Discover Pandipedia
Pandipedia is the world's first encyclopaedia of machine generated content approved by humans. You can contribute by simply searching and clicking/tapping on "Add To Pandipedia" in the answer you like. Learn More
Expand the world's knowledge as you search and help others. Go you!

Since 2022, AI inference costs have fallen[1]. Between 2022 and 2024, the cost-per-token to run language models fell by an estimated 99.7%[1]. This decline was driven by improvements in both hardware and algorithmic efficiency[1].
As inference becomes cheaper and more efficient, the competitive pressure amongst LLM providers increases[1]. What used to cost dollars can now cost pennies, and what cost pennies may soon cost fractions of a cent[1].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Understanding Cosmic Definitions
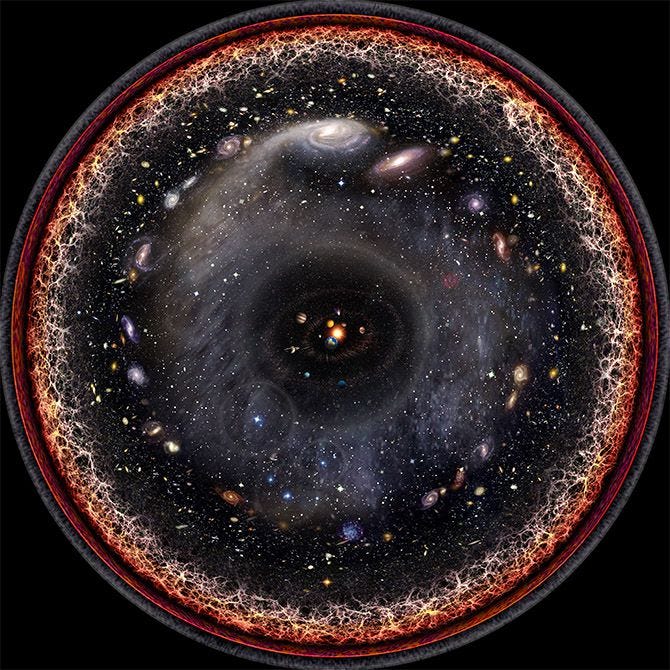
Our understanding of the universe begins with distinguishing between the part we can observe and the entire cosmos. The observable universe refers to the region from which light has had time to reach us since the beginning of cosmic expansion, while the entire universe encompasses all of space and matter—even regions we cannot see. In essence, every observer is at the center of his or her own observable sphere, though the whole universe may have no center and may be vastly larger or even infinite[4][5].
Size of the Observable Universe
Multiple measurements and techniques have led scientists to determine that the observable universe has a diameter of roughly 93 billion light‐years. This value is derived from the fact that, although the universe is about 13.8 billion years old, space itself has expanded over time. As a result, distant objects that originally emitted light 13.8 billion years ago are now approximately 46.5 billion light-years away from us in every direction[3][5]. In other words, the observable universe forms a sphere with a radius of about 46.5 billion light-years, giving it an overall diameter near 93 billion light-years[8][12].
The Entire Universe Versus the Observable Portion
Although the observable universe is enormous, it is only a fraction of the entire cosmos. Many cosmological models suggest that the entire universe may be vastly larger than the portion we can see. Some estimates indicate that the total size could be hundreds of times—if not infinite—in extent compared to the observable region. For instance, one approach based on Bayesian model averaging suggests that our universe might be at least 250 times the size of the observable universe, meaning that while the visible part spans about 93 billion light-years in diameter, the whole universe could be many trillions of light-years across or even unbounded[1][7][6].
How Do Scientists Measure Cosmic Distances?

Measuring the vast scales of the cosmos involves a series of techniques that build one upon the other. Astronomers first use standard candles such as Cepheid variable stars, whose brightness variations are directly related to their intrinsic luminosity. By comparing their actual brightness with how bright they appear from Earth, distances to nearby galaxies can be determined accurately[2][13]. For more distant objects, techniques involving Type Ia supernovae, redshift measurements, and the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation are employed. The CMB, which represents the leftover radiation from the early universe, provides further clues to the scale of cosmic expansion. These multiple distance-measurement techniques—involving parallax at close ranges and redshift at great distances—allow scientists to create a cosmic distance ladder that leads to the current estimates of the observable universe’s dimensions[9][10].
Cosmic Expansion and Future Measurements
One of the key discoveries of the 20th century was that the universe is expanding. Edwin Hubble’s observation that galaxies are receding from us in proportion to their distance laid the foundation for this concept. More recent studies have shown that this expansion is accelerating due to a mysterious component known as dark energy[14]. While the most straightforward model incorporates dark energy as a constant—a term popularized by Einstein’s cosmological constant—new evidence suggests that dark energy may evolve over time, which would have profound implications for the ultimate size and fate of the universe[14]. Advanced instruments like the Hubble Space Telescope, and its successors, continue to refine our measurements and spur new theories. As our tools and methods improve, we may not only refine our estimates of size and age (currently about 13.8 billion years old) but also uncover deeper insights into the nature of dark energy and the universe’s long-term evolution[13][14].
Implications and Ongoing Research
The sheer vastness of the universe has both philosophical and scientific implications. The fact that the observable universe alone spans approximately 93 billion light-years in diameter illustrates how small our local region is compared to the whole cosmos. Nevertheless, this observable part still contains an immense number of galaxies—estimated to be in the trillions—with each galaxy composed of billions of stars and countless other forms of matter[5][11]. The ongoing study of the cosmic distance scale and dark energy is critical not just for understanding the geometry and size of the universe, but also for predicting its fate. Whether the universe will continue to expand indefinitely (leading to a Big Freeze scenario), halt, or even collapse under its own gravity remains an open question. What is clear, however, is that with every new observation, our picture of the universe grows richer and more complex, inviting further research into areas that challenge our current theories[7][14].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.

