Discover Pandipedia
Pandipedia is the world's first encyclopaedia of machine generated content approved by humans. You can contribute by simply searching and clicking/tapping on "Add To Pandipedia" in the answer you like. Learn More
Expand the world's knowledge as you search and help others. Go you!

In Gemini 2.5, we have focused on improving helpfulness / instruction following (IF), specifically to reduce refusals on such benign requests
Unknown[1]
The 2.0 models are substantially safer. However, they over-refused on a wide variety of benign user requests
Unknown[1]

Our primary safety evaluations assess the extent to which our models follow our content safety policies
Unknown[1]
That is, we find it possible that subsequent revisions in the next few months could lead to a model that reaches the CCL. In anticipation of this possibility, we have accelerated our mitigation efforts
Unknown[1]
We are continuing to evolve our adversarial evaluations to accurately measure and monitor the resilience of increasingly capable Gemini models, as well as our adversarial training techniques
Unknown[1]
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.

Using natural makeup offers several health and environmental benefits. Natural ingredients, such as plant extracts and minerals, are often more gentle on the skin and can help prevent irritation and allergic reactions, especially for those with sensitive skin[1][4]. They typically lack harmful synthetic chemicals like parabens and sulfates, which are linked to various health issues[2][5].
Moreover, natural makeup is often produced sustainably and ethically, minimizing the environmental impact[5][6]. By choosing natural products, consumers support brands that prioritize eco-friendly practices and contribute to reducing pollution associated with conventional cosmetics[3][6]. This shift promotes not only healthier skin but also a more sustainable planet.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Melatonin gummies are a popular over-the-counter sleep aid that can help improve sleep quality, particularly for those with certain sleep disorders like delayed sleep-wake phase syndrome and jet lag[3][5]. They work by supplementing the body's natural melatonin, which regulates the sleep-wake cycle, and can help individuals fall asleep faster[3][4]. However, melatonin supplements, including gummies, are not FDA-regulated, leading to variability in dosage and quality, which poses risks of overdose or side effects such as nausea and dizziness[3][2].
It's important to consult a healthcare provider before using melatonin gummies to ensure appropriate dosage and check for potential interactions with other medications[5][2]. Additionally, the gummies should not be the first approach for sleep troubles; good sleep hygiene practices should also be followed[1][2][5].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

Elephants are renowned for their complex social structures, which are primarily matriarchal. These structures revolve around tightly-knit family units that promote cooperation, emotional bonds, and survival within various environmental contexts.
Matriarchal Leadership
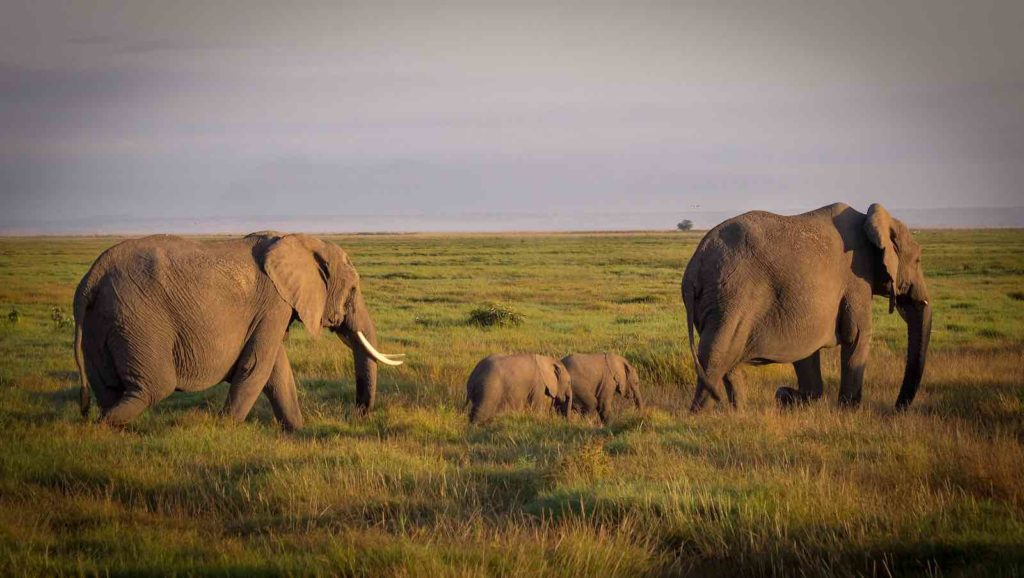

