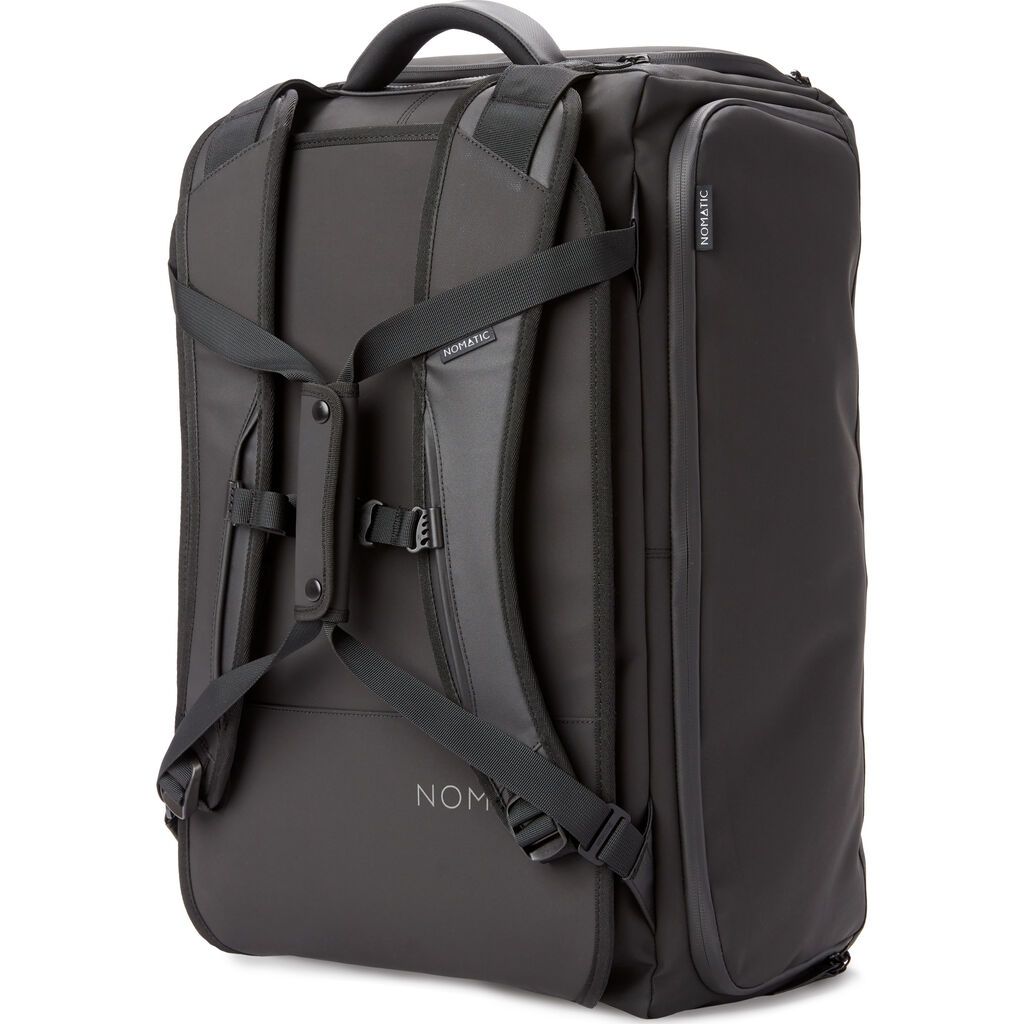
Nomatic Travel Bag (40L)
Highly-featured backpack for digital nomads with multiple organizational pockets and compartments, perfect for minimalist travel[1].