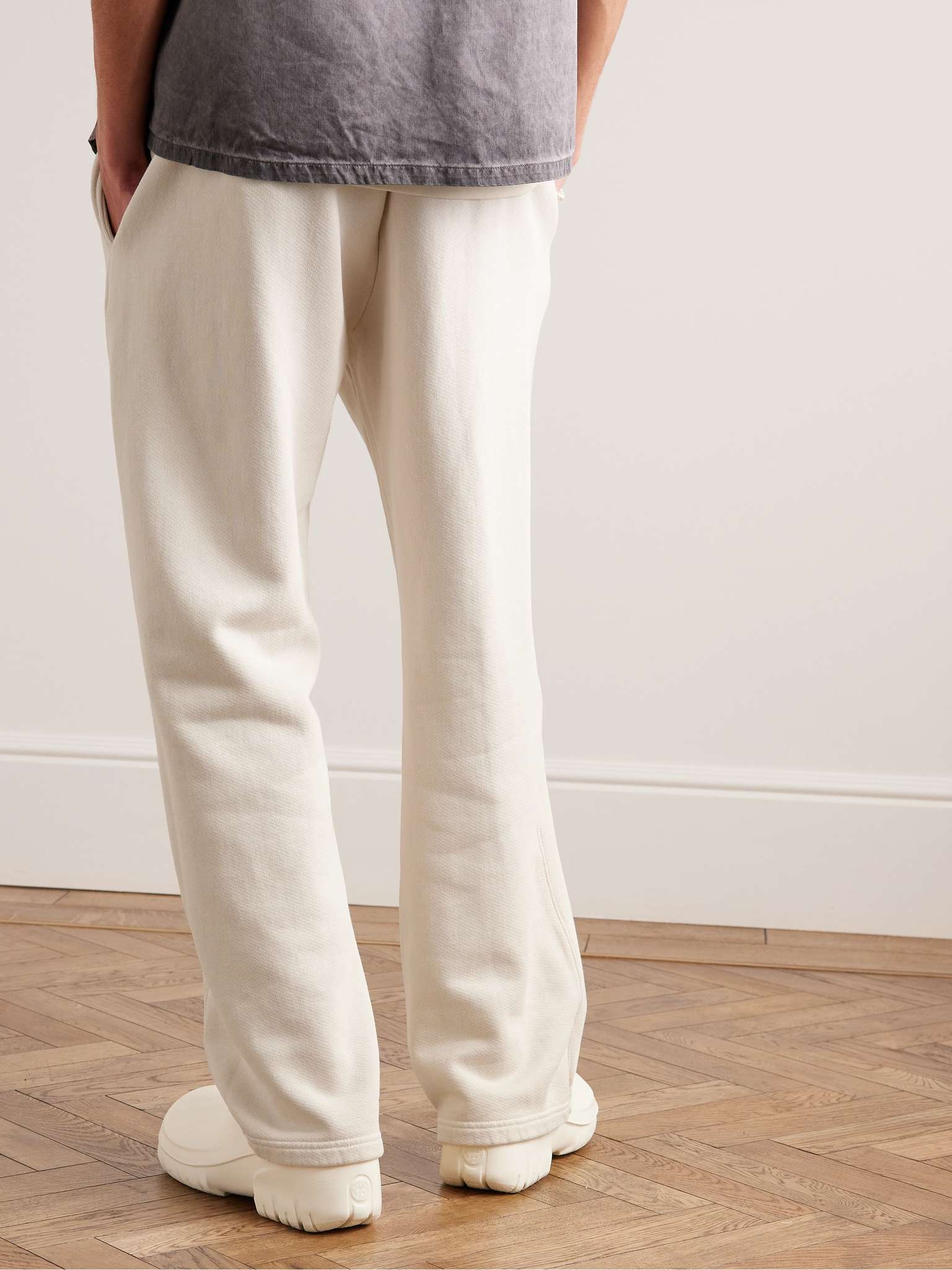
Best Fleece-Lined Sweatpants
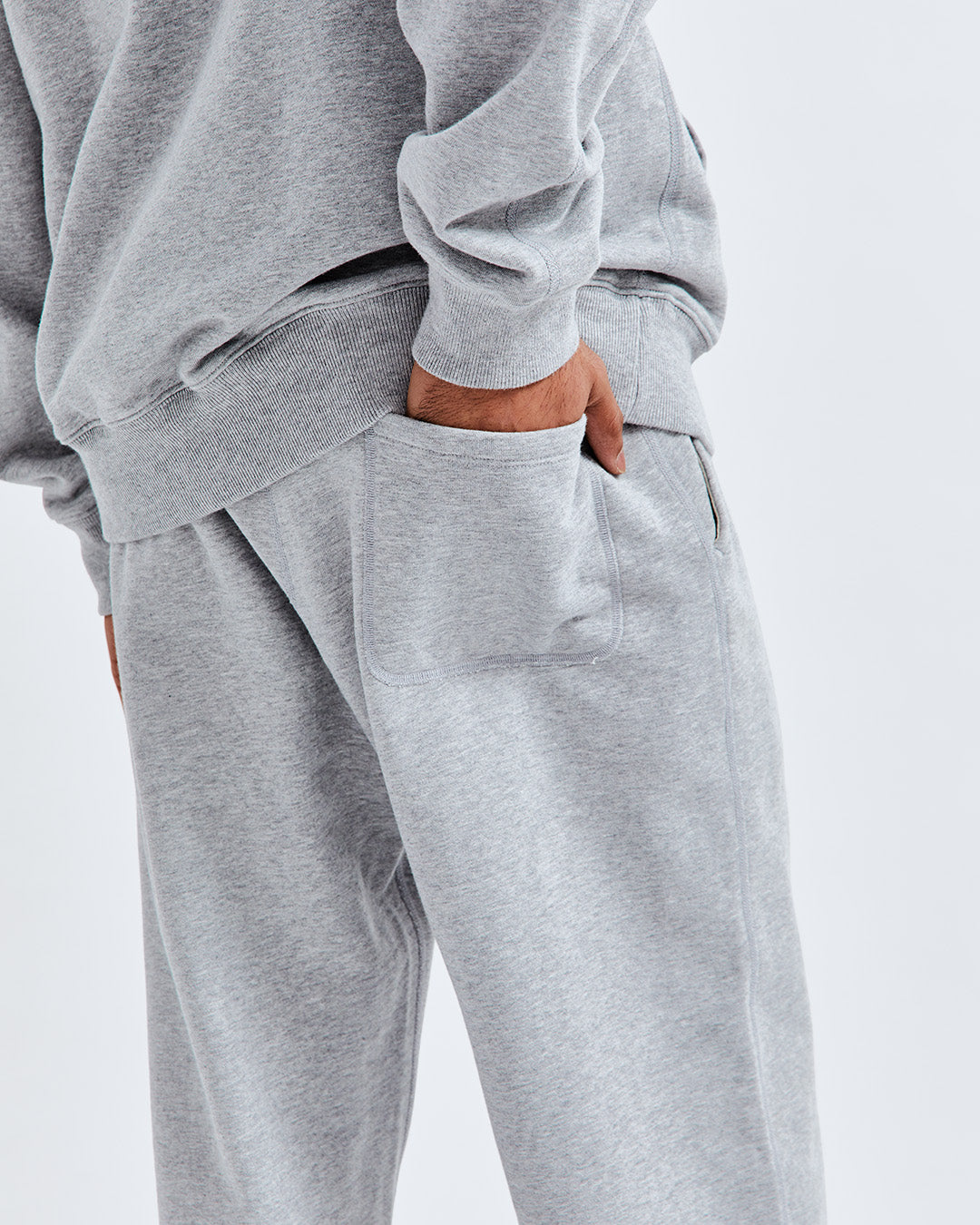
These versatile sweatpants feature a breathable cotton blend and a tapered silhouette, perfect for lounging or working out during winter[1].