At the center of each elephant herd is the matriarch, typically the oldest female. This matriarch plays a critical role in leading the herd, making key decisions about foraging, migration, and social relations. Her accumulated wisdom is indispensable, especially in finding food and water, while also imparting knowledge to younger herd members[1][11]. The matriarch's dominance in the social hierarchy is not just due to her age but also her experience and social skills, which earn her the respect of the entire group[1][3].
Herd Composition
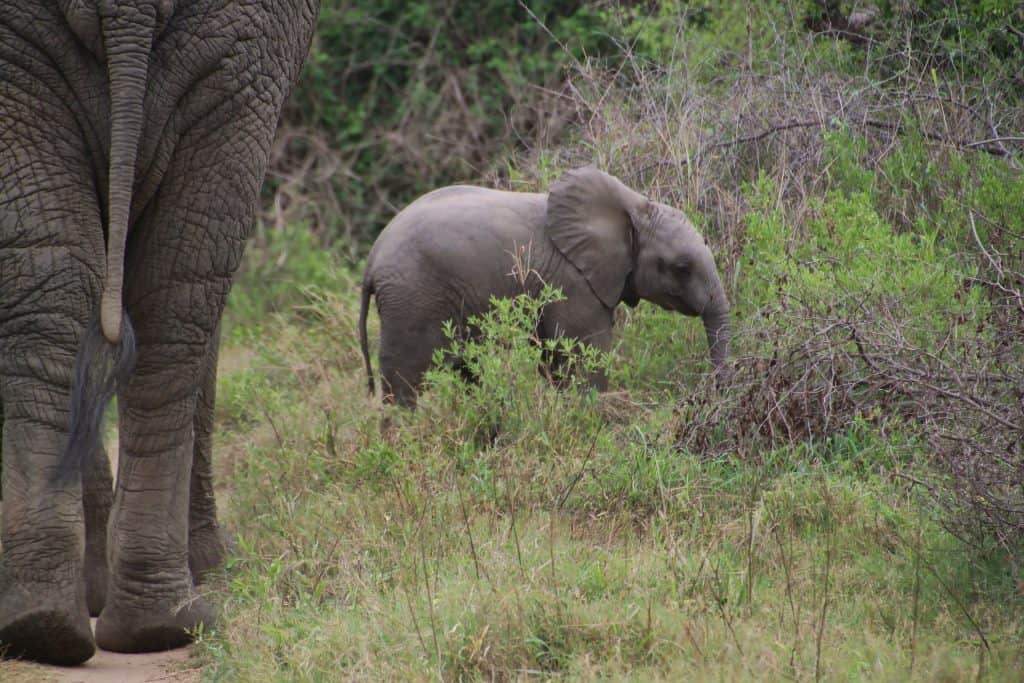

