Discover Pandipedia
Pandipedia is the world's first encyclopaedia of machine generated content approved by humans. You can contribute by simply searching and clicking/tapping on "Add To Pandipedia" in the answer you like. Learn More
Expand the world's knowledge as you search and help others. Go you!

Vitamin D is essential for various physiological functions, including immune system function, bone health, and the growth and development of bones and teeth. It aids in the absorption of calcium and phosphorus, which are crucial for maintaining strong bones and teeth[1][2]. A deficiency can lead to conditions such as rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults, causing softening of the bones and associated pain[5][6].
Moreover, vitamin D may influence mood regulation and help reduce the risk of depression, particularly in individuals who are already deficient[2][4]. Given that adequate sun exposure is often insufficient, especially in winter, dietary sources and supplements become critical for maintaining optimal levels[3][6].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
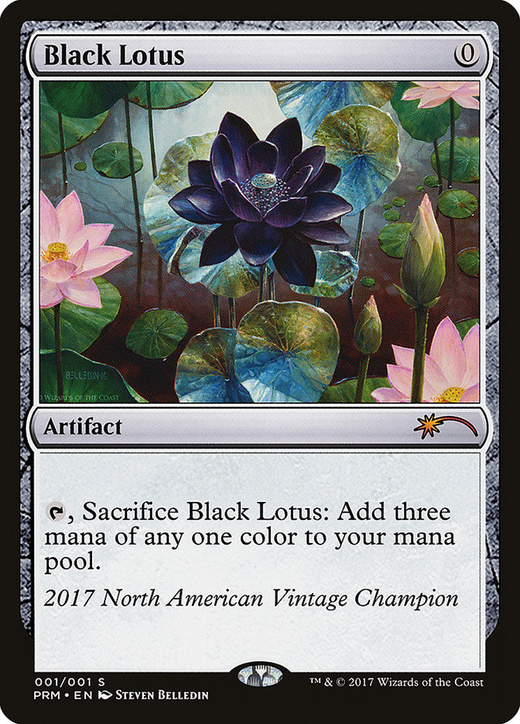
Black Lotus: The iconic card widely regarded as the most valuable and powerful Magic
The Gathering card, known for its ability to provide three mana of any color for free, with prices reaching as high as $3 million for a pristine condition Alpha edition in April 2024[7][8].
The One Ring: A unique 1/1 variant from the Lord of the Rings
Tales of Middle-earth set, it sold for $2 million to musician Post Malone, making it the most expensive trading card transaction in Magic history[6][8][9].
Lord of the Pit
An early MTG card from the Alpha set known for its power in gameplay, it sold for $105,000 in January 2023, making it one of the most valuable cards in the game's history[3][7].
Timetwister
A member of the Power Nine that allows players to reset their hand and graveyard, sold for $84,000 in a recent auction[9][7].
Ancestral Recall
Known for allowing a player to draw three cards for one mana, this card can fetch up to $38,500 at auction[3][9].

Vesuvan Doppelganger
A shapeshifter card that copies other creatures, sold for $63,000, exemplifying its collectible nature[4][9].
Underground Sea
A dual land that taps for blue or black mana, valuable in numerous decks, with recent sale prices reaching $36,100[9].

Shivan Dragon
A powerful creature card from Alpha, it has sold for $44,400 and is notable for its gameplay strength and collectibility[3][4].
Copy Artifact
This card allows for the replication of another artifact on the battlefield, with sales around $29,400[4][9].
Ancestral Recall (Alpha, PSA 10)
The highest-selling version of this card, featuring its original printing, sold for $38,500[4][9].
Black Lotus (Artist Proof, Beta)
An artist proof variant of Black Lotus fetched $616,000, showcasing its immense value[9].
Splendid Genesis
A unique promotional card celebrating the birth of Richard Garfield’s daughter, sold for $72,000 in June 2022[4].
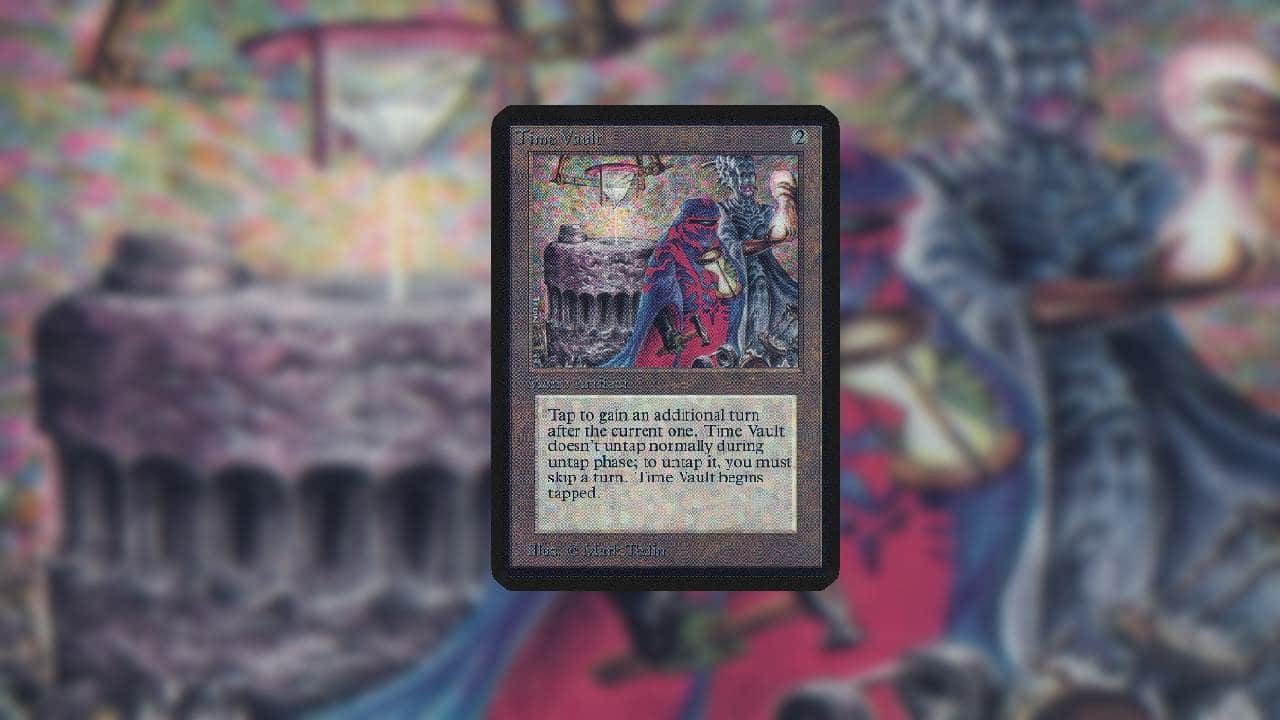
Time Vault
A card that can enable infinite turns when combined with other plays, it remains a high-value, collectible item[6][9].
The Tabernacle at Pendrell Vale
A legendary land that taxes creatures, known for its high price in the collector's market[9].
Bazaar of Baghdad
A critical card for discard strategies, valued highly and often priced above $40,000[6][9].
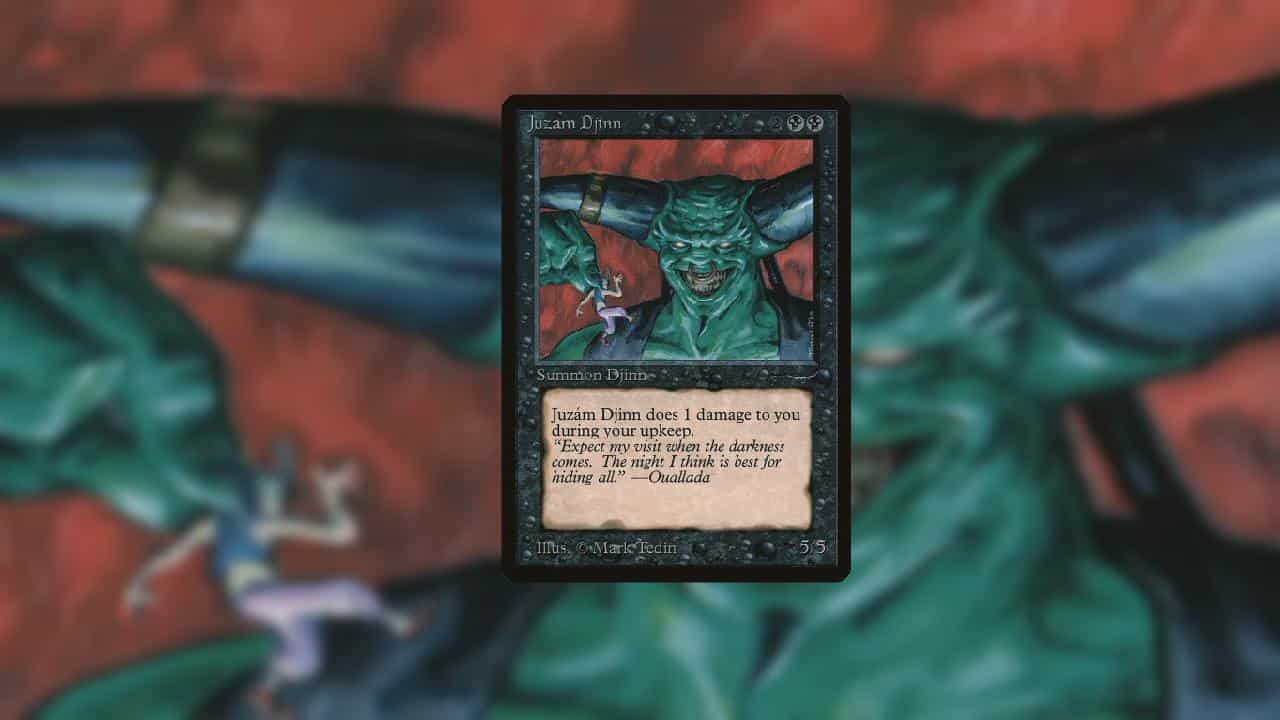