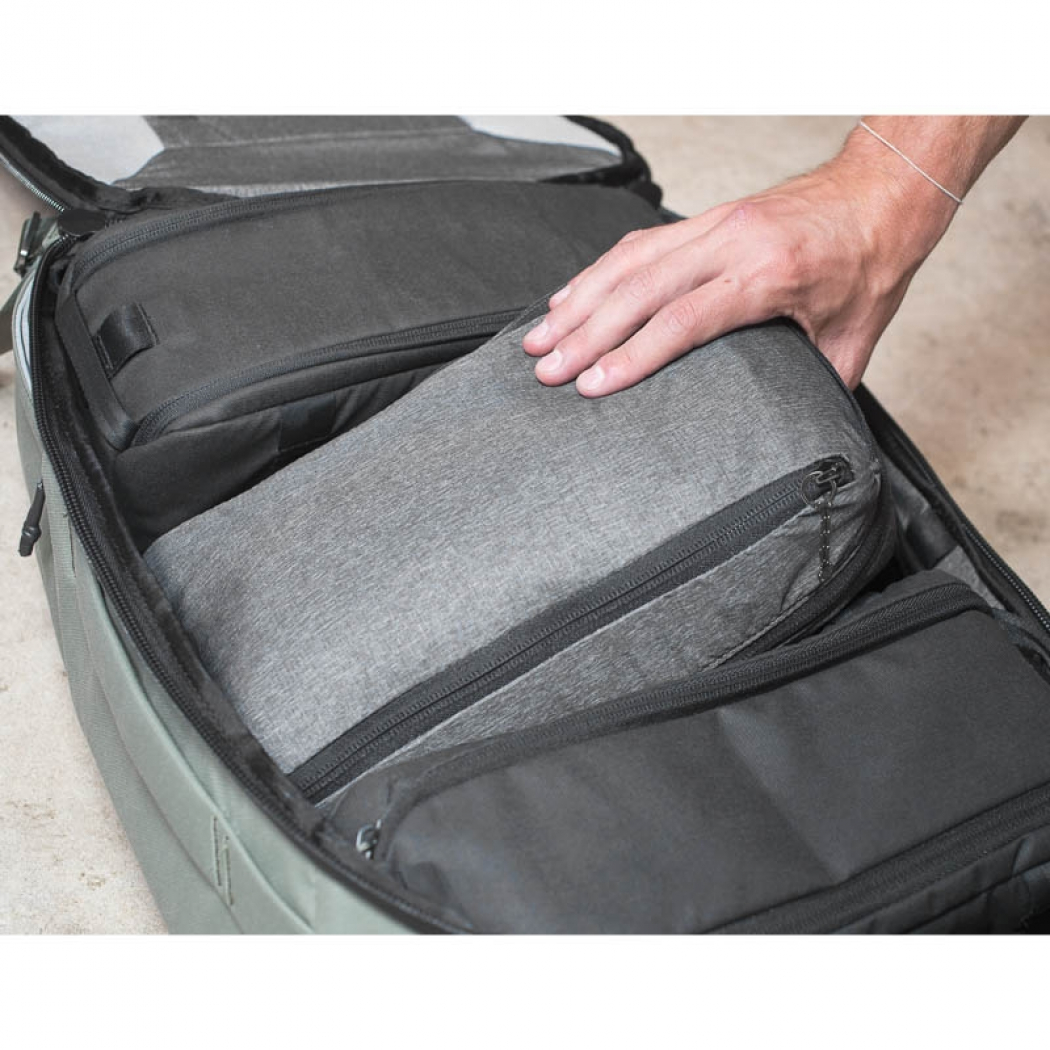
Peak Design Packing Cubes
Quality compression packing cubes for organizing clothing and other items in your backpack[1].

Kindle Paperwhite
Lightweight, water-resistant e-reader, perfect for digital nomads who love reading while traveling[2].
Anker Powercore Portable Charger
Reliable power bank, capable of charging multiple devices multiple times, essential for busy days on the road[2].
GlocalMe G4 Pro Mobile Hotspot
Ultra-slim global wifi hotspot provides reliable internet access, essential for digital nomads traveling to various locations[2].
Seagate Portable 2TB External Drive
Provides backup storage for documents, photos, and videos, ensuring data safety while on the move[2].
NordVPN Subscription
VPN service to ensure secure internet access on public networks, crucial for digital nomads[2].