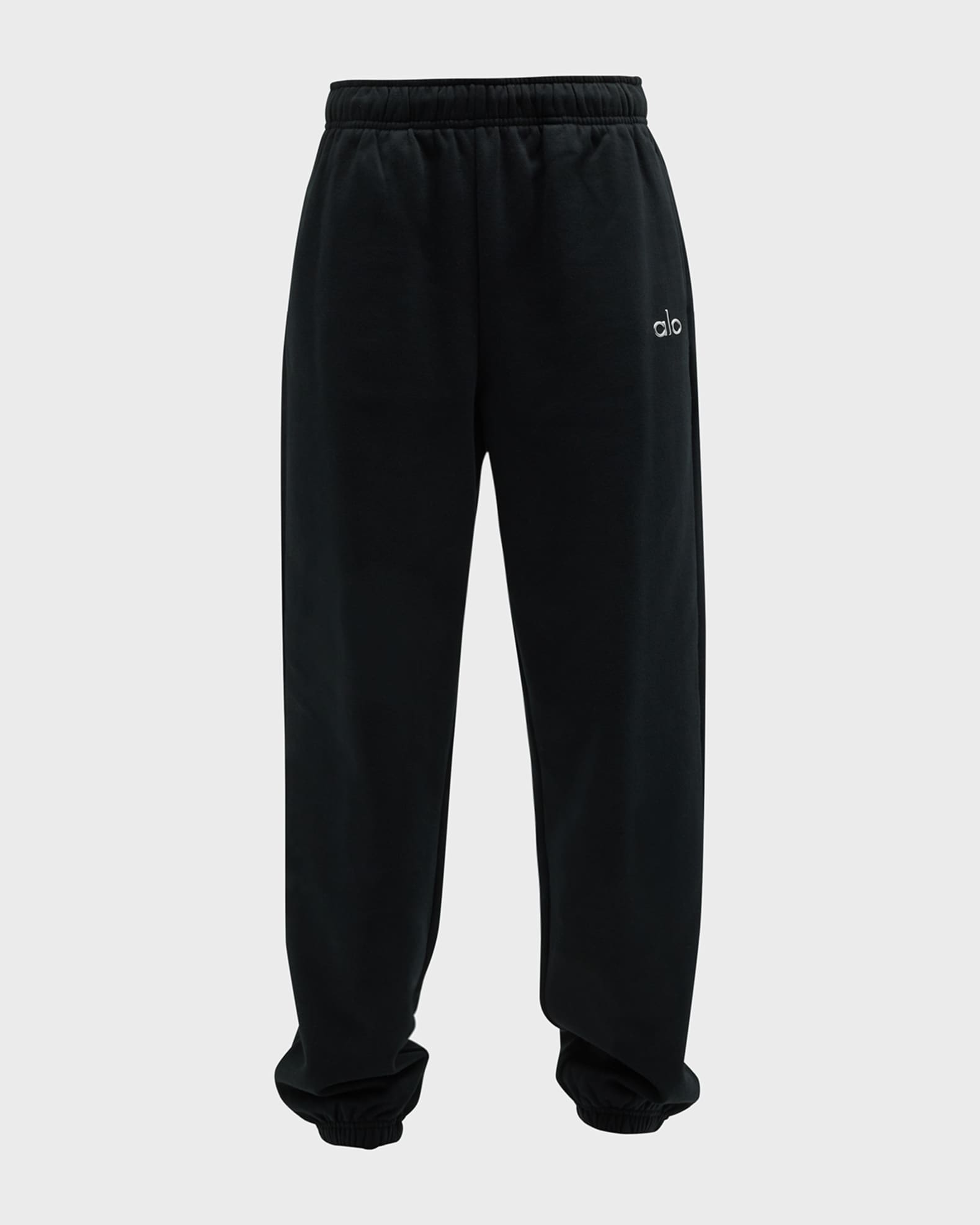
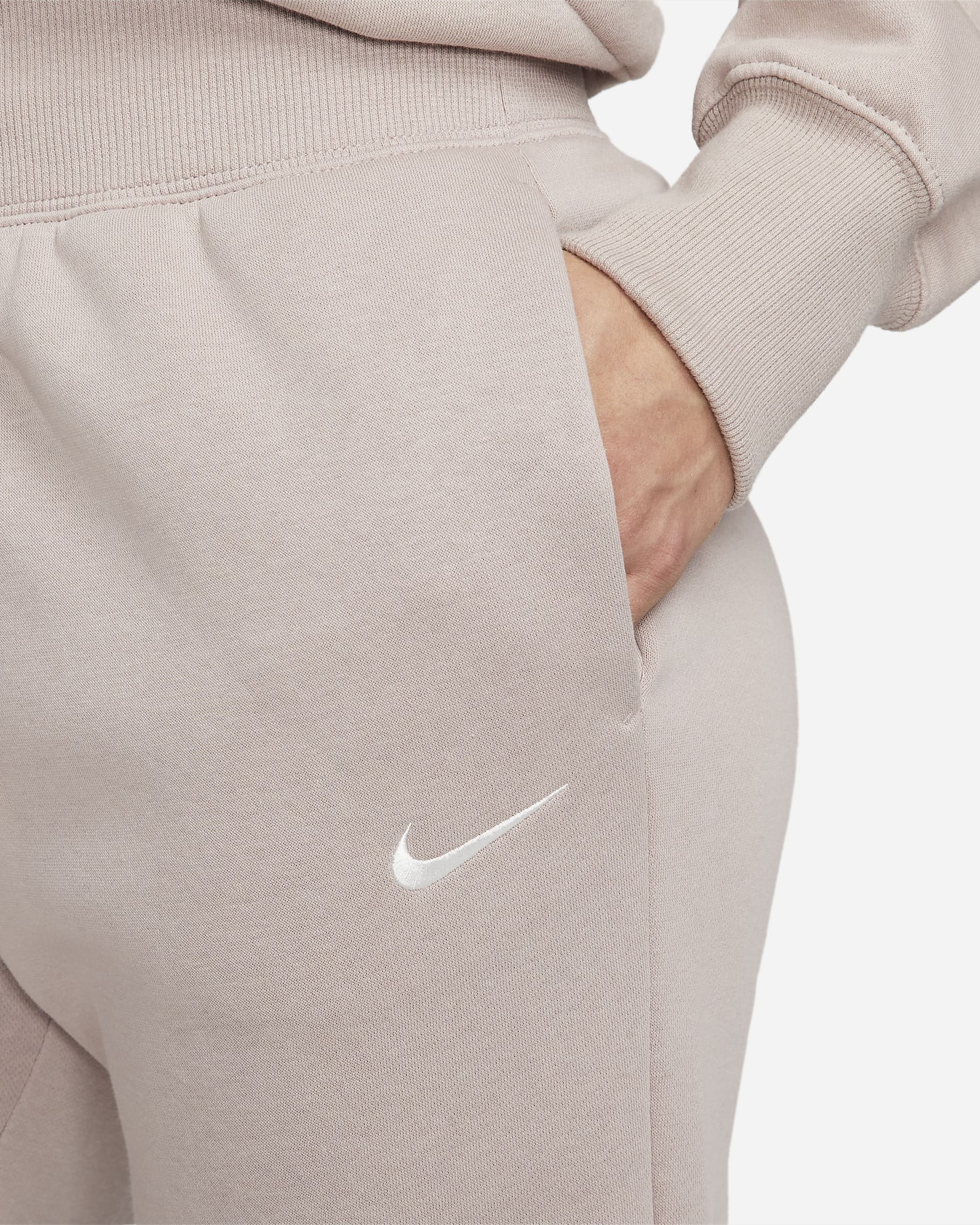
Alo Yoga Fleece-Lined Sweatpants
These stylish bottoms offer warmth and breathability, making them suitable for casual outings or home wear, available in various classic shades[1].
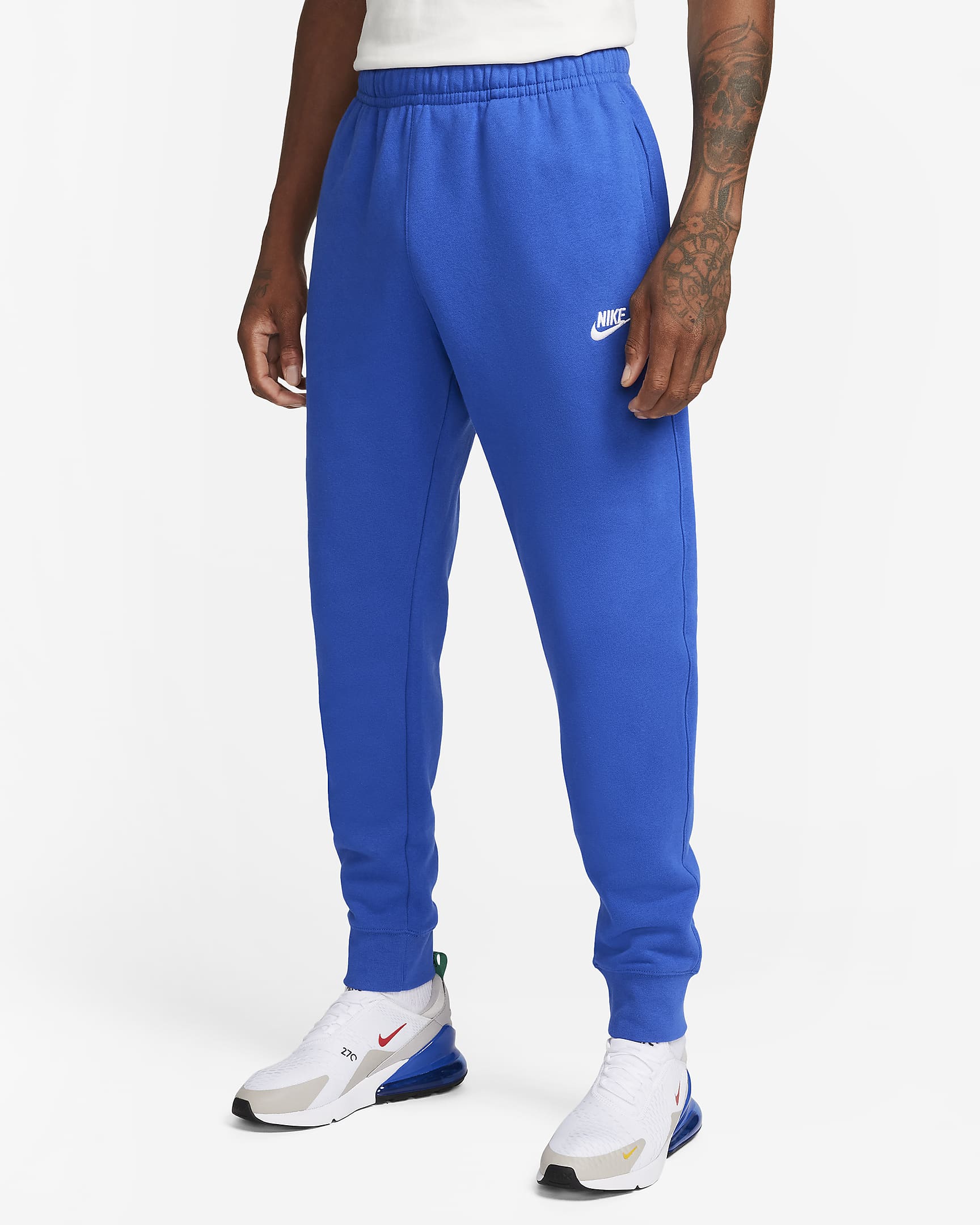
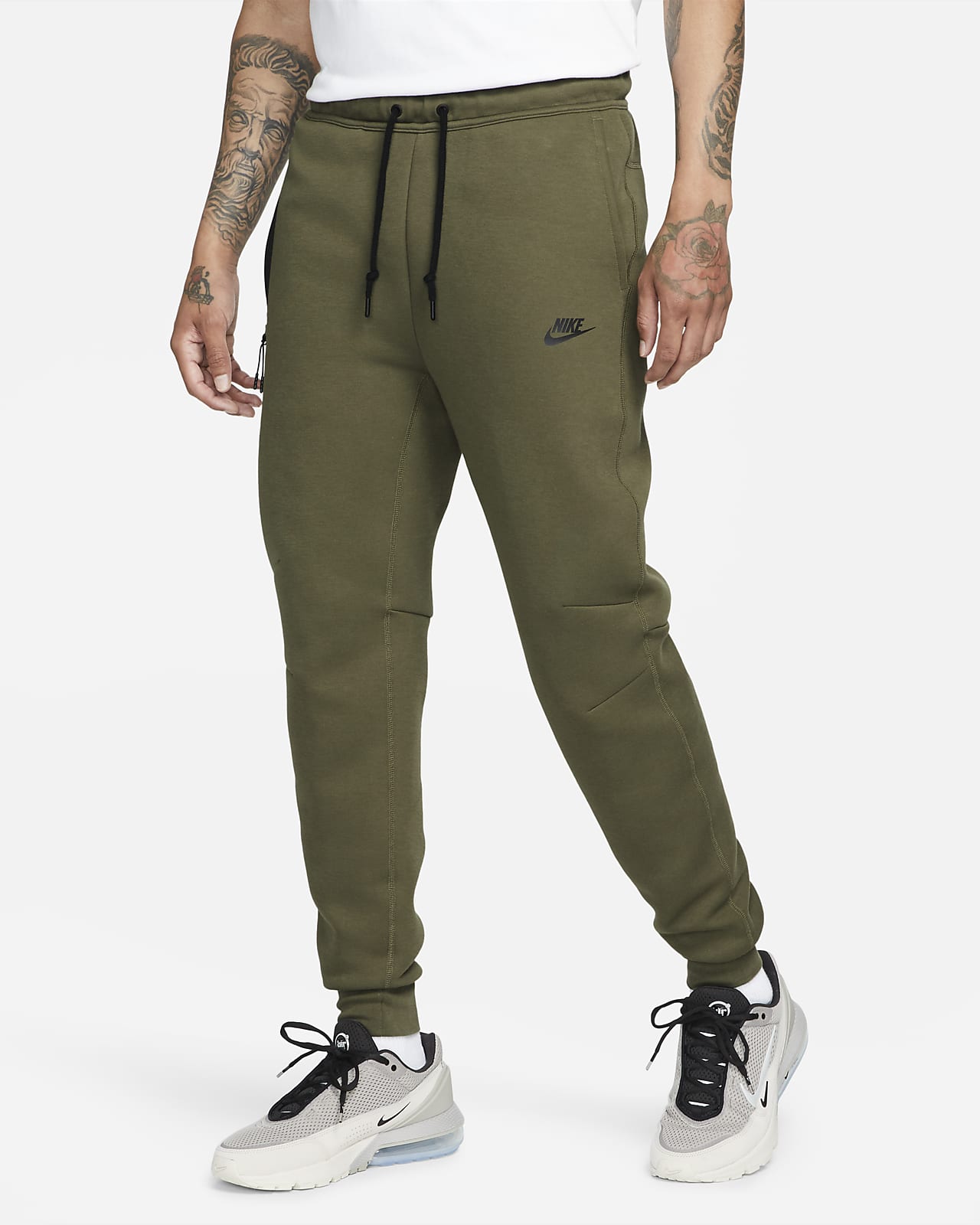
Nike Club Fleece Joggers
Made with brushed-fleece fabric, these sweatpants are soft, smooth, and relaxed, ideal for cozy lounging or running errands[3].
Nike Therma-FIT Joggers
Designed to manage body heat, these joggers provide warmth during workouts and everyday wear, utilizing innovative fabric technology[3].
Champion Powerblend Fleece Open-Bottom Sweatpants
Known for its cozy fleece lining and roomy fit, these classic sweatpants are versatile for many occasions, including lounging or outdoor errands[4].
Reigning Champ Midweight Terry Relaxed Sweatpant
This high-quality cotton French terry option features a relaxed fit that's perfect for year-round comfort without sacrificing style[4].
Under Armour Meridian Tapered Pants
These sweatpants combine a flattering tapered design with a soft and stretchy fabric, suitable for both workouts and lounging[7].
Vuori Performance Sweatpants
Ideal for athleisure, these sweatpants offer moisture-wicking, quick-drying capabilities, ensuring comfort whether working out or relaxing[7].
Todd Snyder x Champion Midweight Slim Jogger
With a tailored fit and vintage-inspired details, these joggers maintain both style and comfort for casual and active wear[4].
Nike Tech Fleece Joggers
Roomy in the thigh but tapered, these joggers provide a polished look while offering insulation and comfort for winter outings[3].
ACG Polartec Joggers
Part of Nike's outdoor gear collection, these sweatpants use Polartec fabric designed to trap warmth while allowing moisture to escape, perfect for harsh conditions[3].
Eco-Friendly Fleece Joggers
Made partly from recycled materials, these sweatpants are cozy, eco-friendly, and feature a relaxed fit with roomy pockets[1].