An elephant herd typically consists of several generations of females, including the matriarch, her daughters, and their offspring[4][10]. Female elephants generally remain with their natal herds for life and share strong familial bonds characterized by cooperation in nurturing and protecting the young. Allomothering, where non-maternal females assist in raising calves, is common and ensures that all young elephants receive the necessary care and education[2][3][5]. This collective rearing is vital for the survival of the calves, as it increases their chances against predators and environmental stressors.
Male Elephants and Social Dynamics
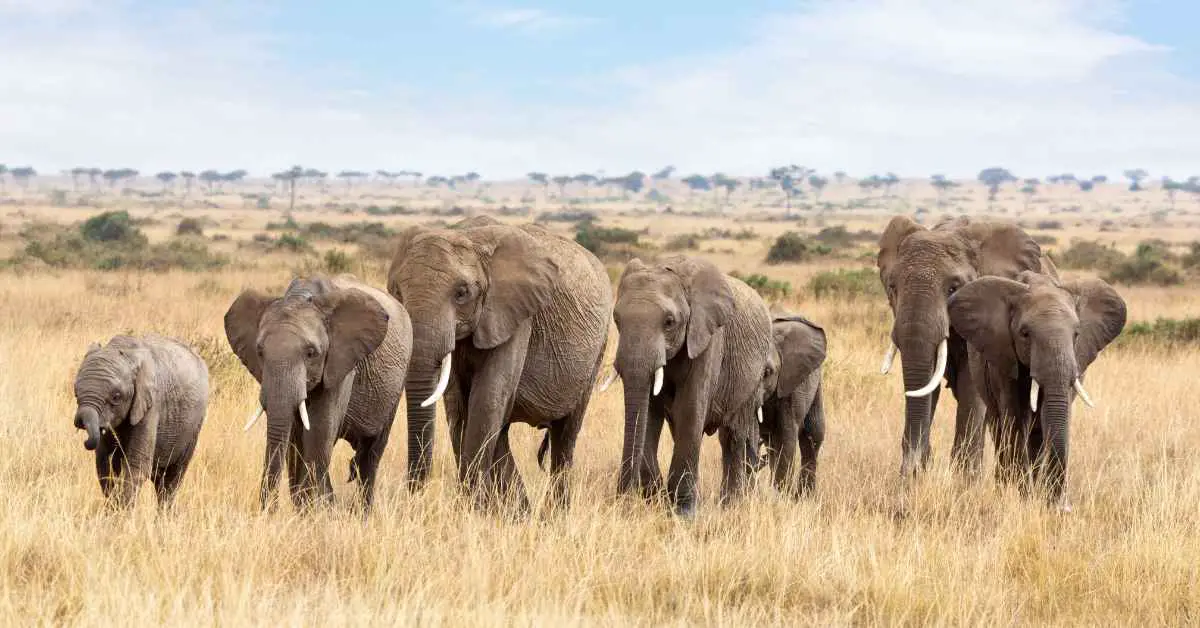

In contrast to the stable female family units, male elephants adopt a more solitary lifestyle or form temporarily cohesive bachelor groups. Young males typically leave their natal herds between the ages of 12 and 15. These bachelor groups, often transient and marked by competitive hierarchies based on size and age, serve as a context for young males to socialize and learn necessary behaviors in preparation for adulthood[3][5][9]. Although males maintain a degree of independence, they occasionally return to their familial herds to interact and ensure their family's well-being[5][10].
Emotional Bonds and Mourning Behavior
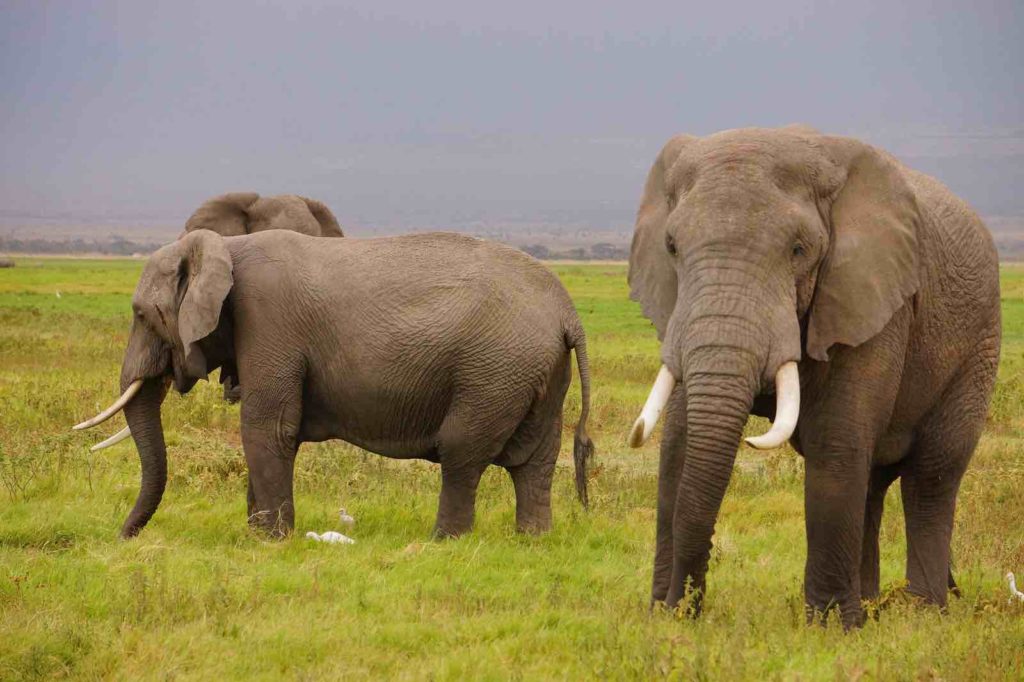