Drimsim eSIM
Global mobile service provider, allows you to keep one phone number and use data across many countries[2].
Universal Travel Adapter (Ceptics Kit)
Includes several plug types for various countries, ensuring you can charge your devices anywhere[2].
Loop Switch Earplugs
Reusable earplugs with customizable tips and sound modes, essential for noisy travel environments[1].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.
Implications of Warren Buffett's Berkshire Hathaway Selling Half Its Apple Stock

Warren Buffett’s decision for Berkshire Hathaway to sell nearly half of its stake in Apple Inc. has far-reaching implications, highlighting a shift in investment strategy and raising questions about the future of both companies. Here, we explore the various dimensions of this significant financial maneuver.
Shift in Investment Strategy
The sale of nearly 390 million shares resulted in a reduction of Berkshire's Apple holdings from $174 billion to approximately $84 billion, signifying a substantial shift in Buffett's typically long-term investment philosophy. This action represents the seventh consecutive quarter in which Berkshire sold more equities than it purchased, suggesting a perhaps cautious or strategic pivot in how Buffett approaches his investments, particularly in the tech sector[3][5].
Buffett has also previously indicated a pattern of trimming his Apple stake, having reduced it by 13% in the first quarter, which hints at a broader reevaluation of how Berkshire positions itself in the technology market and is potentially affected by concerns about Apple’s growth prospects[2][5].
Increased Liquidity and Cash Reserves
Following this substantial sale, Berkshire’s cash reserves rose dramatically to nearly $277 billion, up from $189 billion in the first quarter. This increase in liquidity may signal that Berkshire is preparing for future investment opportunities or acquisitions. Indeed, Buffett has mentioned he is on the lookout for significant acquisitions but is cautious and waiting for conditions that present low-risk, high-reward opportunities[4][8]. The surge in cash reserves serves as a buffer against market uncertainty while allowing for potential strategic moves in the future.
Market Perception and Stock Valuation Concerns
Berkshire's divestment from Apple could also impact broader market sentiments regarding the tech giant. Historically, Buffett’s investments have influenced other investors and market trends. His recent actions suggest a potential loss of confidence in Apple, which has seen declining growth rates and substantial challenges, particularly in markets like China[6]. As a major investor in Apple, Buffett's shift away from the company could lead other stakeholders to reevaluate their positions, potentially driving down the stock's valuation further.
Additionally, Apple's struggles to deliver compelling innovations, particularly in the face of increasing competition in artificial intelligence, raise concerns regarding its market position and growth trajectory. The implications of these challenges are amplified by Buffett's sell-off, as he is known for his conservative approach to high valuations and volatile market conditions[5][6].
Tax Strategy Considerations
Buffett’s sales appear to be aligned with considerations regarding potential increases in capital gains tax. His comments at the annual meeting suggested that he views selling part of his stake as a way to benefit Berkshire shareholders in the long run, should tax rates change in the future. This strategic move to liquidate 'a little Apple' amidst favorable market conditions may also reflect Buffett's philosophy of profit-taking while the market is strong[4][5].
Broader Market Context
This significant divestment coincides with a broader market correction, particularly impacting the tech-heavy Nasdaq Composite, which has recently experienced a downturn. Analysts suggest that the scale of Berkshire's sales could signal a broader sell-off trend among investors in tech stocks, which have been subject to increased volatility in light of global economic uncertainties, including rising unemployment rates and concerns regarding monetary policy decisions by the Federal Reserve. This environment adds layers of complexity to Buffett's decision-making and investment approach[7][8].
Future of Berkshire Hathaway's Portfolio

Despite the reduction in its Apple stake, the tech giant remains the largest investment within Berkshire's portfolio, underscoring the paradox in Buffett's strategy—while he has sold off a significant portion, he continues to maintain a substantial position. The recent moves within Berkshire’s portfolio, which has seen its allocation in publicly traded stocks decline from 63% to 53%, suggest a strategic pivot towards greater liquidity and caution amid perceived market volatility[6][8].