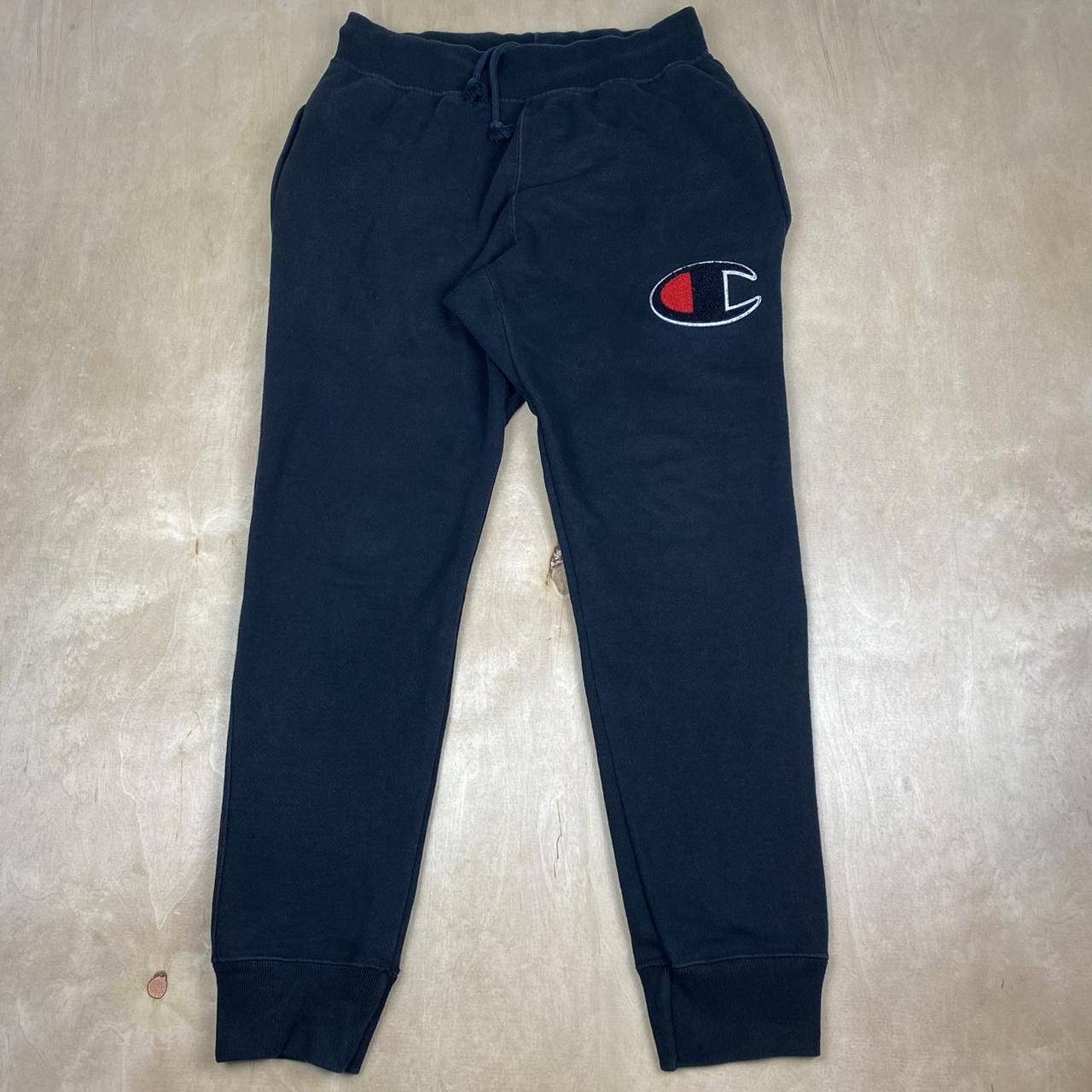
Champion Reverse Weave Sweatpants
A classic choice known for sturdy construction and comfortable fit, featuring a heavyweight fleece fabric that stands up to winter wear[6].
Reigning Champ Heavyweight Fleece Joggers
Crafted for durability and warmth, these joggers from Canada are perfect for lounging and casual outings during the colder months[6].
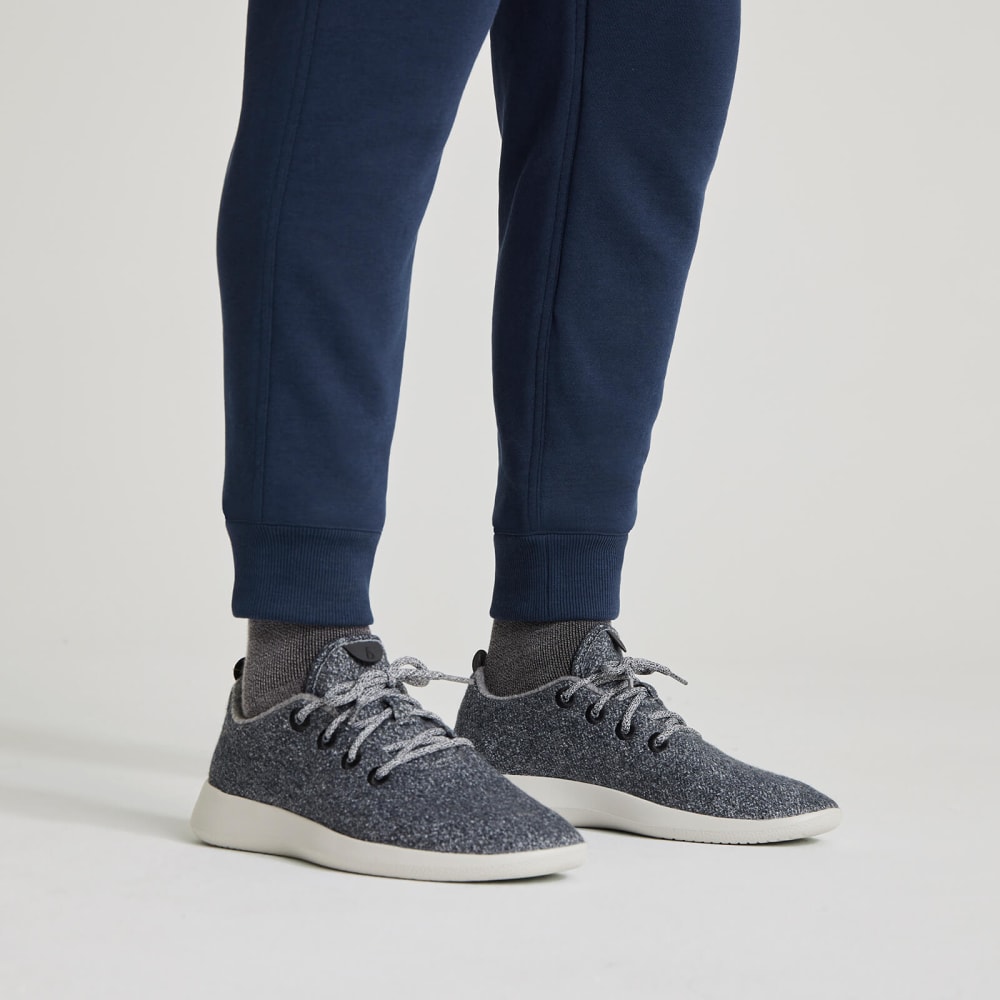
Allbirds R&R Sweatpants
These performance-friendly sweatpants offer a blend of comfort and style, suitable for casual wear and light workouts[4].
Public Rec Travel Sweatpants
Designed for travel, these sweatpants are soft yet stylish enough for casual outings while offering the comfort typical of activewear[4].
Vuori Kore Joggers
With a soft DreamKnit fabric, these joggers provide comfort and are versatile enough for both at-home lounging and outdoor activities[7].
Nike Phoenix Fleece Joggers
These sweatpants offer a cozy interior and smooth exterior, perfect for staying warm during cold weather while looking stylish[3].
Lululemon License to Train Joggers
Made from recycled materials and featuring moisture-wicking properties, these joggers are great for working out in cooler weather[7].