Juzam Djinn
A nostalgic card from Arabian Nights, valued for its history and rarity within the game[6].
Candelabra of Tawnos
Valuable in artifact decks, known for enabling mana rituals while reaching high auction prices[6][9].
Mox Sapphire
A blue mana artifact, part of the Power Nine, with notable sales reaching over $46,800[9].
Time Walk (Alpha, PSA 10)
Recorded sales similar to the standard Time Walk card but emphasizing its pristine condition within the Alpha set[9].
Candelabra of Tawnos
Useful for mana manipulation, this card finds itself frequently sought after within competitive formats[6].
Lord of the Pit (BGS 10)
A pristine condition variant of this card reached $105,000, highlighting its collector's demand and scarcity[9].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.

Self-deprecation is a common technique used by comedians to create humor and connect with their audiences. This style of humor involves making oneself the target of jokes, highlighting personal flaws or shortcomings. It is often perceived as an embodiment of the human condition, allowing both the performer and the audience to confront and laugh at their imperfections.
Understanding Self-Deprecation
Comedians utilize self-deprecating humor as a way to navigate their own insecurities while simultaneously entertaining their audience. According to one perspective, 'self-deprecating humor is most emblematic of the human condition. We’re all flawed in ways that if we don’t laugh about, we’ll cry'[2]. This humor serves as a coping mechanism, allowing comedians to deal with their vulnerabilities and share them in a way that resonates with others.
In the context of performance, self-deprecation acts as a protective barrier; comedians might find that there is 'absolutely no criticism that you can throw at a comic who is mocking himself that’s gonna be any worse than what they’ve already turned into material'[2]. This technique not only draws laughter but also preemptively disarms potential criticism from the audience.
Connection with the Audience
Self-deprecating humor establishes a rapport with the audience. By openly acknowledging their flaws—whether it’s about their appearance, intelligence, or life choices—comedians create a space of relatability. As Jim Gaffigan articulates, the appeal of self-effacing comedy lies in 'the appeal of humility which I think we’re really kind of grappling for'[1]. In doing so, comedians foster a sense of comfort and ease among audience members, who may see reflections of their own struggles.
Audiences often appreciate the transparency that self-deprecating humor entails. When comedians voice insecurities they share with the crowd, it evokes laughter as a collective acknowledgment of shared human experience. The surprise factor plays a role as well; when a comedian humorously critiques themselves, it often aligns with what the audience might have been thinking, producing a delightful, unexpected comedic moment[1].
Psychological Underpinnings

Self-deprecating humor also taps into deeper psychological dynamics. Gaffigan notes a common 'victimization complex' that many people experience, suggesting that everyone has their own struggles, even if they are not comparable to greater societal issues[1]. This shared recognition of personal battles can empower audiences, fostering empathy and understanding. Comedians can explore this theme humorously, which encourages both the performer and their audience to find comfort in their vulnerabilities.
Moreover, studies have demonstrated that comedians often display high levels of emotional and social intelligence, which are crucial for understanding and engaging their audiences effectively. This intelligence allows them to adjust their performances to resonate well with diverse audiences, utilizing self-deprecating humor to elicit laughter while being sensitive to the perceptions of those present[3].
Balancing Self-Deprecation and Self-Defeating Humor
While self-deprecating humor can be effective, there is a thin line between self-deprecation and self-defeating humor. Self-defeating humor, which can often signal low self-esteem, may be less well-received. Comedians who rely heavily on self-defeating humor might be perceived as insecure or lacking confidence, which can undermine their appeal[3]. Successful comedians often strike a balance, using self-deprecation to connect with their audience while ensuring they do not fall into a pattern of negative humor that could diminish their effectiveness on stage.
In this regard, Gaffigan emphasizes the importance of self-awareness and the nuances of humor: 'the line of self-effacing just as the line of irreverence is always moving,' indicating an understanding of the evolving nature of comedic boundaries[1]. Mastering the art of self-deprecation without tipping into self-defeating humor can enhance a comedian's stage presence, making them more relatable and endearing.
Conclusion
Comedians skillfully employ self-deprecating humor as a method to engage with their audiences, explore personal vulnerabilities, and foster a sense of shared humanity. This comedic style serves functional purposes, allowing performers to confront criticism preemptively and connect with listeners on an emotional level. While mastering this humor style requires a delicate balance, successful comedians leverage it to create moments of joy and laughter that resonate deeply with their audiences. By doing so, they not only entertain but also invite collective reflection on the imperfections of the human experience.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
iPhone 16 Pro Max
The best iPhone, offering a larger 6.9-inch screen, upgraded camera, and impressive battery life of over 18 hours on tests, while introducing Apple Intelligence features[1][4].