Conclusion
Warren Buffett’s significant reduction in Berkshire Hathaway's holdings in Apple reflects a complex interplay of market dynamics, liquidity management, and strategic foresight in uncertain economic conditions. While it raises eyebrows regarding Apple’s future growth potential, it also underscores Buffett's cautious yet adaptable investment philosophy. By prioritizing liquidity and maintaining important stakes in select companies, Berkshire Hathaway is positioning itself for possible future opportunities, even as it navigates the shifting landscape of technology investments.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
DIY Birdhouse
A simple beginner project helping to learn the essential woodworking skill of box building[2].
DIY Book Rack
A very easy project that requires cutting a few boards to length and screwing them together[2].
Wooden Coasters
Simple square cutouts that can be finished with polyurethane, making them beginner-friendly[2].
DIY Charcuterie Board
A wooden serving tray that can be shaped with a jigsaw and sealed for food safety[2].
DIY Earring Holder
A basic project using frames that fit within one another, customizable for vertical or horizontal display[2].
DIY Bird Feeder
Requires minimal tools and is easy to make with basic supplies like wood and screws[2].
DIY Key Holder
Features hooks for organizing keys and shelves for small items, easily made in an afternoon[2].
DIY Easy Step Stool
A simple project to help reach higher shelves, requiring common woodworking tools[2].
DIY Cutting Board
An essential kitchen item that beginners can easily craft using untreated hardwood[6].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Character development in long-running series is executed through several key strategies. First, creators establish clear archetypes for characters, allowing audiences to connect quickly and facilitating their growth over time. This is evident in shows like “SpongeBob SquarePants,” where character dynamics are defined early on[1].
Additionally, maintaining continuity while allowing evolution poses challenges, as characters must grow in response to new experiences without deviating too far from their established traits[2]. Producers often introduce new storylines and deepen existing characters' backgrounds to ensure ongoing development and prevent stagnation, thereby keeping the narrative engaging and relatable[1][3].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.

Early light-houses had problems with using coal fires, and mirror-glass reflectors[1]. The use of coal-fireshad been laidaside, and oillights, with reflectors, had been introduced[1]. The mirrors were made of glass, but a better design employed sheets of copper coated with silver[1]. The older light-houses were made of wood, which was shut off from the air and dried to the state of tinder[1].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
The fascination with seemingly simple, yet oddly satisfying content on platforms such as social media and video-sharing sites raises intriguing questions about human psychology and neuroscience. This report synthesizes insights from various research articles to explore the neural mechanisms and psychological frameworks that explain why people are drawn to such content.
The Neuroscience of Pleasure
At the core of enjoying satisfying content lies the neurobiology of pleasure. Researchers Kringelbach and Berridge (2010) propose that pleasure is not merely a sensation or thought but is the result of specific brain activities in dedicated 'hedonic systems' located throughout the brain. These systems are involved in processing a range of pleasures, from basic sensory enjoyment—such as food and sex—to higher-order pleasures like artistic appreciation and altruism. The hedonic hotspots primarily include subcortical structures such as the nucleus accumbens and the ventral pallidum, as well as cortical areas including the orbitofrontal cortex, known for coding subjective experiences of pleasure[1][2].
The neural systems activated during pleasurable experiences also demonstrate significant overlap between simple sensory pleasures and more complex emotional rewards. For instance, similar circuits are engaged when one experiences joy from eating a favored dessert as when appreciating beautiful art[1][2]. This overlap suggests that the appeal of satisfying videos—such as those showcasing the mixing of colors or the perfection of a well-executed task—exploits the same neural pathways that govern sensory pleasure.
Psychological Channels of Enjoyment

The enjoyment derived from satisfying content may also stem from its ability to harness an individual's desire for emotional regulation and mood enhancement. According to mood management theory, people often seek media that helps them manage their emotional states, whether to amplify positive feelings or to distract from negativity[3][4]. This aligns with findings that shared experiences, which often do not yield a significant increase in enjoyment, are chosen primarily for the social connection they provide rather than their direct hedonic benefit[6].