Elephants exhibit profound emotional connections within their herds. When a member dies, the herd engages in elaborate mourning rituals, which may include touching the deceased with their trunks, covering the body with earth, and pausing in silence to show respect. This behavior underscores the strong emotional bonds and social cohesion within the group[8][11]. Additionally, elephants are known to revisit grave sites, displaying signs of grief and recognizing the remains of dead relatives[10][11].
Communication and Social Learning
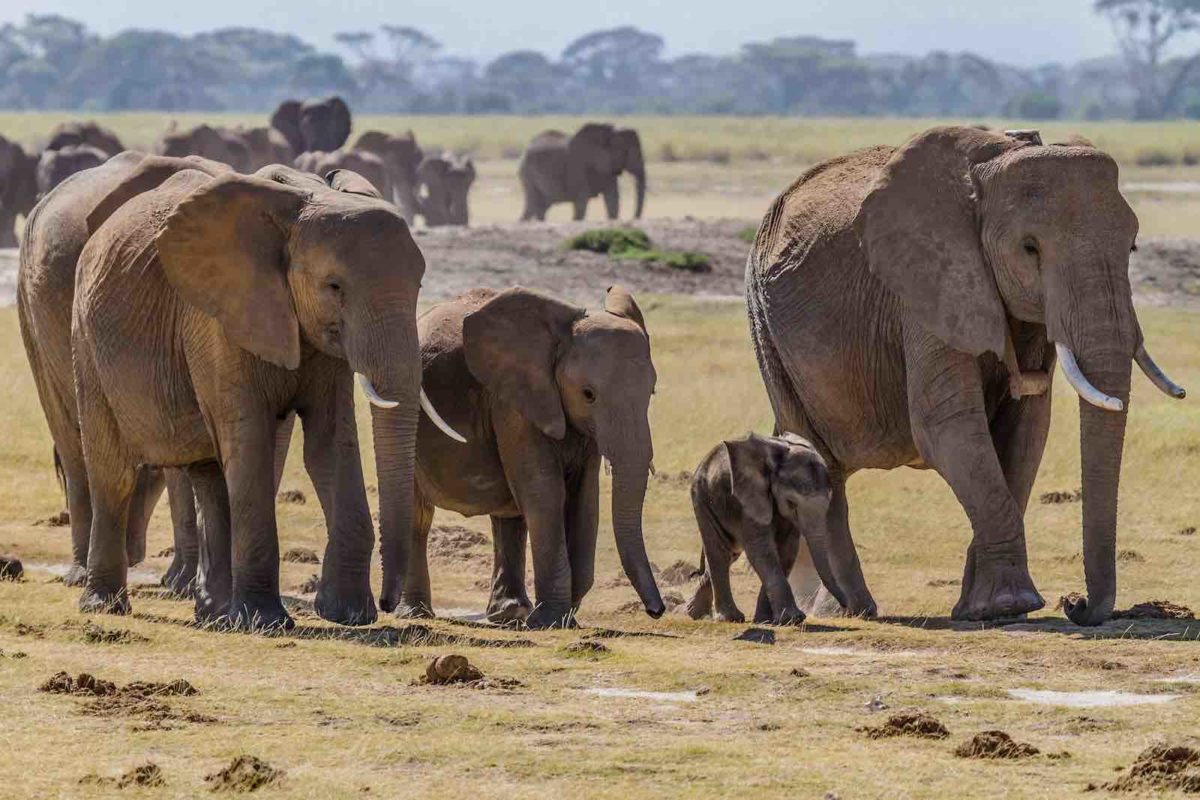