Samsung Galaxy S24 Ultra
The top Android flagship with a stunning display, a powerful Snapdragon 8 Gen 3 processor, and improved AI capabilities; also offers excellent camera performance with its 200MP main sensor[2][3][4].
Google Pixel 9 Pro
Known for its impressive camera capabilities and AI features, including a new ultrawide sensor and substantial image processing advancements[1][2][4].

Google Pixel 8a
The best budget phone, offering excellent camera performance, AI features, and seven years of software support at a price under $500[1][4][8].


OnePlus 12
A high-value Android flagship offering strong specs, great camera performance, and fast charging capabilities[2][3][10].
Asus ROG Phone 8 Pro
The best gaming phone with Snapdragon 8 Gen 3, a long-lasting battery, and features that benefit gamers[3][10].

Google Pixel 9
A cheaper alternative to the Pixel 9 Pro, equipped with similar AI features but lacking a telephoto lens; excellent for photography enthusiasts[2][10].
Samsung Galaxy Z Fold 6
The best large-screen foldable phone, with an expansive inner screen and multiple productivity features[3][4].
Samsung Galaxy S24 FE
A more affordable version of the Galaxy S24, still featuring premium specifications and seven years of software support[1][2].

Apple iPhone 15 Pro Max
A powerful device with a durable titanium design, a stunning display, and advanced camera features[6][8].
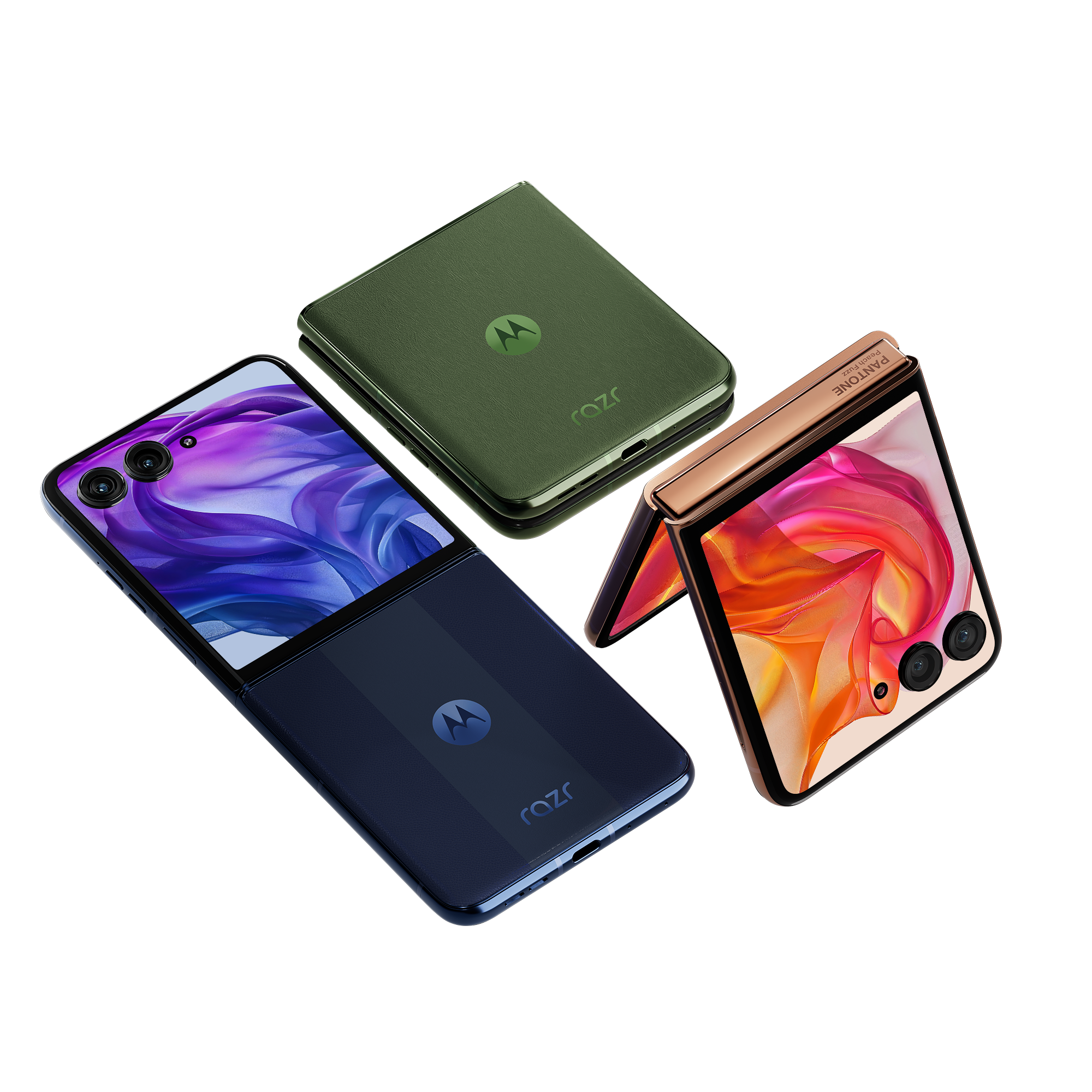
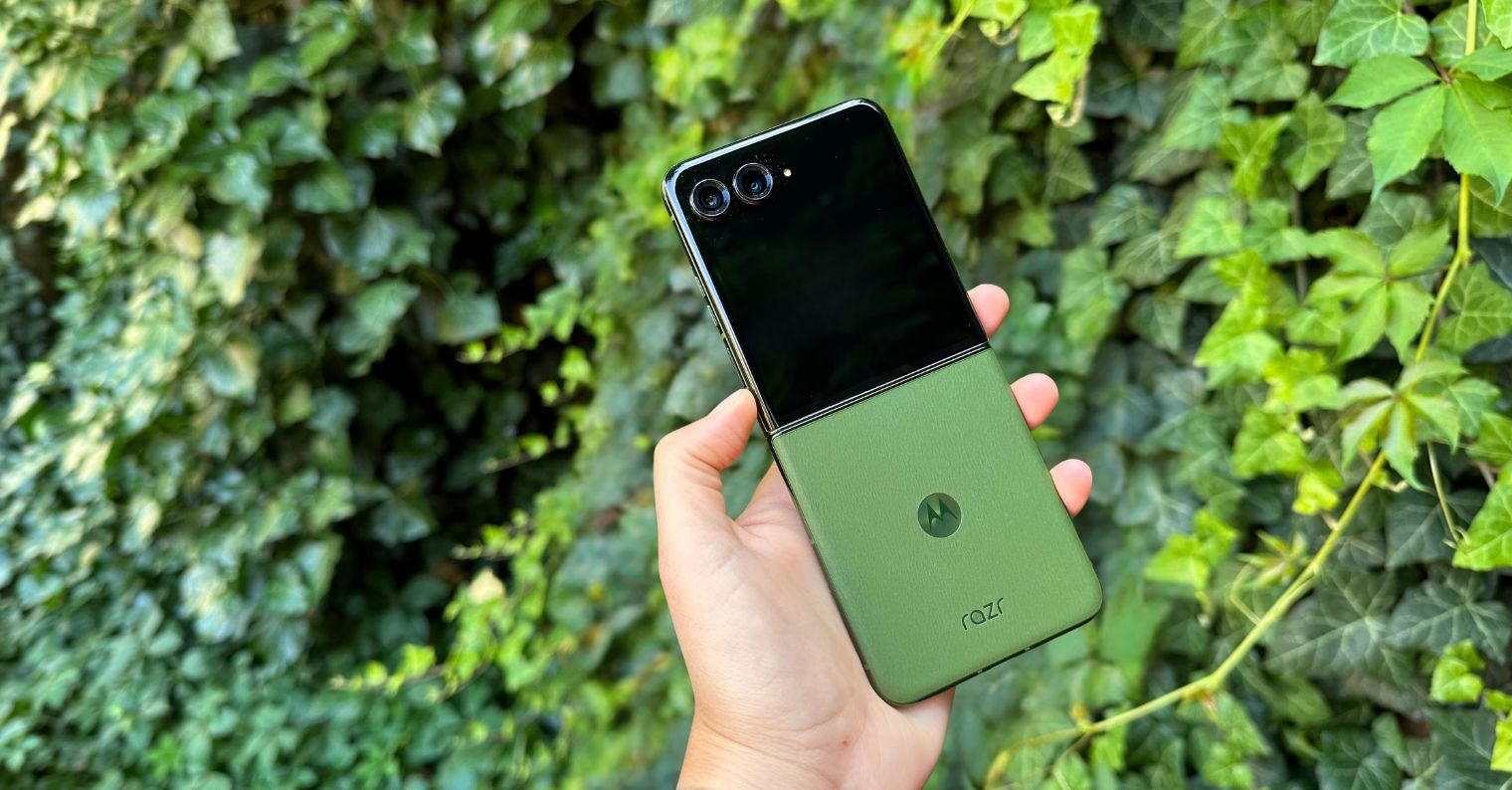
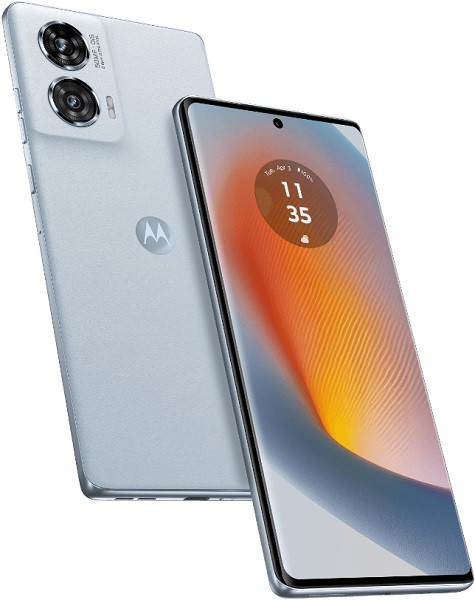
Motorola Razr 50 Ultra