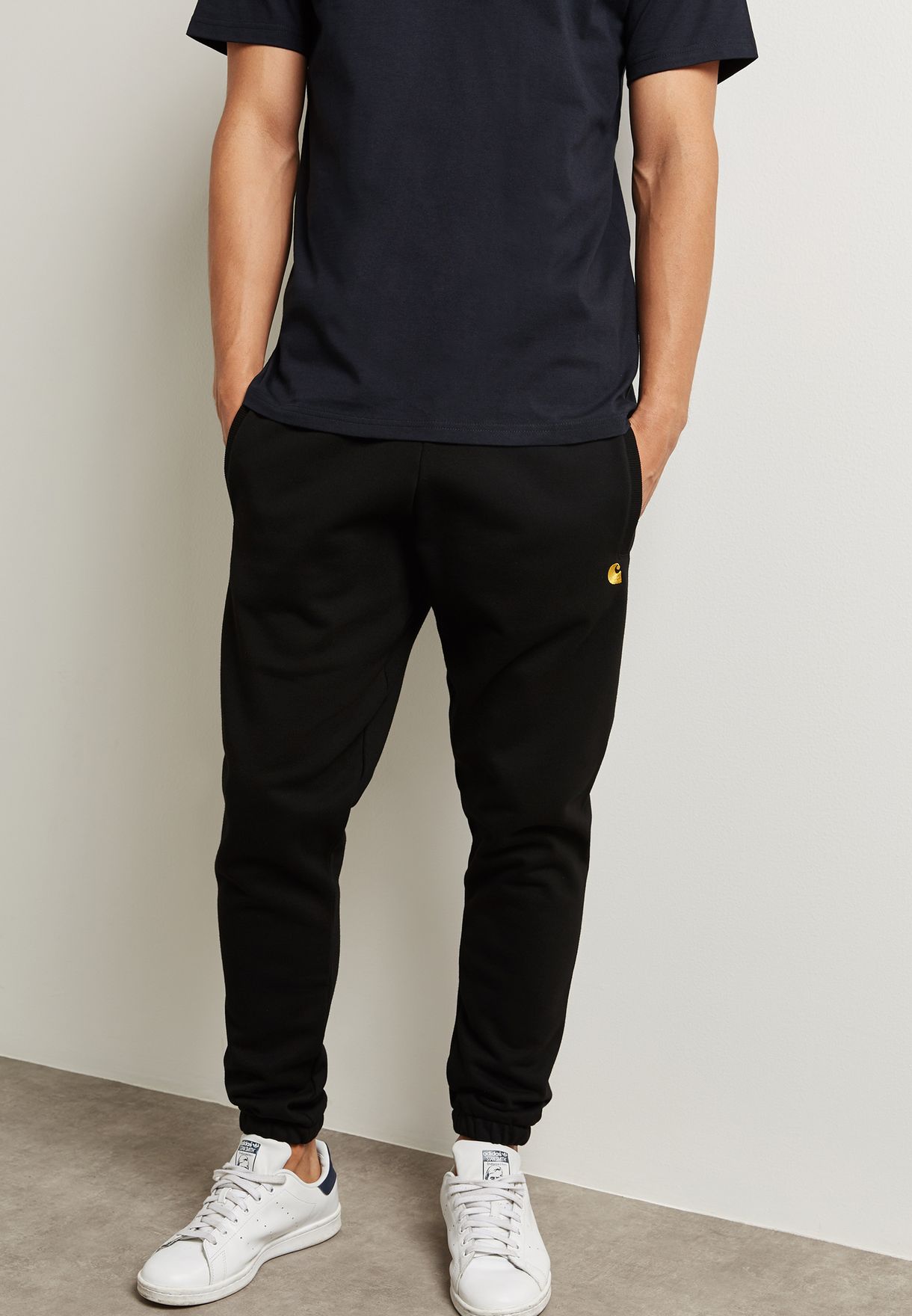
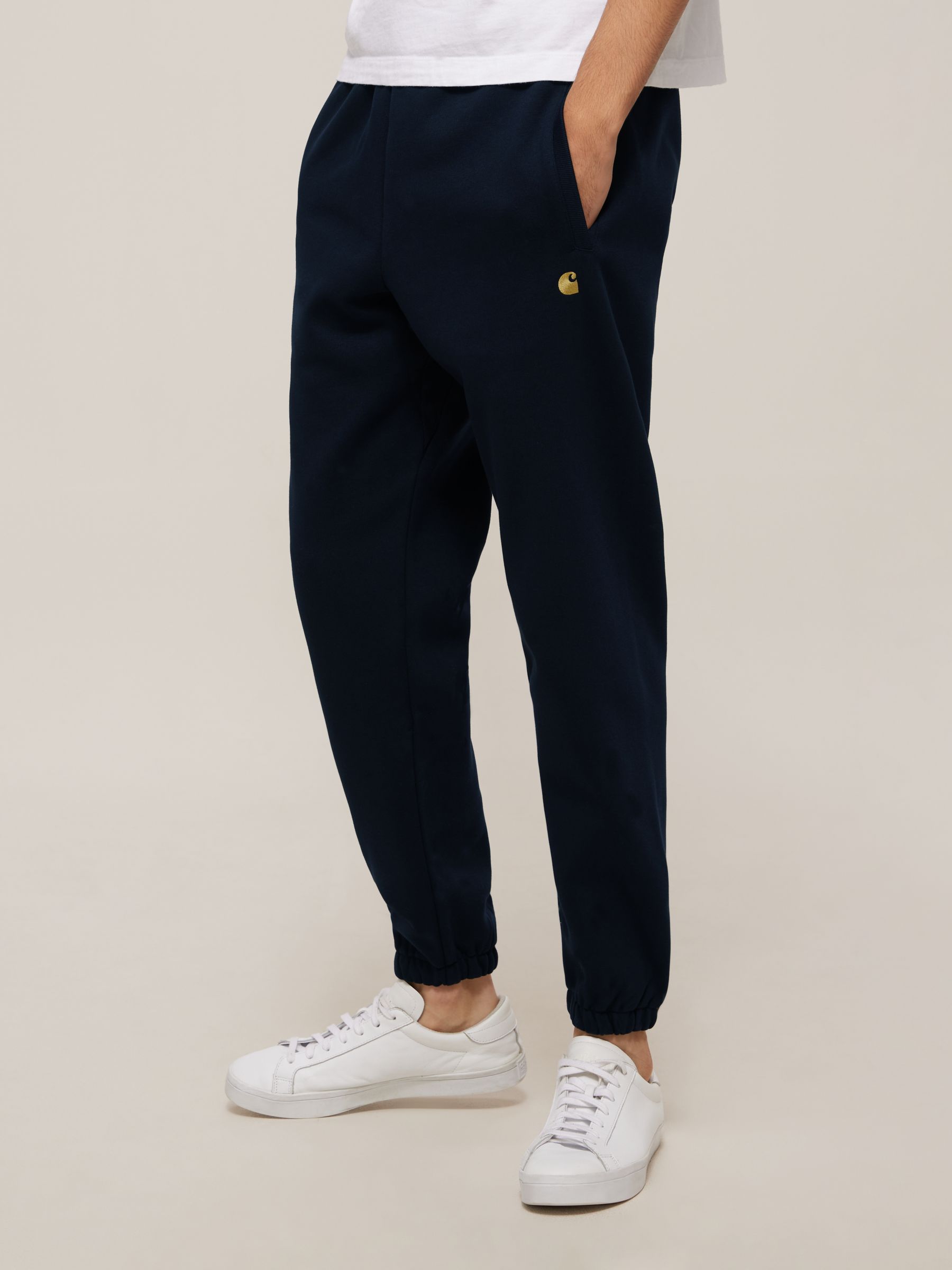
Carhartt WIP Chase Sweatpants
Renowned for their durability and warmth, these sweatpants are perfect for both work and leisure during the winter[6].
Cole Buxton Heavyweight Warm-Up Pants
Inspired by vintage gym wear, these thick sweatpants offer maximum warmth and a timeless style for everyday wear[6].
MKI Heavyweight Joggers
Made with a substantial 650gsm fabric, these joggers are among the heaviest available, providing exceptional warmth and comfort for winter[6].
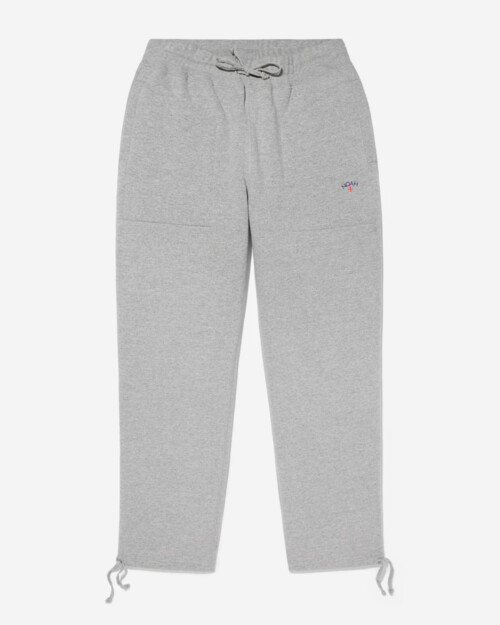

Noah Heavyweight Sweatpants
Built for comfort and style, these sweatpants are made from a cozy 15oz fabric, providing both durability and warmth[6].