Elephants possess a highly developed communication system comprising vocalizations, body language, and tactile signals. Their ability to produce low-frequency calls, which can be perceived over great distances, helps maintain connections between individuals separated by considerable space[2][5][6]. These communication methods facilitate social learning, where younger elephants learn critical survival skills from their elders, including foraging techniques and social behaviors essential for thriving within their complex social system.
Fluidity of Social Structures

While matriarchal herds are the norm, elephant social structures can be fluid. Elephants adapt their social dynamics based on environmental factors such as resource availability. In areas with plentiful food and water, herds can grow larger, while in less hospitable regions, they may break into smaller family groups or bond units to enhance survival prospects[4][5][10]. This adaptability demonstrates the resilience of elephant herds as they navigate changing landscapes and social challenges.
Conclusion
The social structures of elephant herds are intricate and multifaceted, characterized by matriarchal leadership, deep emotional bonds, and cooperative parenting. The matriarch’s role is crucial for the herd's survival, fostering unity and guiding younger generations. Male elephants adopt different social dynamics, often leading solitary lives after leaving their natal herds. Elephants' rich emotional lives are evident in their mourning rituals, while their communication and social learning abilities highlight the complexity of their interactions. Understanding these social structures is vital for conservation efforts aimed at preserving elephant populations and their intricate social fabric.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Get more accurate answers with Super Search, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.

Sleeves of mail afforded considerable protection to the front of the body[1].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.

The primary diet of carnivores, specifically the carnivore diet, consists entirely of meat and animal products, including beef, chicken, pork, fish, and eggs. It excludes all plant-based foods like fruits, vegetables, legumes, grains, nuts, and seeds, aiming for a zero-carb intake. This restrictive diet claims to support weight loss and improve various health issues, but lacks sufficient scientific research to back these claims[2][5][6].
While proponents argue it can lead to weight loss and other benefits, experts warn it may be high in saturated fat and cholesterol, increasing risks for heart disease and other health problems. Furthermore, the diet is deficient in essential nutrients such as fiber and certain vitamins[1][2][4][6].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Overview of Biomes
Biomes are large geographic regions characterized by specific climate conditions, vegetation, and animal life. They are vital to understanding the Earth's ecosystems, as each biome supports unique communities of flora and fauna that have adapted to their environments. The classification of biomes varies depending on criteria such as climate, soil type, and geographic location, with some researchers agreeing on five major categories while others identify more specific types.
Major Types of Biomes
1. Terrestrial Biomes
Terrestrial biomes are primarily land-based ecosystems, and they can be further divided into several categories based on specific conditions and characteristics.
Tropical Rainforest: These biomes are located near the equator and are known for their high biodiversity, receiving over 200 cm of rain annually. They have a warm, humid climate and a complex structure with multiple layers of vegetation, including emergent, canopy, understory, and forest floor[2][3]. The Amazon rainforest is a prime example.
Temperate Forest: Found in regions such as North America, Europe, and parts of Asia, temperate forests experience four distinct seasons. They consist of a mix of deciduous and evergreen trees. In these forests, trees like oak, maple, and ash dominate, and various animal species inhabit them, adapting to seasonal changes[6][10].
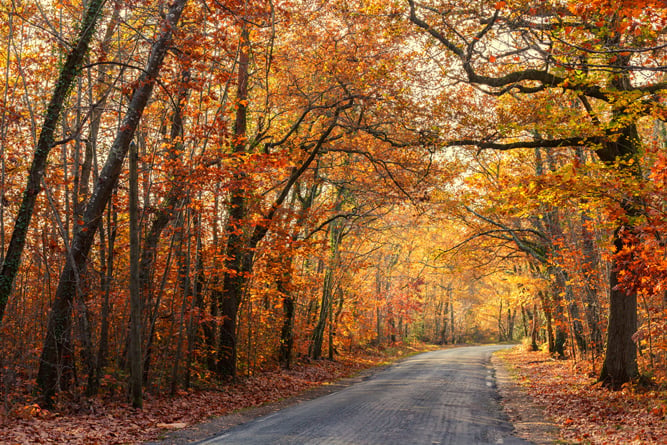

title: 'Road passing through a beautiful temperate forest at fall(Stephane Bidouze)S' and caption: 'a road with trees and leaves on the side' Desert: Deserts are characterized by extremely low precipitation, usually less than 25 cm annually, and can be either hot or cold. Vegetation includes cacti and drought-resistant shrubs, with animals showing adaptations such as nocturnal behavior to conserve water[5][11]. The Sahara Desert in Africa and the Gobi Desert in Asia are notable examples.