The best clamshell foldable, featuring a large cover display and decent camera capabilities for a compact phone[3][10].
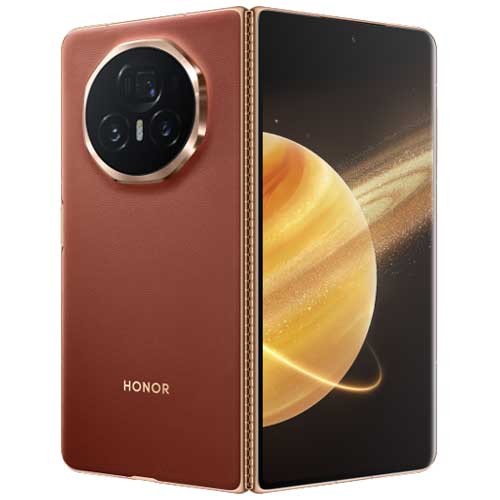
Honor Magic V3
A thin and light book-style foldable with strong performance and good battery life[3][4].
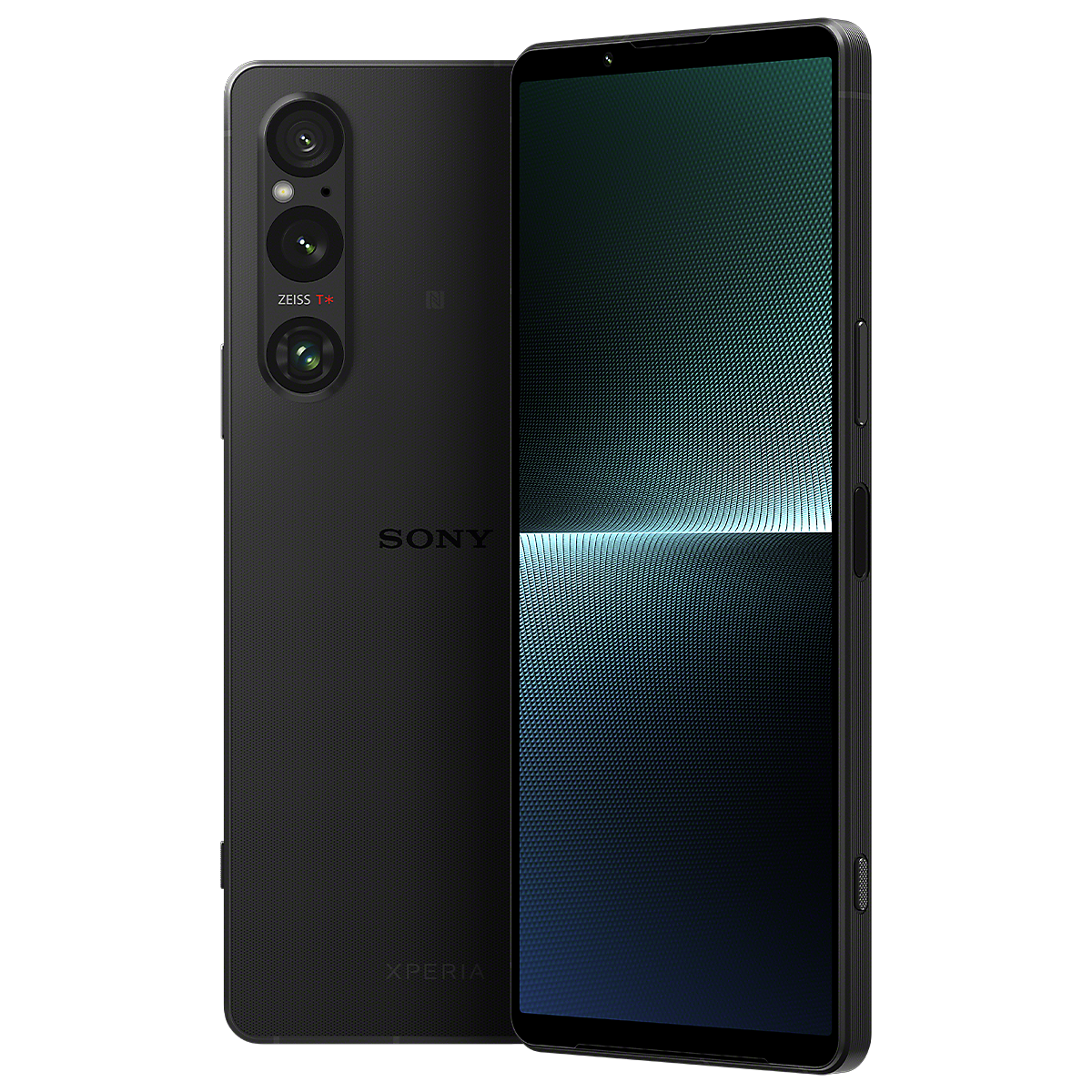
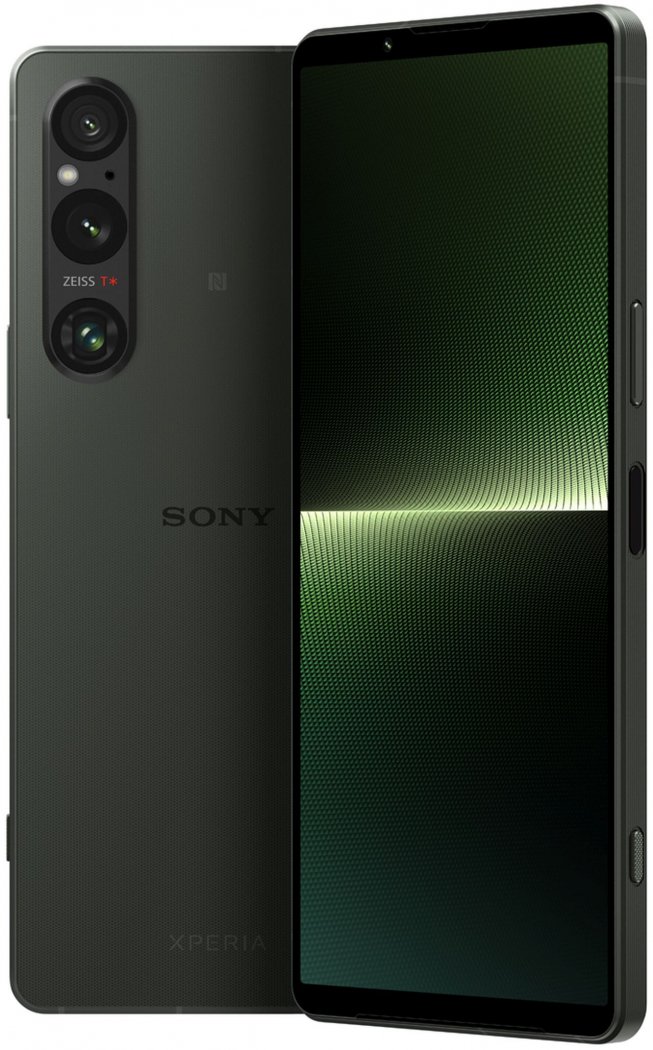
Sony Xperia 1 V
Known for its impressive display and camera accuracy, particularly in color reproduction[8][10].
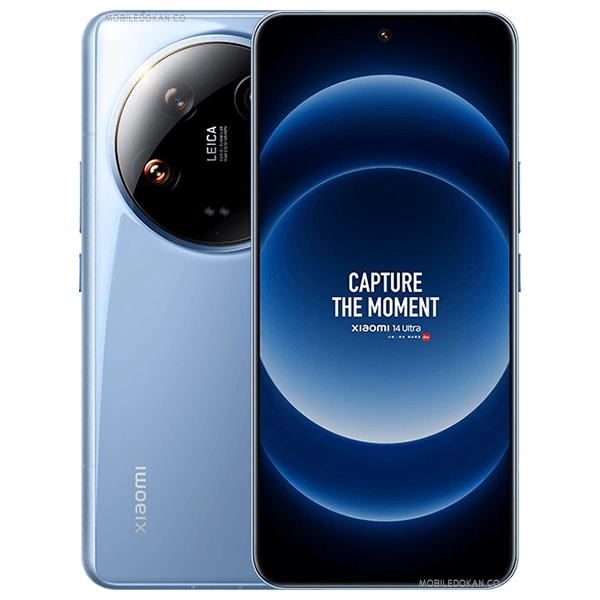
Xiaomi 14 Ultra
A competitive camera phone offering high-resolution photography and excellent overall performance[9][10].
OnePlus 12R
A more affordable option in the OnePlus lineup, delivering good performance and impressive battery life[1][9].
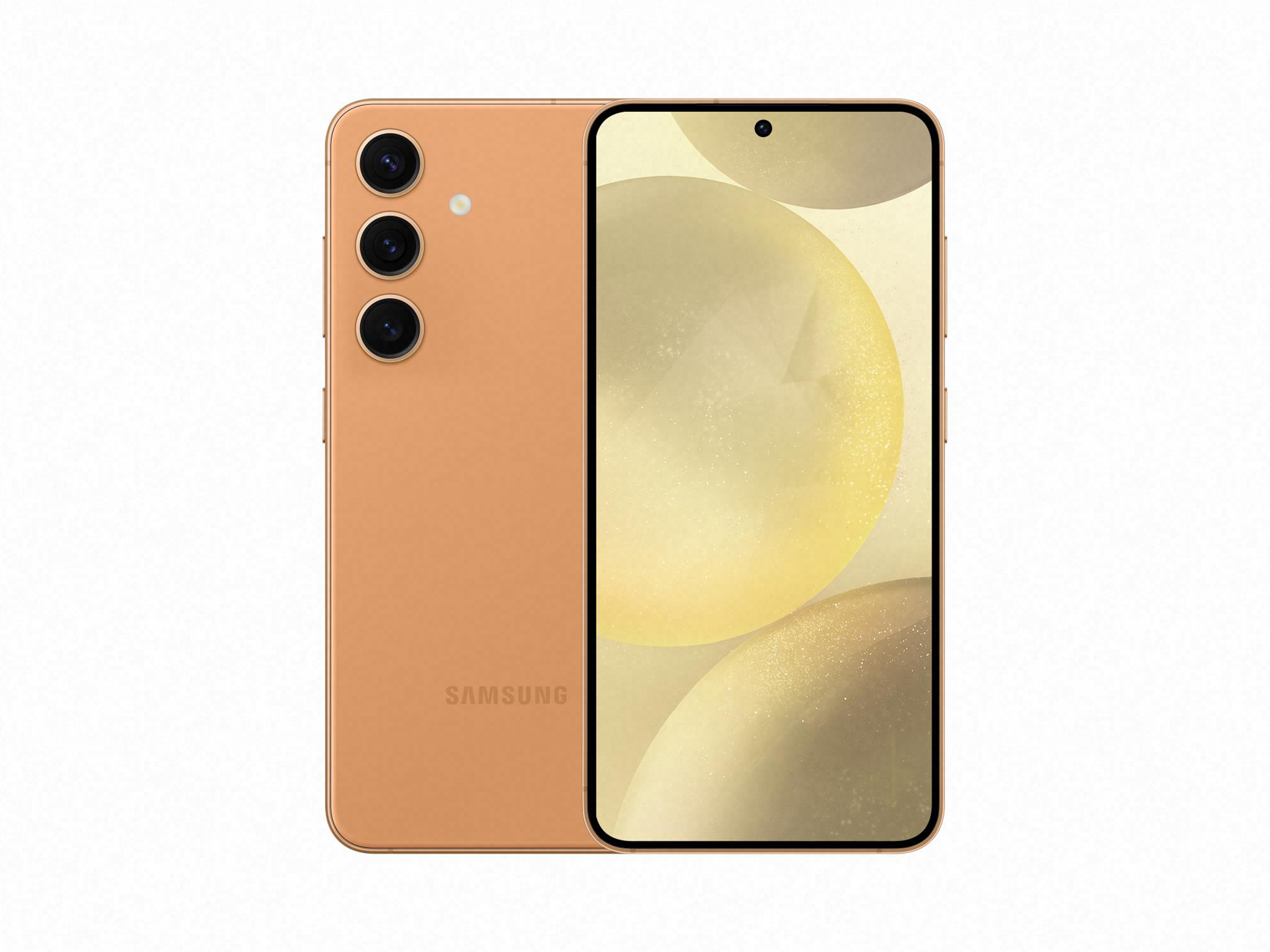