Aimé Leon Dore Sweatpants
Known for their fashionable cuts and comfortable fit, these sweatpants combine modern style with the snugness you need for winter[6].
Les Tien Cotton-Jersey Sweatpants
Distinguished by their high-quality cotton material, these sweatpants are soft and chic, striking the right balance for a versatile winter wardrobe[4].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Air purifiers offer various benefits, such as improving indoor air quality by capturing airborne pollutants like dust, smoke, allergens, and pet dander, which can alleviate allergy and asthma symptoms[1][4][6]. They may also help reduce unpleasant odors and harmful chemicals, contributing to a healthier living environment[4][6].
However, there are drawbacks, including the initial cost and ongoing maintenance for filter replacements[1][4]. Some models can generate noise and may produce ozone, which can worsen respiratory conditions, particularly in older units[3][4]. Additionally, air purifiers might not eliminate all pollutants, particularly gaseous ones, so it's essential to set realistic expectations[3][4].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.

Social media has increasingly become a critical platform for public discourse, influencing opinions on various topics in real-time. Its impact has been profound and multifaceted, especially in the context of political engagement, information dissemination, and emotional sentiment.
Influence on Political Opinions and Engagement

Social media platforms serve as significant channels for political communication. A recent analysis highlights that 'most supporters of both former President Donald Trump and Vice President Kamala Harris say they’ve thought a lot about the candidates this year and say the outcome of the race really matters'[3]. Such findings indicate a high level of political engagement among users, likely fueled by discussions and endorsements circulating on social media.
Research has shown that social media endorsements—through likes, shares, and retweets—can significantly influence individuals' opinions on policy issues. In one study, participants exposed to pro-economy posts with a high number of likes were less likely to favor pandemic-related restrictions, while those who viewed pro-public health posts with similar endorsements showed increased support for such measures[6]. This demonstrates the ability of social media metrics to sway opinions, especially among active users.
The interaction between social media usage and political engagement is notable, as individuals who frequently use these platforms are also more likely to participate in political discussions both online and offline. This correlation suggests that social media not only reflects public sentiment but actively shapes it, especially during election cycles[6].
The Spread of Misinformation and its Consequences

While social media facilitates the rapid spread of information, it also raises concerns about misinformation and its implications for public opinion. The year 2024 has heightened these concerns, coinciding with significant global elections. Experts express worry over the 'gutting of moderation teams and their election integrity efforts' across major platforms, which could exacerbate the spread of false information[7]. This lack of oversight is particularly crucial in an election year where misinformation could potentially disrupt public trust.
The dynamic nature of social media also allows for the rapid dissemination of emotionally charged content. For instance, discussions surrounding the Israel-Hamas conflict have led to a spike in polarizing sentiments and misinformation, likened to 'lighting a match in a giant, very dry forest'[7]. The ability of social media to amplify emotional responses can lead to significant shifts in public opinion, making it necessary for users to critically evaluate the information they consume.
Emotional Sentiments and Social Media Discourse

The emotional landscape of social media discussions has evolved, particularly during crises like the COVID-19 pandemic. Social media has been shown to harbor 'negative sentiments' regarding economic conditions and unemployment, with studies indicating a correlation between unemployment rates and the negative tone of related news articles[2]. This relationship suggests that social media does not merely reflect public sentiment but can also amplify emotional responses—ranging from fear and sadness to anger—around significant societal events.
In analyzing sentiments expressed in unemployment-related articles, the predominant emotion identified was 'fear,' particularly during the peak of job losses in 2020[2]. This underscores how social media shapes perceptions and emotional sentiment, influencing how individuals respond to prevailing economic and social developments.
Moreover, sentiment and emotion analysis on platforms like Twitter highlights the prevalence of pessimistic sentiments. While studies have noted a slight rise in optimism amid the ongoing discussion of economic recovery, negative sentiments still dominate[5]. Such emotional undercurrents play a significant role in shaping public opinion as users react to the shared experiences and narratives presented online.
Social Media and Information Accessibility

Beyond influence and emotional impact, social media serves as a conduit for accessing information more democratically than traditional media. During the pandemic, for example, social media allowed for the swift sharing of news and updates related to COVID-19, which underscored its role in public health discourse. However, this rapid flow of information also required users to navigate the challenge of distinguishing between reliable and unreliable sources[5].
As platforms continue to evolve, their structure can significantly affect how information is consumed and shared. Changes such as those implemented by Twitter to modify retweet functionalities aim to encourage users to engage more thoughtfully with content[6]. Yet, modifications like these can also yield unintended consequences, affecting how information spreads and how users interpret it.
The Future of Public Discourse via Social Media
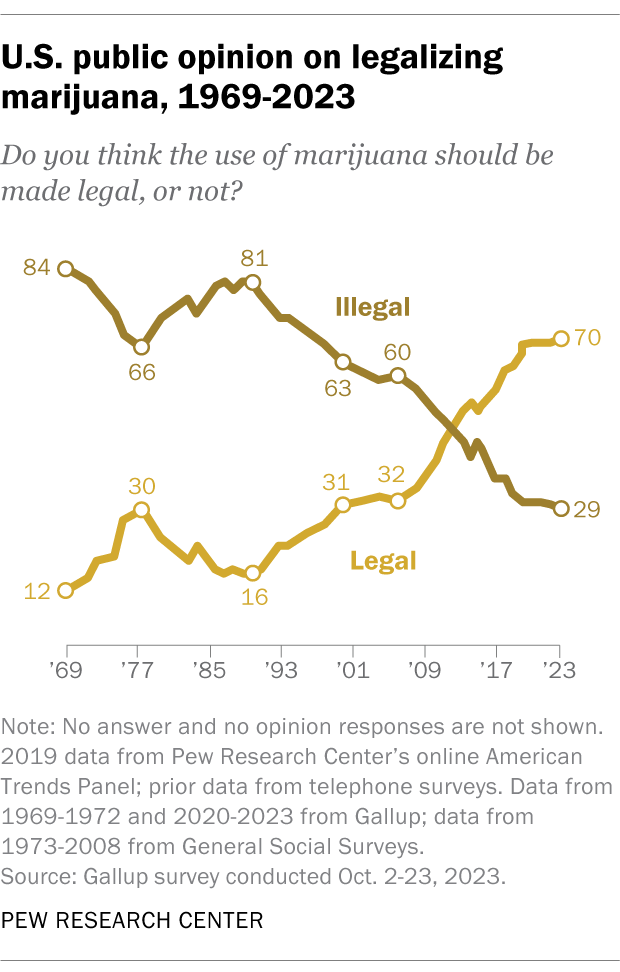
Going forward, the interplay between social media and public opinion remains complex. As we edge closer to significant political events in 2024, the stakes surrounding social media's influence on public sentiment will only increase. Ensuring responsible usage and enhanced moderation appears essential to mitigate the adverse effects of misinformation.
In conclusion, social media is increasingly central to shaping public opinion in real-time. Its capability to influence political engagement, emotions, and the dissemination of information highlights both its potential benefits and inherent challenges. As a space for dynamic public discourse, social media will continue to be pivotal in how society processes and responds to collective events in the future.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

User's information needs have literally exploded; they're inundated with information.
Sundar Pichai[1]
If the user's not satisfied, they're not going to come back to Google anymore; correct?
Mr. Dahlquist[5]

Today there are over 5 billion people with phones connected all over the world.
Sundar Pichai[1]
An effect on search quality is substantial when a change, whether positive or negative, would be sufficiently large.