title: 'Chutes d'Ekom - a waterfall on the Nkam river in the rainforest near Melong, in the western highlands of Cameroon in Africa.' and caption: 'a waterfall with a rainbow in the middle of a forest' Tundra: This biome is the coldest on Earth, characterized by low temperatures, minimal precipitation, and permafrost. Vegetation is limited to mosses, lichens, and a few hardy shrubs. Arctic tundra and alpine tundra are the two main types, hosting specialized fauna like polar bears and caribou[8][12].
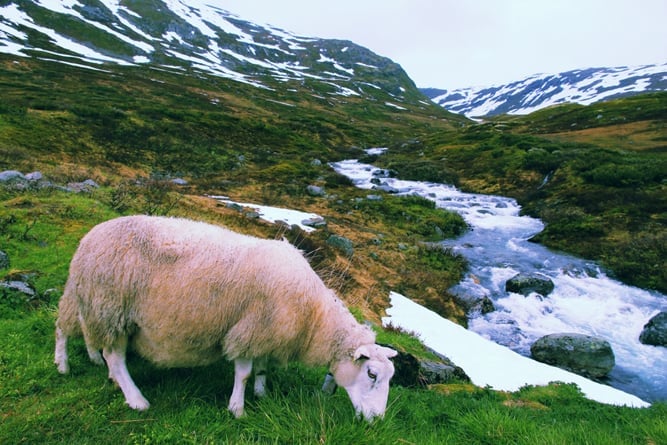

title: 'Sheep in tundra biome landscape in Norway(Tupungato)s' and caption: 'a sheep grazing in a grassy area' Taiga (Boreal Forest): Taiga is the largest terrestrial biome, primarily found in high latitudes across North America and Eurasia. It features coniferous forests, with species such as pine, spruce, and fir, thriving in cold climates where winter lasts much longer than summer[4][6].
Grassland: Grasslands are expansive areas dominated by grasses, with few trees or shrubs. They are characterized by moderate rainfall and are often found in regions like the American prairies and the steppes of Russia. These biomes are crucial for grazing animals and support many herbivore and predator species[3][5][11].
Savanna: Savannas are tropical grasslands with scattered trees, primarily located in Africa and parts of South America. They experience a distinct wet and dry season, and large herbivores like elephants and zebras are commonly found here[6][11].

title: 'White cloud formations in a bright blue sky over the beautiful African savannah(Cobus Olivier)s' and caption: 'a field with trees and blue sky'
2. Aquatic Biomes
Aquatic biomes encompass freshwater and marine environments, each with unique characteristics.
Freshwater Biomes: This category includes lakes, rivers, ponds, and wetlands, characterized by low salt concentration. Freshwater systems are crucial for biodiversity and human water supply[5][6]. They support a variety of species from fish to amphibians and often feature rich vegetative communities around their shores.