Additionally, the appeal of these materials can be linked to the concept of Autonomous Sensory Meridian Response (ASMR). This is characterized by a tingling sensation some experience in response to specific auditory or visual stimuli, leading to profound relaxation[3]. Many satisfying videos, such as those featuring techniques in painting or crafting, create an ASMR effect through their rhythmic, meticulous movements and nuanced sounds, eliciting similar responses in viewers.
Social Connection and Shared Experiences
The human inclination toward shared experiences is profoundly tied to the drive for social connection. Psychology research supports the idea that shared moments amplify enjoyment and emotional responses[6]. Indeed, Keedy (2021) suggests that engaging with others, albeit virtually, satisfies an intrinsic need for connection—a motive that can outweigh any hedonic value derived from the experiences themselves. Individuals will often choose to share experiences not necessarily for the enjoyment but to foster meaningful social bonds[6].
Interestingly, Boothby et al. (2014) found that participants who shared experiences of both enjoyment and sorrow reported feeling those emotions more intensely compared to when they experienced those emotions alone. However, this increase did not always correspond with higher reports of enjoyment[6]. This indicates a complex relationship where social interaction enhances emotional experiences without necessarily improving personal enjoyment.
Aesthetic Preferences and Evolutionary Influences

The phenomenon of finding pleasure in orderly and aesthetically pleasing visuals is thought to be tied to evolutionary psychology. Humans may have developed preferences for symmetrical patterns and beautiful forms as a survival advantage, as these traits are often associated with health and viability[3]. Satisfying videos often include elements of symmetry and finesse, invoking a primal appreciation for balance and beauty that many find universally appealing, further driving engagement with content that delivers that “just right” feeling.
Conclusion
The science behind why we enjoy satisfying content encompasses a combination of intricate neurological, psychological, and evolutionary factors. Pleasure pathways engage both basic and complex emotions while shared experiences foster connections, amplifying feelings of joy and togetherness. Ultimately, the engagement with this type of content serves not solely as a fleeting distraction but as a means to fulfill deeper psychological needs for pleasure and social connection. As our understanding of these dynamics grows, so too may our appreciation for the simple content that allows us to experience pleasure in its many forms.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
The hottest planet in our solar system is Venus. Despite being the second planet from the Sun, Venus has an average surface temperature of approximately 864 degrees Fahrenheit (462 degrees Celsius), which is hot enough to melt lead. This extreme heat is primarily due to its thick atmosphere, composed of 96% carbon dioxide, which creates a runaway greenhouse effect that traps heat[1][3][6].
In contrast, Mercury, the closest planet to the Sun, is not the hottest, as it lacks a significant atmosphere to retain heat, leading to drastic temperature fluctuations[1][2]. While Mercury can reach daytime temperatures of 800 degrees Fahrenheit (430 degrees Celsius), its nighttime temperatures can plummet to minus 290 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 180 degrees Celsius)[5].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Overview of the SpaceX Raptor 3 Engine Improvements

The SpaceX Raptor 3 engine signifies a major advancement in rocket engine technology, showcasing multiple enhancements over its predecessors. These improvements focus on increasing thrust, efficiency, and manufacturability while simplifying the design. This report synthesizes key insights into the main enhancements of the Raptor 3 engine.
Increased Thrust and Specific Impulse
One of the most significant improvements in the Raptor 3 is its increased thrust capability. The engine produces a whopping 280 tons-force (tf) at sea level, representing a 51% increase from Raptor 1 and a 21% increase from Raptor 2[3][1]. Further iterations of the engine may potentially exceed 300 tf, suggesting ongoing enhancements in power output[3][1]. The specific impulse of Raptor 3 has also been improved to 350 seconds, marking a focus on efficiency which allows for greater payloads and improved mission capabilities[3][1].