Samsung Galaxy S24
A flagship that balances features and price, with solid performance for most users[3][9].
Google Pixel 8
A step below the Pixel 9, but still boasts excellent software support and camera capabilities[4][9].
Motorola Edge 50 Fusion
An affordable option with good performance, a vibrant display, and a strong camera setup[9][10].
Asus ROG Phone 8
Combines gaming capabilities with everyday usability, designed for gamers who value performance[3][4].

Nothing Phone (2)
A unique design with a clear back, customizable LED notifications, and solid performance for everyday tasks[9][10].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Animals have evolved a diverse array of feeding strategies, adapting their behaviors and physiological traits to maximize their chances of survival in varying environments. These adaptations allow them to locate, acquire, and consume food efficiently, providing insights into the intricate relationship between species and their ecosystems.
Physical Adaptations for Feeding

Many animals have unique physical adaptations that enhance their ability to feed. For instance, the long neck of a giraffe has evolved specifically to reach leaves high up in trees, allowing them to access a food source that few other herbivores can utilize. This structural adaptation enables giraffes to thrive in the grasslands of East Africa, where competition for lower foliage can be fierce[6].
In the aquatic realm, fish are equipped with gills, which allow them to extract oxygen from water efficiently. This adaptation is vital for their survival in a submerged environment. Additionally, animals like whales have developed powerful lungs to extract oxygen from the surface, showcasing another form of physiological adaptation[4].
Predators often exhibit sharp claws or teeth that facilitate hunting and eating. For example, crocodiles possess strong jaws and serrated teeth that help them grasp and hold onto slippery prey, such as fish or birds, in their aquatic habitats[7]. Similarly, the specialized beaks of birds, such as raptors, allow them to catch and tear flesh effectively, supporting their carnivorous diet[9].
Behavioral Adaptations in Foraging
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/2a/1e/2a1e4c35-2d3d-44d0-916c-23606a5b65da/42-28850284edit.jpg?AWSAccessKeyId=AKIAQT4QH3CHNPX5WHX7&Signature=vTgHLHA%2B0oTSkhi3tj5%2BYh%2F84wc%3D&Expires=1750552490)
Behavioral adaptations are equally critical in shaping feeding strategies among animals. Many species exhibit foraging behaviors that optimize their search for food. For instance, nocturnal animals like raccoons take advantage of the night to scavenge through garbage and hunt in the cover of darkness, reducing the risk of predation while maximizing feeding opportunities[7].
Migration is another significant behavioral adaptation seen in various species. Birds often undertake long migrations to follow food sources or suitable breeding grounds, such as the Arctic Tern, which travels vast distances between breeding and wintering locations. This seasonal movement ensures access to abundant resources and helps them avoid competition during certain times of the year[9]. Fish like salmon are also known for their migratory habits, swimming upstream to spawn in nutrient-rich freshwater streams[9].
Cooperative and Competitive Strategies
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/03/09/0309200c-28c4-4e87-b4cd-0709e3ddfd4a/42-33360317edit.jpg?AWSAccessKeyId=AKIAQT4QH3CHNPX5WHX7&Signature=J0ggqqNNUPZUSGBhRgHGGE1qxXw%3D&Expires=1750552490)
Some animals have evolved to use collaborative methods to enhance their feeding strategies. For example, wolves hunt in packs, allowing them to take down larger prey by coordinating their efforts. This social behavior increases their hunting success rate, enabling them to effectively feed their group[9]. Similarly, elephants exhibit cooperative foraging, where individuals work together to dig for roots or access water in arid environments, demonstrating social behavior that boosts their survival[7].
Competition among species can also shape feeding strategies. Predators and prey often develop adaptations in response to one another; for instance, while prey species enhance their stealth and speed to evade capture, predators become more efficient hunters. The concept of mimicry plays a role here as well. Some harmless species mimic the appearance of toxic or dangerous organisms to deter predators, effectively reducing their likelihood of being targeted while feeding[7][9].
Specialized Feeding Adaptations

Certain species have developed unique adaptations tailored to their specific diets. Carnivorous plants, for example, have evolved mechanisms to capture and digest insects, supplementing their nutrient intake in nutrient-poor environments. These adaptations allow them to thrive in conditions where other plants may struggle[6][7].
Moreover, the Texas blind salamander has adapted to its lightless cave environment by evolving enhanced sensitivity to vibrations in water, compensating for its lack of eyesight. This adaptation is essential for locating prey in complete darkness, demonstrating how animals can adjust their sensory modalities to improve their feeding efficiency[8].
In the harsh environments of deserts, animals like camels have evolved both physical and behavioral adaptations for feeding. They can store fat in their humps, allowing them to survive long periods without water and regulate their energy use efficiently[7]. This ability to adjust their feeding strategies to utilize limited resources effectively is crucial for survival in such extreme habitats.
Conclusion
Through a combination of structural, behavioral, and physiological adaptations, animals have developed diverse feeding strategies that enable them to survive and thrive in a plethora of environments. From the impressive foraging tactics of wolves to the specialized beaks of birds of prey, these adaptations underscore the intricate interconnectedness of life and the driving force of natural selection in shaping behaviors and traits that foster survival in the ever-changing landscape of the animal kingdom. Understanding these adaptations not only enhances our knowledge of biodiversity but also emphasizes the importance of conservation efforts to protect these complex ecosystems and the remarkable species that inhabit them.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Effective study techniques are essential for learners at any stage, particularly for beginners who may be adjusting to more rigorous academic expectations. Understanding and implementing various methods can significantly enhance the learning experience and improve retention of information. Below are several techniques that aspiring students can adopt to make their study sessions more productive.
The Importance of Organization and Planning
Being organized is a foundational aspect of effective studying. Carrying a homework planner at all times ensures that students keep track of assignments, projects, and tests. This practice helps prevent forgetting important tasks and allows for better time management in preparing for exams or completing homework[1]. Additionally, setting up a study schedule that includes specific goals for each session can guide learners in effectively pacing their studies across different subjects[2][3].
Active Engagement During Learning