Professor Oard[4]
The challenges of delivering localized information matter significantly.
Benedict Gomes[2]
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Market Context and Sustainability Trends
The European car rental industry is undergoing a period of rapid growth, with market size projections increasing from USD 31.23 billion in 2024 to USD 73.95 billion by 2035. A key factor influencing this upward trajectory is the focus on sustainability. According to the analysis, changing consumer behavior combined with technological advancements has led rental companies to re-evaluate their fleet compositions. The industry is experiencing a notable trend where many companies are expanding their offerings with electric and hybrid vehicles. This move is driven by environmental concerns as well as the need to remain competitive in a market that is increasingly influenced by sustainable travel preferences[1].
Regulatory Impact and Environmental Policy
Government regulations in Europe have been a significant force propelling the industry towards sustainability. European Union directives emphasize the reduction of carbon emissions, presenting both a challenge and an opportunity for car rental companies. For example, new regulations call for a 55% reduction in CO2 emissions from new cars by 2030. As a result, companies must adapt not only to regulatory pressures but also to consumer demand for eco-friendly options. This regulatory landscape has prompted rental companies to invest more in green fleets, ensuring their offerings meet the strict emission standards and align with current environmental policies[1].
Fleet Transformation and Technological Integration
The need for sustainable operations has led major industry players to integrate more eco-friendly vehicles into their fleets. Brands are increasingly investing in both electric and hybrid models, aiming to reduce their carbon footprint while capitalizing on growing market trends. For instance, the text describes how several companies are already expanding their fleets with vehicles that cater to environmentally conscious customers. Alongside this shift, there is a growing adoption of digital solutions such as mobile applications and online platforms that facilitate seamless, contactless rental experiences. This technological integration not only enhances customer convenience but also supports operational efficiencies, allowing companies to manage diverse fleets more effectively as they transition to greener options[1].
Changing Consumer Preferences and Market Opportunities
Consumer behavior in Europe is increasingly favoring sustainability, which shapes the strategies of car rental companies. A significant portion of the market is poised to benefit from a shift in consumer preferences – with over 50% of Europeans reportedly willing to choose electric cars if available. This behavioral shift is further bolstered by broader trends, such as the rising importance of sustainable travel options and the impact of remote work encouraging domestic travel. As these trends continue to evolve, rental companies are seizing the opportunity to cater to eco-friendly consumers by offering specialized rental services, including eco-conscious options for both leisure and business travel. This consumer-driven demand reinforces the need for dynamically adapting business models that prioritize environmental sustainability along with customer convenience[1].
Future Outlook and Competitive Positioning
Looking ahead to 2035, sustainability is expected to play a critical role in shaping the competitive strategies of car rental companies. Firms that adapt quickly to integrate electric and hybrid vehicles, while also investing in digital innovations, are likely to position themselves as leaders in the market. The commitment to sustainability is not merely about regulatory compliance; it is also a strategic move aimed at enhancing brand reputation and capturing a growing segment of environmentally aware consumers. The industry growth forecast, supported by progressive market trends and expanding tourism, further indicates that companies demonstrating early adaptation to these sustainable practices will reap the benefits of increased market share and customer loyalty. In summary, sustainability is set to redefine operational strategies, fleet management, and customer engagement within the European car rental industry by 2035[1].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Overview and Rationale
Regulators are increasingly scrutinizing the dominant position held by Google in the search and advertising markets, with a central focus on its Chrome browser. Recent proposals by antitrust authorities argue that Google’s control over Chrome—integral both as a web access point and as a data collection tool—has allowed the company to consolidate power, maintain a near-monopoly in online search, and shape advertising practices in ways that disadvantage rivals[1][4][11]. The idea of spinning out Chrome means that the browser would become an independent entity, separated from Google’s tightly integrated ecosystem, with the intention of promoting fairer competition and reducing self-preferencing practices that have stifled innovation from other players in the digital market[2][14].
Impact on the Digital Advertising Ecosystem
A central argument among regulators is that Chrome has long served as a cornerstone of Google’s advertising dominance. By integrating Chrome with a suite of data-driven advertising products—such as Google Ads and Analytics—the company has been able to collect detailed user data and channel this information to further enhance targeted advertising[1][7]. If Chrome were spun out, advertisers and digital marketing professionals could face significant disruption. On one hand, independent ownership might lead to a more balanced competitive landscape where multiple browsers—each with their own approaches to data privacy and ad delivery—compete on a level playing field. On the other hand, the transition could disrupt established advertising workflows, as tools formerly optimized for the integrated Google ecosystem may need to be reconfigured to work with a standalone Chrome[13][16]. This fragmentation could diminish the precision of targeted advertising and force marketers to reassess strategies across a more heterogeneous browser market[2][9].
Consumer Experience and Technological Implications
From a consumer perspective, the detachment of Chrome from Google’s broader ecosystem would be felt in several ways. Currently, many users enjoy a seamless experience that integrates Chrome with Google services like Search, Gmail, and Drive. Forced independence, however, may lead to changes in user interface design, altered privacy policies, and potential disruptions in service integration[3][5]. A new owner of Chrome would need to establish its own policies for data collection and protection, which may result in either enhanced privacy measures or, conversely, new vulnerabilities if support and investment in security measures decline[6][8]. Additionally, the technical challenges of transferring developer control and maintaining the open-source Chromium project could impact the pace of innovation and the stability of security updates. These technical uncertainties highlight the delicate balance between maintaining a high level of performance and assuring robust user privacy under a fragmented model[8][23][24].
Regulatory, Financial, and Market Competition Considerations
The proposed spin-out of Chrome is also expected to have broad regulatory and financial implications. Antitrust regulators argue that forcefully divesting Chrome would help dismantle the feedback loop that reinforces Google’s market dominance by linking its search engine with a near-universal browser[11][14]. Such a breakup could moderate the incidence of exclusionary deals—such as securing default status on devices—and open up new opportunities for competitors like Firefox, Safari, and emerging smaller browsers, potentially revitalizing innovation in the space[4][18][20]. However, there is substantial uncertainty about who might acquire Chrome and whether that entity would possess the deep pockets or technical expertise required to maintain the browser’s high standards. Financial analysts warn that the forced divestiture could lead to significant valuation shifts for Alphabet, especially if the separation weakens the synergistic revenue streams from advertising and AI investments that currently benefit from integrated user data[7][17][21]. In addition, potential buyers may face a steep integration challenge as they work to preserve the user base and stability of a product that some estimate is worth up to $20 billion, while also generating billions in advertising revenue[9][10][20].
Long-Term Market and Ecosystem Consequences

Looking ahead, a spun-out Chrome could transform the broader digital landscape. Increased browser diversity may lead to a more dynamic web environment where no single entity holds overwhelming influence over market standards and technology adoption[1][5]. This could foster more competitive search markets and engender innovation in ad tech by giving rivals improved access to key user data—subject, however, to new privacy and regulatory frameworks[12][15]. At the same time, the overall experience for users might be marked by fragmentation, as disparate browsers implement differing policies on tracking, privacy, and integration of features. The real impact will hinge on how well the transition is managed by regulators, Google, and any eventual new owner of Chrome. If handled effectively, the breakup could level the competitive playing field, benefiting consumers and smaller tech companies alike, though it may also bring short-term disruptions to advertising and digital service provision[16][19][22].
Conclusion

In summary, forcing Google to spin out Chrome is poised to trigger a major reshuffling of the digital ecosystem. The move is intended to reduce monopolistic distortions in online search and advertising, promote fairer competition, and empower alternative players in the market[1][4][14]. However, the implications are far-reaching and complex. Advertisers might face transitional disruptions and potential decreases in targeting efficiency, while consumers could encounter changes in service integration and privacy practices. Furthermore, the technical and financial challenges of managing a standalone browser may impact innovation, security, and overall market stability. Ultimately, the long-term benefits of increased competition will depend on the strategic decisions made during and after the breakup, and on how well new market entrants capitalize on the opportunity to reshape the digital landscape[7][13][17].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.