Weight Reduction and Structural Simplification
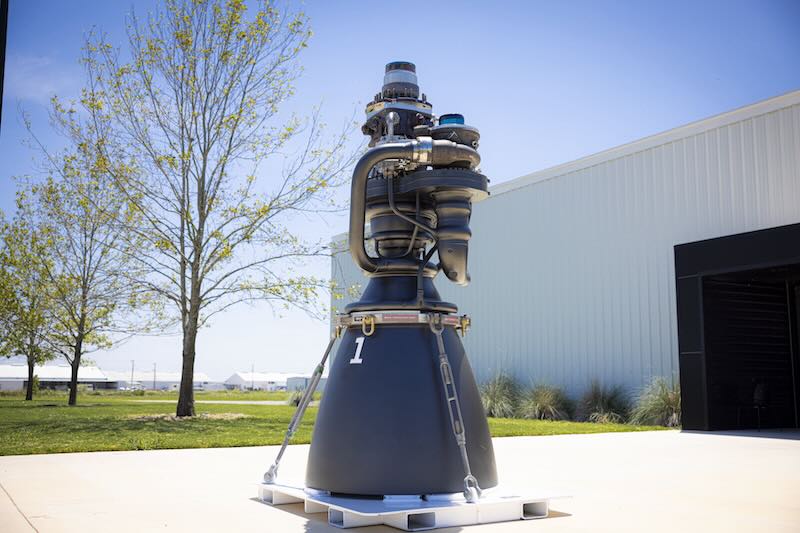

The Raptor 3 engine reflects a concerted effort to reduce weight, coming in at 36% lighter than Raptor 1 and 7% lighter than Raptor 2, with a total weight of 1,525 kg[3][1]. This weight reduction is largely attributed to a streamlined design that eliminates unnecessary components, resulting in fewer parts and simplified manufacturing processes[11][10]. The elimination of the heat shield is particularly notable, as the Raptor 3 engine utilizes regenerative cooling instead, which enhances not only its structural integrity but also its efficiency[6][2].
Enhanced Cooling Mechanisms
The integration of advanced cooling technologies in Raptor 3 is another critical improvement. The engine boasts integrated cooling channel walls, allowing for more effective thermal management[4][1]. This development leads to a streamlined appearance and maintains high efficiency even at higher operational loads. The regenerative cooling system replaces the need for a traditional heat shield, further simplifying engineering requirements and reducing overall mass[5][10].
Design Innovations
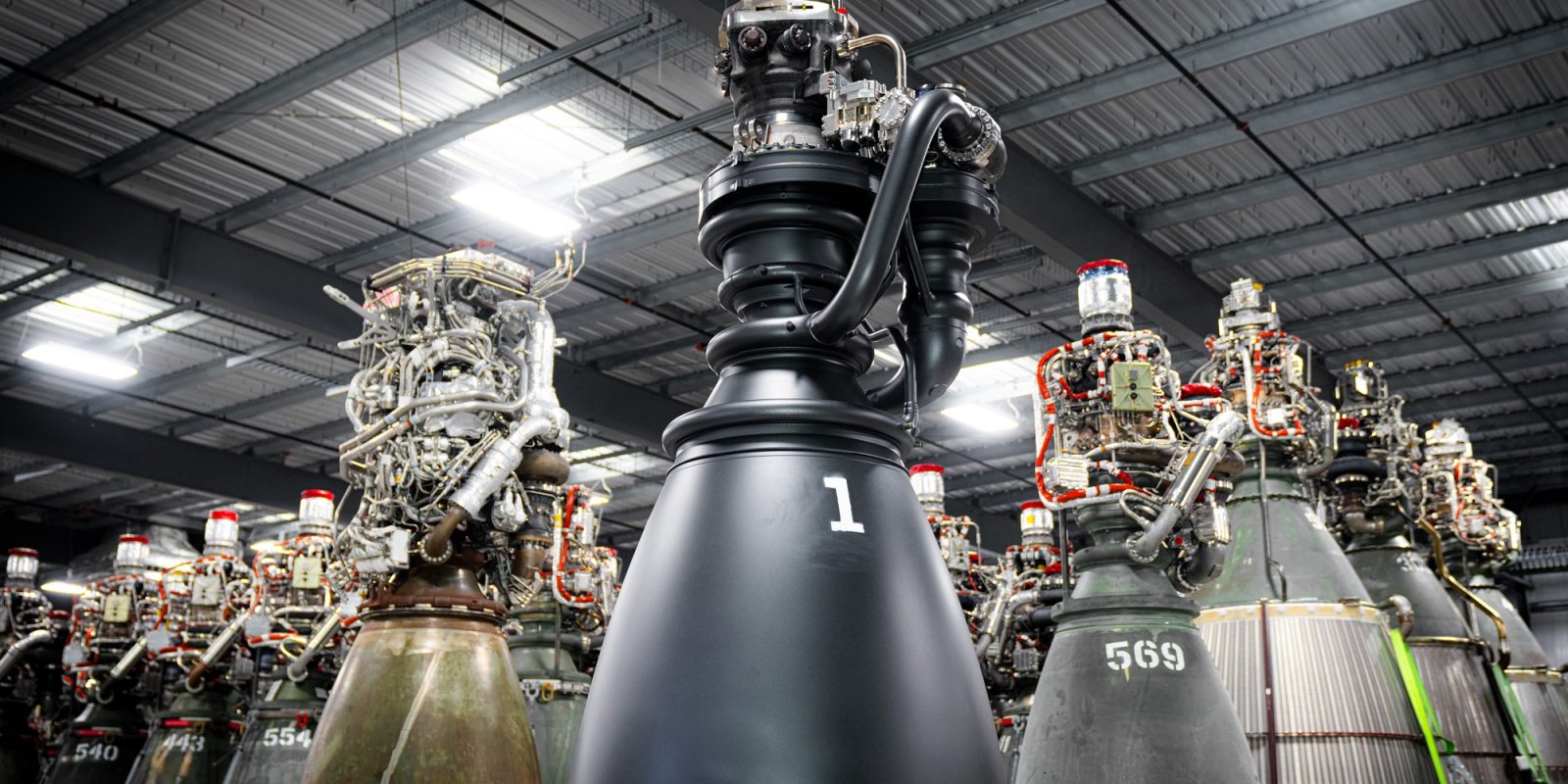