One effective technique for beginners is to practice active listening during classes. Concentrating fully on what teachers are saying and taking notes in one’s own words not only aids comprehension but also helps in processing the material more deeply[1]. When students hear a topic or concept being taught, they should avoid distractions, such as phones or social media, to maintain focus.
Furthermore, after class, reviewing and expanding upon notes strengthens retention. This practice transitions information from short-term to long-term memory, which is crucial for performance in upcoming tests[1].
Discovering Personal Learning Styles
Understanding one's learning style is crucial in tailoring study techniques that best suit individual needs. Techniques like the Feynman Technique encourage students to teach what they've learned to someone else, making it easier to grasp concepts deeply. Teaching necessitates simplifying knowledge, which reveals any gaps in understanding[3].
Experimentation with various methods, such as visual aids or verbal recitations, contributes to identifying what techniques resonate most effectively with a learner’s style[4].
Implementing Effective Study Strategies
Spaced Repetition and Active Recall
Two of the most widely recognized techniques for memory retention include spaced repetition and active recall. Spaced repetition involves revisiting material at increasing intervals, which helps combat the forgetting curve inherent in human memory. For example, instead of cramming for an exam, students might review their notes multiple times over several days[3][4].
Active recall, or self-testing, encourages students to retrieve information without looking at the source material. Utilizing methods like flashcards or practice tests helps solidify knowledge and identify areas needing improvement[3][5].
The SQ3R and PQ4R Approaches
The SQ3R method—Survey, Question, Read, Recite, Review—is designed to enhance understanding and retention of reading materials. Students begin by skimming the text (Survey), posing questions (Question), thoroughly reading (Read), teaching back what they learned (Recite), then reviewing the material[5]. Similarly, the PQ4R method (Preview, Question, Read, Reflect, Recite, Review) provides a structured approach that encourages critical thinking and engagement with the material[5].
Utilizing the Pomodoro Technique
Time management is also a key factor in effective studying. The Pomodoro Technique suggests dividing study sessions into intervals (typically 25 minutes) followed by short breaks (5 minutes). After completing four intervals, a longer break is taken. This method not only prevents burnout but allows for sustained focus during study sessions[4][6].
Creating a Conducive Study Environment
A well-organized and quiet study space can significantly enhance concentration and productivity. The study area should be free from distractions and provide all necessary materials at hand. Personal preferences regarding lighting, seating, and ambient noise levels can also influence study effectiveness. Some individuals may prefer complete silence, while others might find background music beneficial[1][6].
Maintaining a clutter-free, organized space helps to minimize anxiety and improve focus, which is pivotal for effective learning[6].
The Role of Consistency and Reflection
Consistency is key in developing effective study habits. Establishing a daily routine not only promotes discipline but also enables better memory retention[6]. After each study period, reflecting on what techniques were effective or what can be improved is essential for ongoing development in study skills. This practice helps to adapt strategies for future tasks, ensuring continuous improvement and greater success in studies[4][5].
Conclusion

By integrating these effective study techniques—such as organization, active engagement, understanding personal learning styles, employing specific study methods, creating a conducive environment, and establishing consistency—beginners can enhance their academic performance significantly. With patience and practice, mastering these techniques will not only aid in immediate educational goals but also cultivate lifelong learning skills.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.
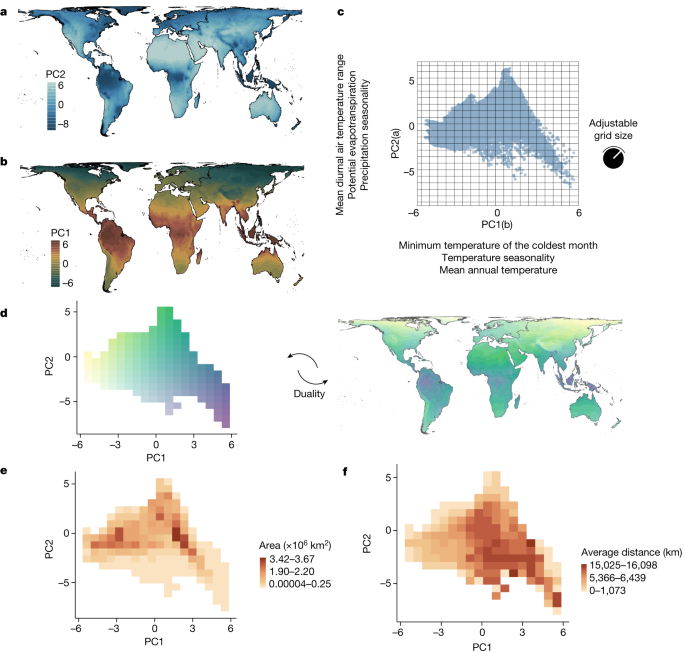
Biodiversity, defined as the variety and variability of life on Earth, is critically shaped by geographic factors. Geography influences not only climate and habitat variety but also species distribution patterns across different environments. This report synthesizes insights into how geographical elements impact biodiversity, drawing on recent research findings.
Geographic Variability and Biodiversity
The relationship between geography and climate plays a vital role in determining the diversity of life. Regions near the equator, characterized by stable, warm, and humid environments, tend to support diverse ecosystems, leading to higher species richness compared to cooler or drier regions. This phenomenon is evident in the tropics, where climatic conditions promote a great variety of plant and animal life that is often not found elsewhere[2][3][6].
Geographic barriers, such as mountains and oceans, also significantly contribute to biodiversity by preventing gene flow and fostering unique species evolution. For example, the Himalayas create diverse ecological conditions leading to varied life forms at different elevations[2]. Similarly, isolated islands and unique geographic formations are often biodiversity hotspots, housing large numbers of endemic species[3].
Climate's Role in Species Distribution
Climate is a primary driver of biodiversity, with its variability across geographic landscapes leading to different ecological niches. For instance, the patterns of species richness observed globally align strongly with temperature and water availability, which are influenced by geographical factors[1]. The concept of 'climate space' offers a fresh perspective on biodiversity, emphasizing the need to consider how the geography of climate (area and isolation) affects species richness beyond mere climatic conditions[3][6].
A study revealed that greater species richness in warmer, humid regions is not solely due to climatic conditions themselves but also to how these climates are distributed across the Earth's surface. This approach highlights the importance of considering both the extent of a given climatic condition (climate area) and its isolation, which can lead to increased opportunities for speciation and reduced extinction rates[1][5].
Historical and Contemporary Influences
The evolution of biodiversity is also shaped by historical geographic changes. Over time, climate change, continental drift, and the emergence of geographic barriers alter the distribution and isolation of species. These historical processes mean that species must adapt to their environments, impacting their evolutionary trajectories[7]. For example, during glacial periods, shifts in climatic conditions led to population bottlenecks that have long-lasting effects on genetic diversity within species[7].
In contrast, current geographic configurations significantly influence the dynamics of biodiversity. Urbanization, agriculture, and deforestation often occur in ecologically favorable areas, leading to habitat loss and fragmentation, which exacerbate the decline of biodiversity[2][5]. Understanding how geography interacts with these contemporary changes is essential for conservation efforts aimed at preserving biodiversity.
The Area-Isolation Hypothesis
Recent research suggests modifying the Area Hypothesis—which explains patterns of species diversity based on geographic area—into an Area-Isolation Hypothesis. This refined understanding takes into account the geographical distribution and isolation of similar climatic zones[1][5]. For instance, while tropical climates cover extensive areas, they are also highly fragmented and isolated, promoting speciation through increased ecological differentiation[1][3].
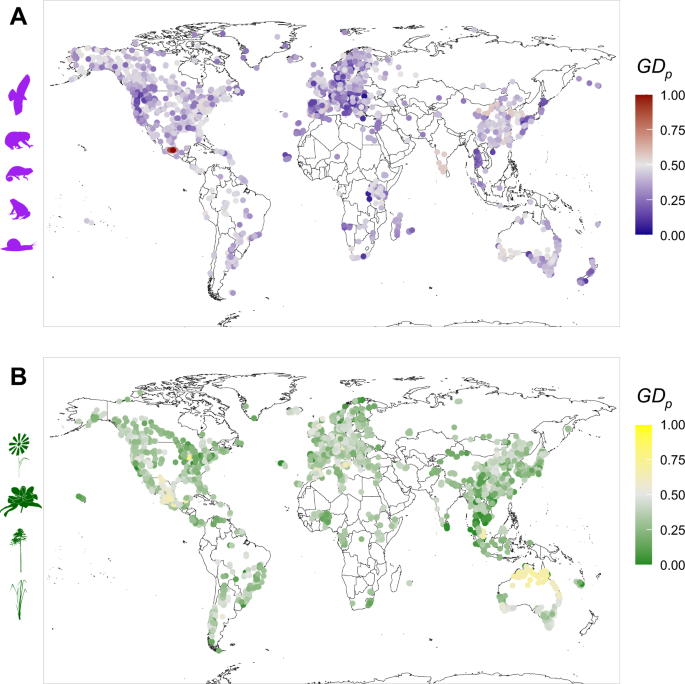
Findings indicate that regions with larger and more isolated climates tend to exhibit not only increased species richness but also greater turnover rates in community composition. This suggests that independent pools of species evolve due to dispersal limitations and historical fluctuations in climate geography[5][6].
Biodiversity Conservation in the Face of Climate Change
Understanding the interplay between geography and biodiversity is crucial for effective conservation strategies. As anthropogenic climate changes alter geographic distributions and climate dynamics, it becomes imperative to adapt conservation frameworks that consider the geography of climate. This includes recognizing how climate area and isolation contribute to species richness and developing targeted conservation measures for areas at risk of fragmentation and habitat loss[2][3].