title: 'Underwater Nurse Shark in the Florida Keys(Andrew Jalbert)s' and caption: 'a shark swimming under water' Marine Biomes: Covering about 70% of the Earth's surface, marine biomes include oceans, coral reefs, and estuaries. Oceans are the largest saltwater environments, supporting extensive biodiversity, including fish, marine mammals, and invertebrates[3][11]. Coral reefs, often referred to as the 'rainforests of the sea,' are hotspots for marine life, boasting thousands of species in a small area[4].
3. Classification Challenges
The classification of biomes can be complex and sometimes contentious among scientists. While some commonly accept five major types—terrestrial (forest, grassland, desert, tundra) and aquatic (freshwater, marine)—others expand this number to include various subcategories and ecoregions based on finer distinctions in vegetation and climate[2][9][12].
Conclusion
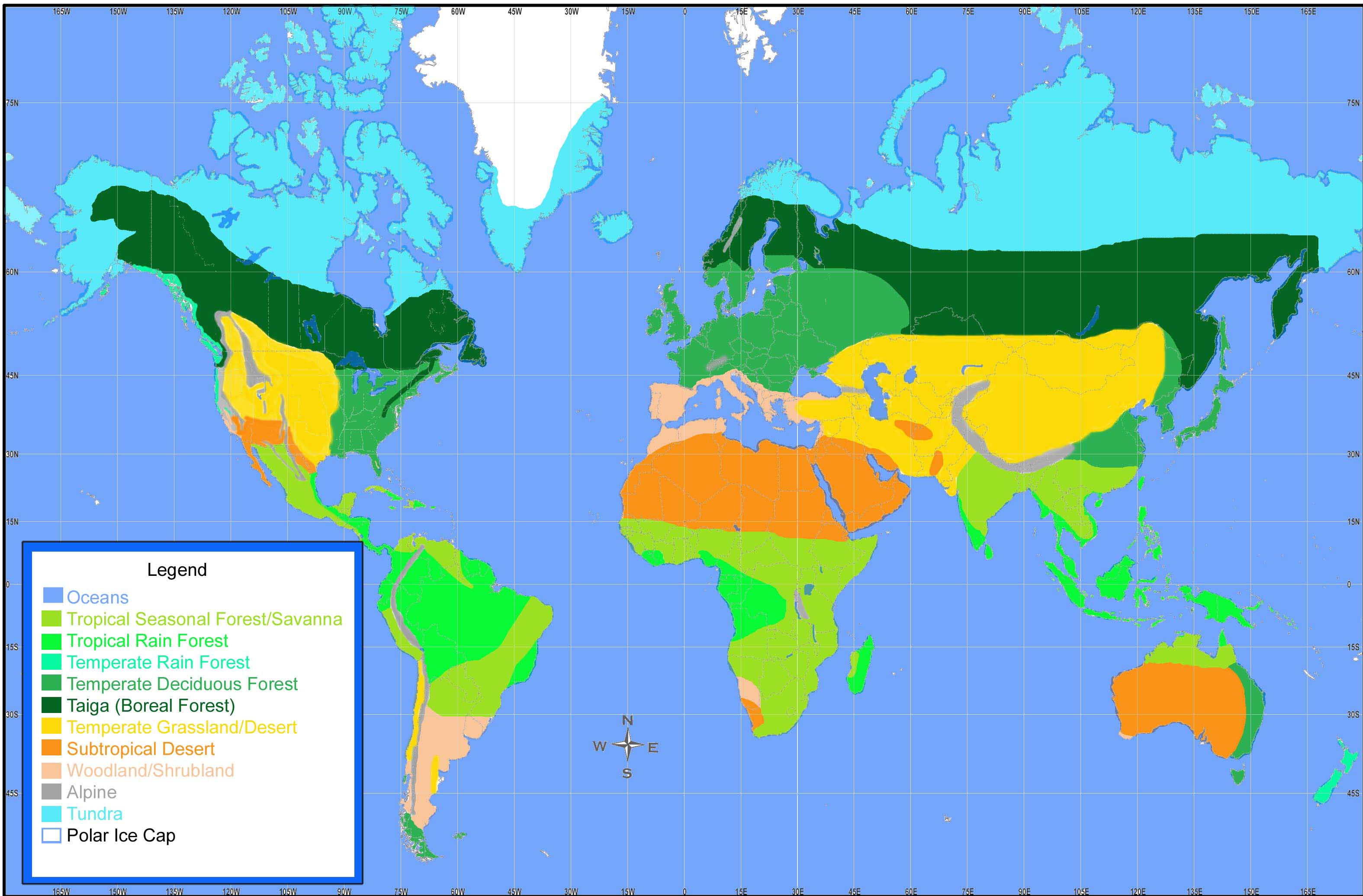
Understanding the diverse biomes of our world is essential for conservation efforts and for understanding how climate change and human activities impact these ecosystems. Each biome plays a critical role in sustaining life on Earth, and preserving their integrity is vital for the health of the planet and its inhabitants.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
- Request a manual search from our human research team.