SpaceX has emphasized a design philosophy that incorporates simplicity in Raptor 3, a shift from the complexity seen in earlier versions[4][2]. The integration of components, such as secondary plumbing into the main pump, contributes to a lighter engine while improving reliability[4][1]. This includes a reduction in bolted joints, which enhances structural integrity and simplifies servicing[7][1]. Musk himself described Raptor 3 as having a 'simpler-looking' design compared to previous models, reflecting a trend towards minimizing complexity without sacrificing performance[6].
Manufacturing Efficiency
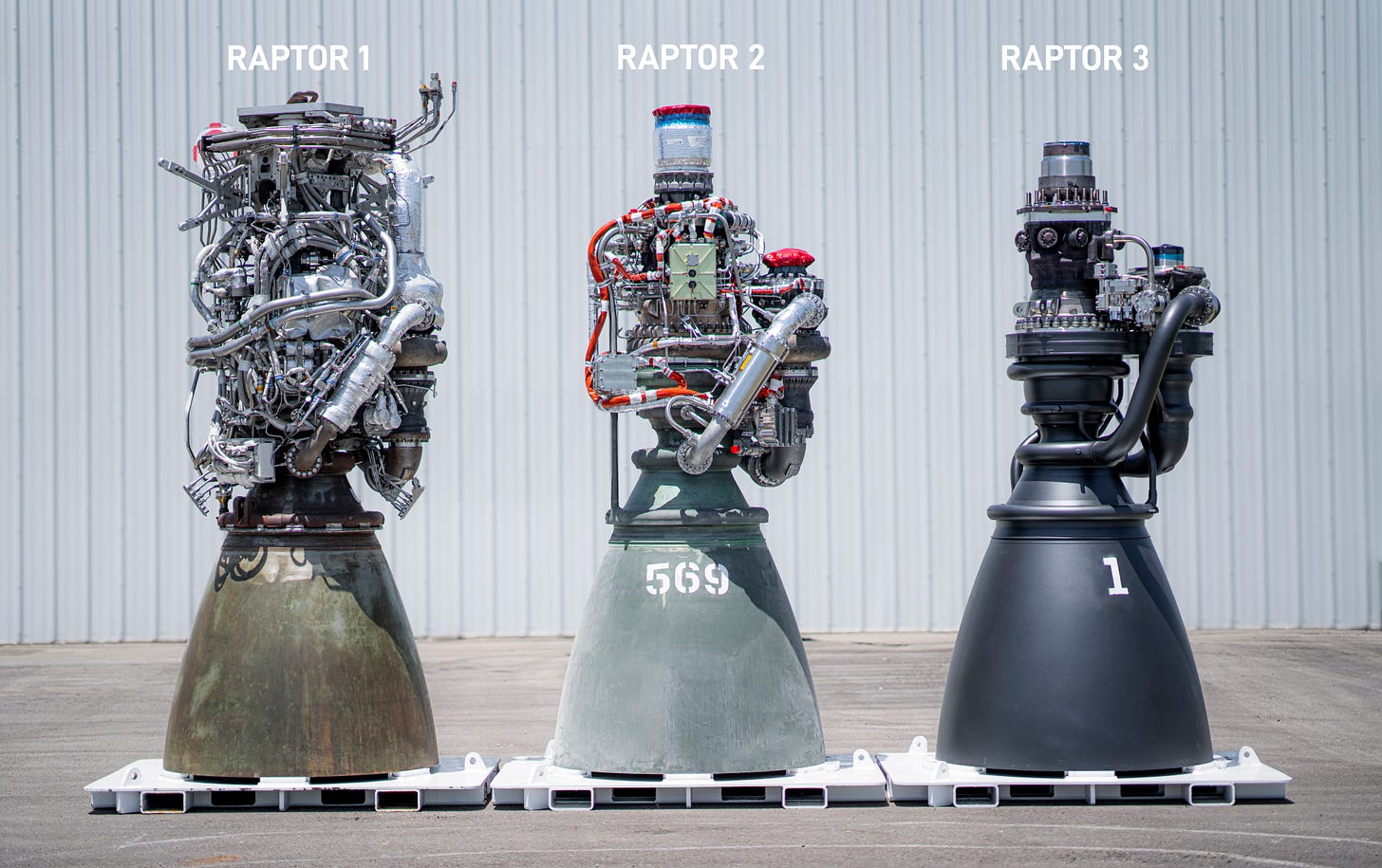
The improvements in the Raptor 3’s design facilitate enhanced manufacturability. SpaceX aims to streamline production processes and cut down on costs associated with manufacturing[11][10]. The adoption of advanced manufacturing techniques such as 3D printing is likely being employed to tackle the challenges posed by intricate cooling channels and components[4].
The foundational approach of 'no part is the best part' suggests a significant reduction in assembly requirements, indicating that fewer parts lead to faster production and potentially lower costs[10]. This commitment to manufacturing efficiency aligns with SpaceX’s broader goal of increasing flight frequency for its Starship system.
Future Prospects

Elon Musk has indicated that while Raptor 3 is an impressive achievement, there is still substantial potential for future improvements, including an additional 8-10% increase in thrust through subsequent iterations[3][1]. This visionary outlook underscores SpaceX’s dedication to pushing the boundaries of rocket propulsion technology.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the SpaceX Raptor 3 engine embodies a significant leap forward in rocket technology through a combination of increased thrust, weight reduction, advanced cooling mechanisms, innovative design, and enhanced manufacturing efficiencies. These improvements not only set new standards for the performance of rocket engines but also align with SpaceX’s objectives for rapid reusability and cost effectiveness in launching missions to space. The Raptor 3 engine demonstrates how thoughtful engineering and design philosophy can lead to groundbreaking advancements in aerospace technology.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.


