The urgent need to account for geographic variations in climate impacts signifies that conservation efforts must be nuanced and context-driven, taking into consideration the distinct ecological and evolutionary processes shaped by geographic features[1][4]. By integrating geographical and climatic understandings, conservation strategies can be more effective in mitigating biodiversity loss in the face of ongoing climate change.
In summary, the interplay between geography and biodiversity is a complex narrative shaped by environmental conditions, historical changes, and contemporary challenges. Recognizing and understanding these intricacies is crucial as we strive to preserve the rich tapestry of life on our planet amidst the changing global landscape.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

The advent of autonomous vehicles (AVs) presents a potential paradigm shift in transportation, bringing with it a mixture of enthusiasm for innovation and apprehension about societal impacts. A thorough examination of the advantages and disadvantages reveals nuances that merit close attention.
Benefits of Autonomous Vehicles
Safety Improvements

A fundamental advantage of autonomous vehicles is their capacity to reduce traffic accidents, as they remove human error—the leading cause of over 90% of road accidents. High-precision sensors and advanced algorithms enable AVs to respond to immediate surroundings more effectively than human drivers. It has been suggested that fully autonomous vehicles could significantly lower traffic-related fatalities by minimizing driver-related issues such as fatigue and distraction, which account for numerous incidents on the roads[3][6][11].
Increased Mobility and Accessibility
Autonomous vehicles promise greater mobility for individuals who cannot drive due to disabilities, age, or other factors. By providing independent transportation options, AVs can free such individuals from dependence on public transport or others, thus improving their quality of life[1][4][10]. The convenience of AVs may also attract users from various demographics, extending their potential utility across urban and rural communities.
Reduced Traffic Congestion
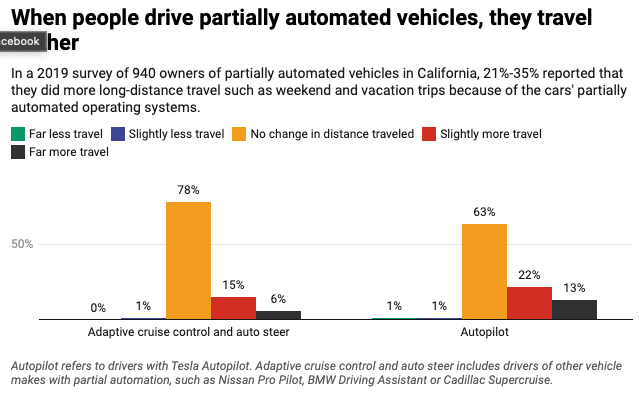
The introduction of AVs could lead to smarter traffic management and decreased congestion. Connected AVs are capable of communication with each other and infrastructure, allowing for optimized routes and more efficient use of road space. This interconnectedness can significantly reduce stop-and-go traffic and encourage more fluid flow, potentially decreasing overall travel times[6][10].
Environmental Benefits

When properly integrated, AVs have the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions considerably. Many current AV technologies are being developed with electric propulsion, which can lead to lower fuel consumption. Advanced driving algorithms designed for eco-driving can further enhance energy efficiency, resulting in decreased environmental footprints[1][5][8]. Some models predict that the overall energy use and emissions could drop substantially as AVs gain traction alongside the transition to renewable energy sources[11].
Land Use Optimization
The shift toward autonomous vehicles may redefine urban landscapes by decreasing the need for extensive parking infrastructure. As AVs can drop passengers off and park themselves in remote locations, urban areas may repurpose parking spaces for green areas or housing, potentially revitalizing city environments[12][3].
Drawbacks of Autonomous Vehicles
Job Displacement
A major concern surrounding the mass adoption of autonomous vehicles is their potential to displace millions of jobs within the driving industry. Professions such as taxi, truck, and delivery drivers face significant threats from automation, as companies may opt for AVs to cut costs associated with human labor. This employment shift could exacerbate economic inequalities and challenge workers to find alternative employment opportunities[9][10][12].
Liability and Legal Challenges
The rise of AVs introduces complex liability questions regarding accidents. Determining responsibility—whether it lies with the vehicle owner, manufacturer, or software developer—remains unresolved. This ambiguity could lead to significant legal disputes and challenges for the insurance industry, which is currently grappling with the implications of automated driving technology[6][10][9].
Cybersecurity Risks
As AVs rely heavily on software and connectivity, they may be susceptible to cyberattacks. Hackers gaining control of AV systems pose a serious risk, as compromised vehicles could be turned against their passengers or used in malicious activities[8][9]. The extensive data collection required to operate AVs also raises privacy concerns, particularly regarding how personal information is stored and used.
Environmental Considerations
While there is potential for reduced emissions from autonomous electric vehicles, there are caveats. If the energy sources used to charge these vehicles remain non-renewable, their environmental benefits could be undermined. Moreover, increased convenience may encourage longer commutes and higher overall vehicle miles traveled, potentially leading to greater energy consumption and emissions overall[11][12].
Uncertain Public Acceptance
Finally, despite the technological advances, a significant portion of the public remains skeptical about fully autonomous vehicles. Factors contributing to this hesitance include fears over safety and a lack of understanding regarding the technology’s capabilities and limitations. Effective public education and trust-building will be essential to facilitate the wider acceptance of AVs in society[9].
Conclusion
The development of autonomous vehicles holds enormous promise, poised to revolutionize transportation through enhanced safety, accessibility, and efficiency. However, it also presents serious challenges that society must navigate, such as job displacement, liability questions, and cybersecurity risks. As this technology continues to evolve, ongoing discourse and innovative policy-making will be necessary to maximize benefits and mitigate drawbacks. The balance struck between these competing interests will ultimately shape the future landscape of mobility.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.


























































?unique=673d1de)
?unique=9ef4739)














